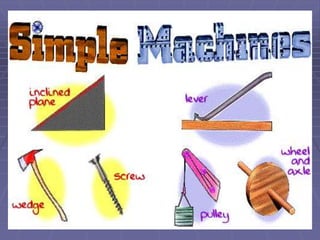
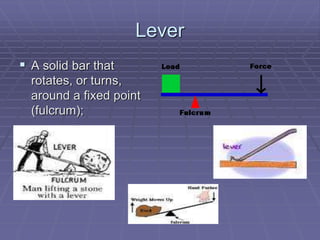
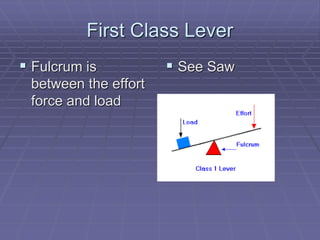
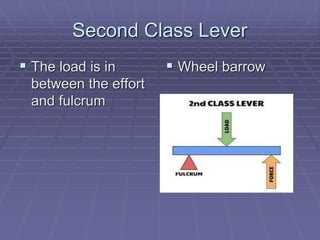
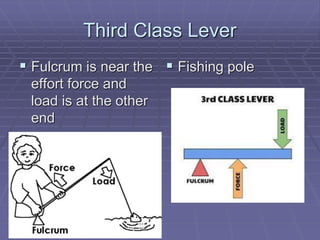
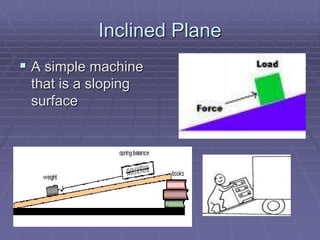
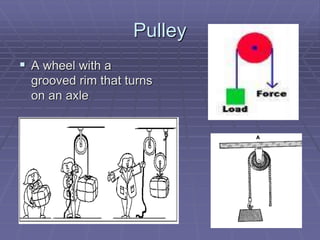
This document defines key vocabulary related to machines and their operation. It describes six simple machines - the lever, inclined plane, wheel and axle, pulley, wedge, and screw. Each simple machine is defined and examples are provided of how it multiplies force or changes the direction of force. The document also explains how machines transfer energy and do work, noting that their efficiency is always less than 100% due to energy lost to friction and other forces. It provides the formulas for calculating mechanical advantage and defines compound machines.