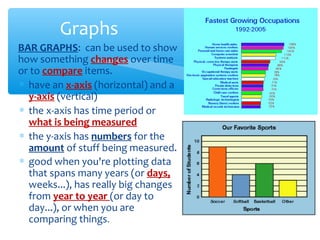
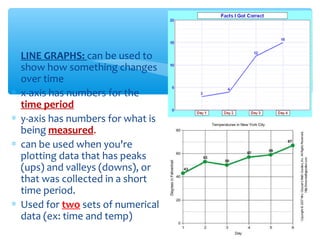
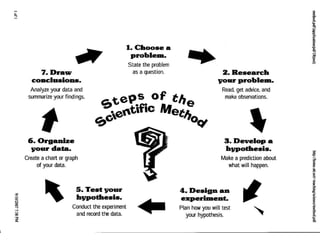
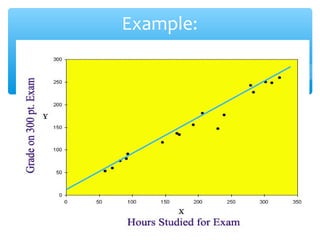
The document discusses the scientific method, which is a process used to answer questions about the world through experiments and observations. It involves identifying a problem, developing a hypothesis, designing and conducting an experiment, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing conclusions. Key parts of the scientific method include formulating hypotheses, identifying independent, dependent, and controlled variables, developing procedures, and organizing and presenting results. The document provides examples of experiments and identifies the variables involved.