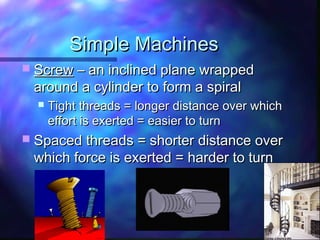
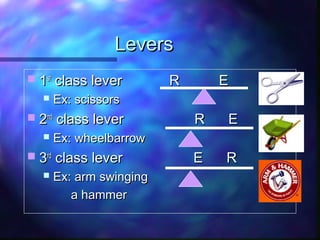
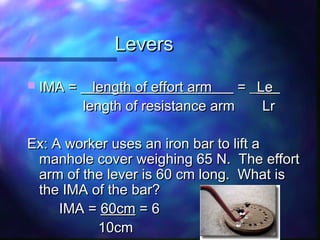
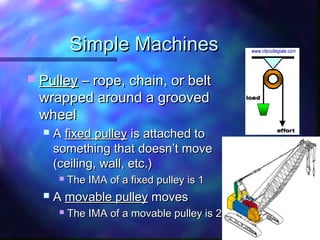
This document defines and provides examples of simple machines including inclined planes, wedges, screws, levers, pulleys, wheel and axles. It explains work as a force acting over a distance, and power as the rate at which work is done. Examples are provided for calculating work, power, and mechanical advantage. Compound machines are described as combinations of two or more simple machines.