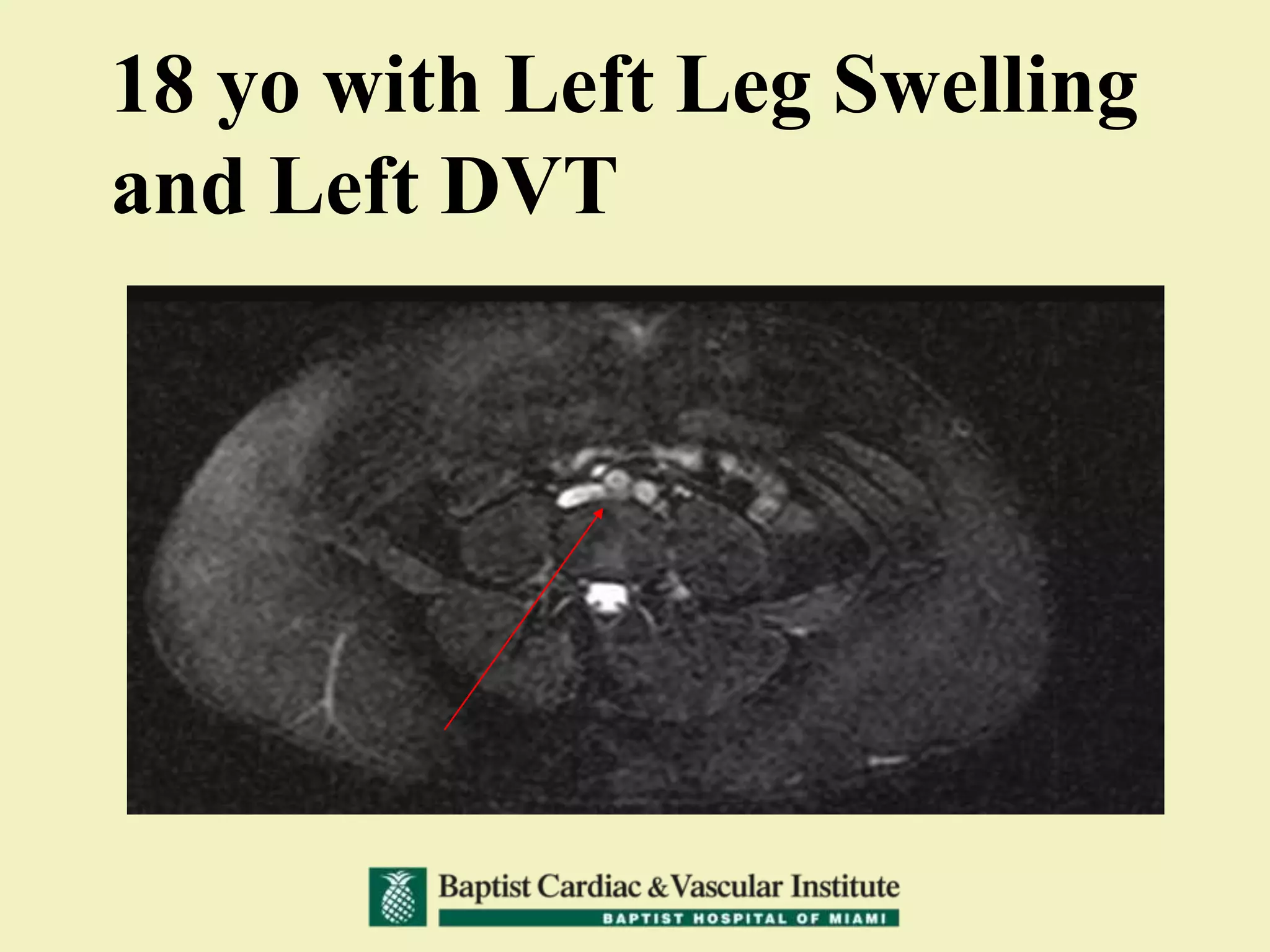
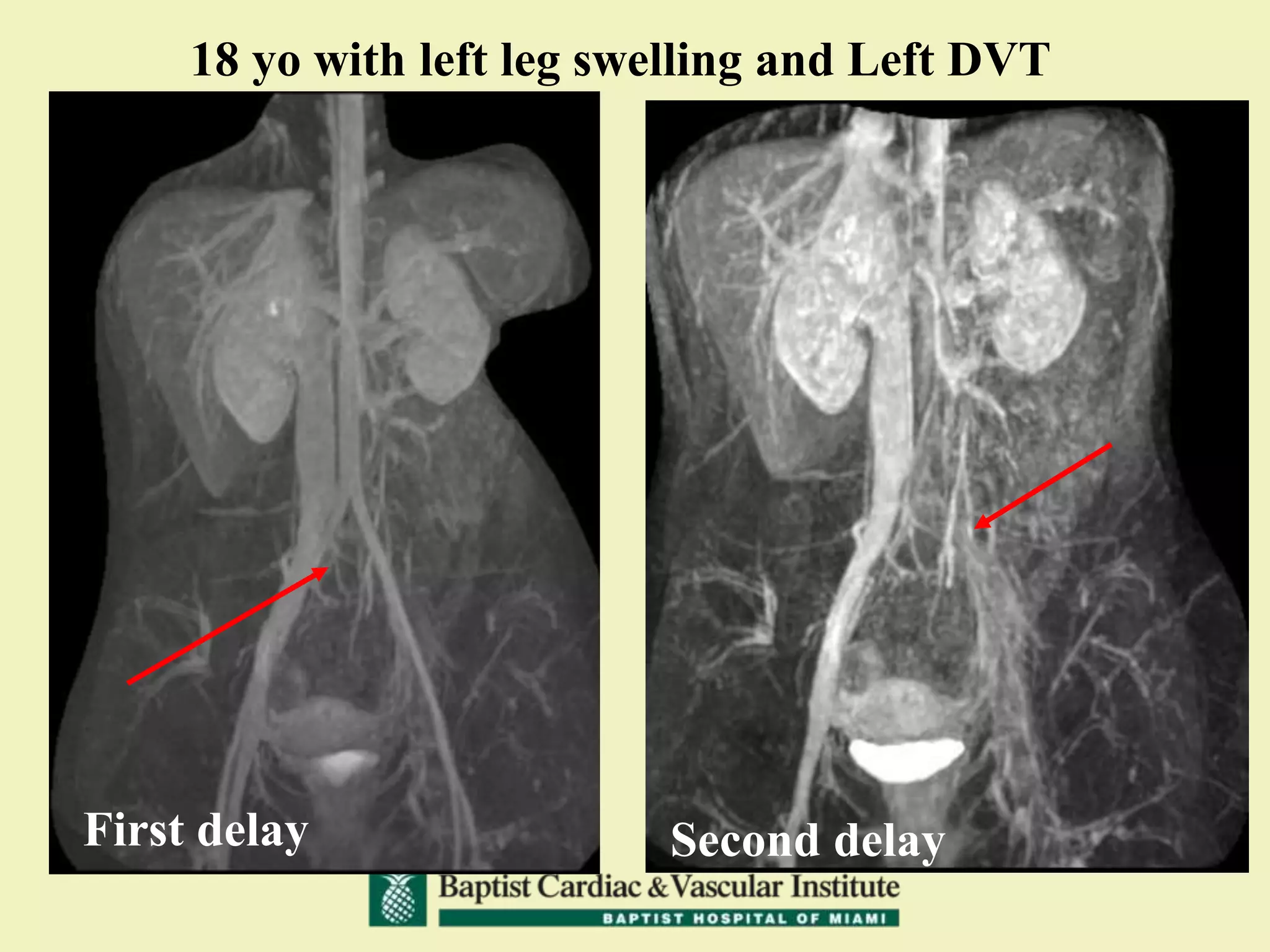
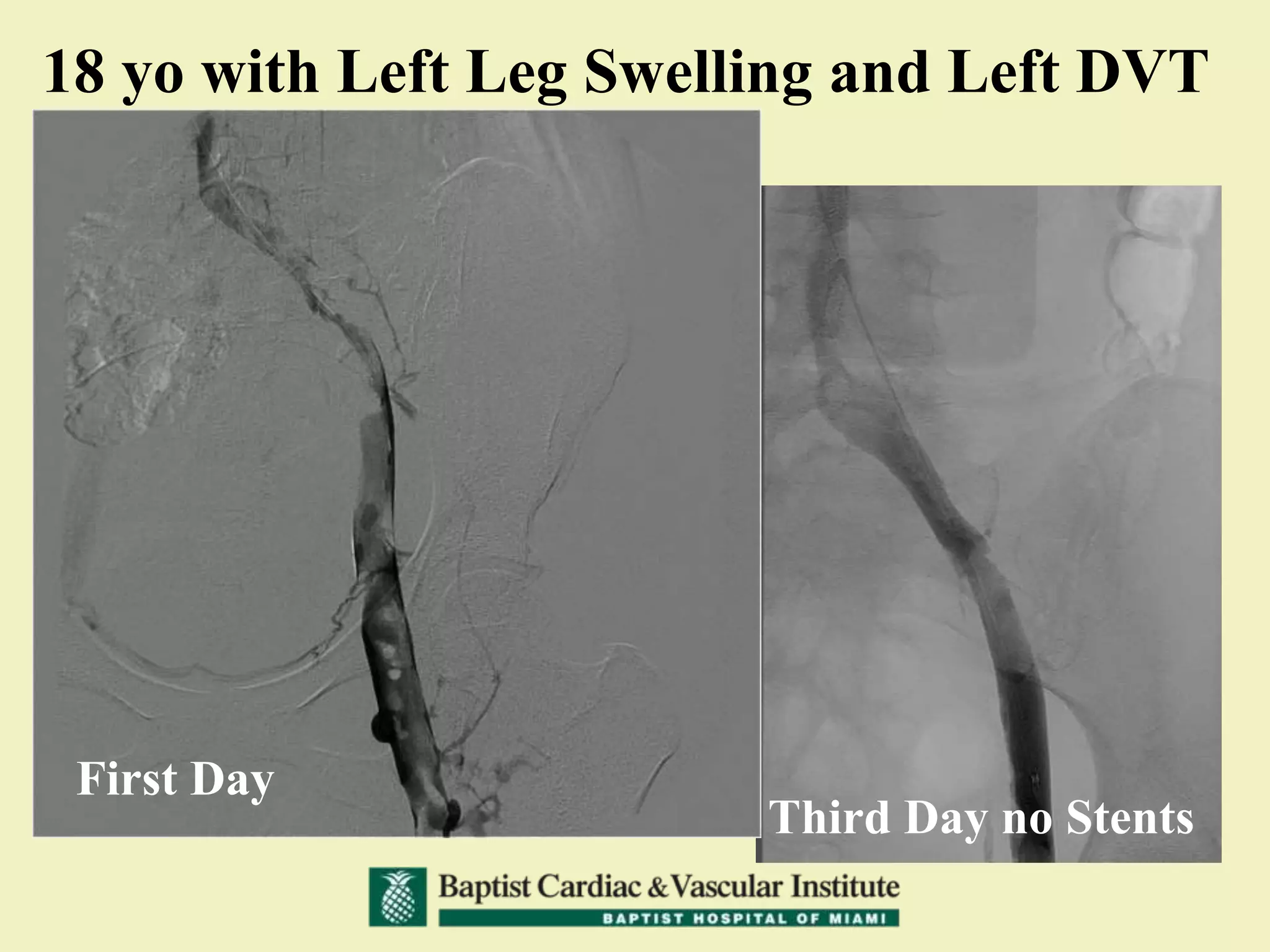
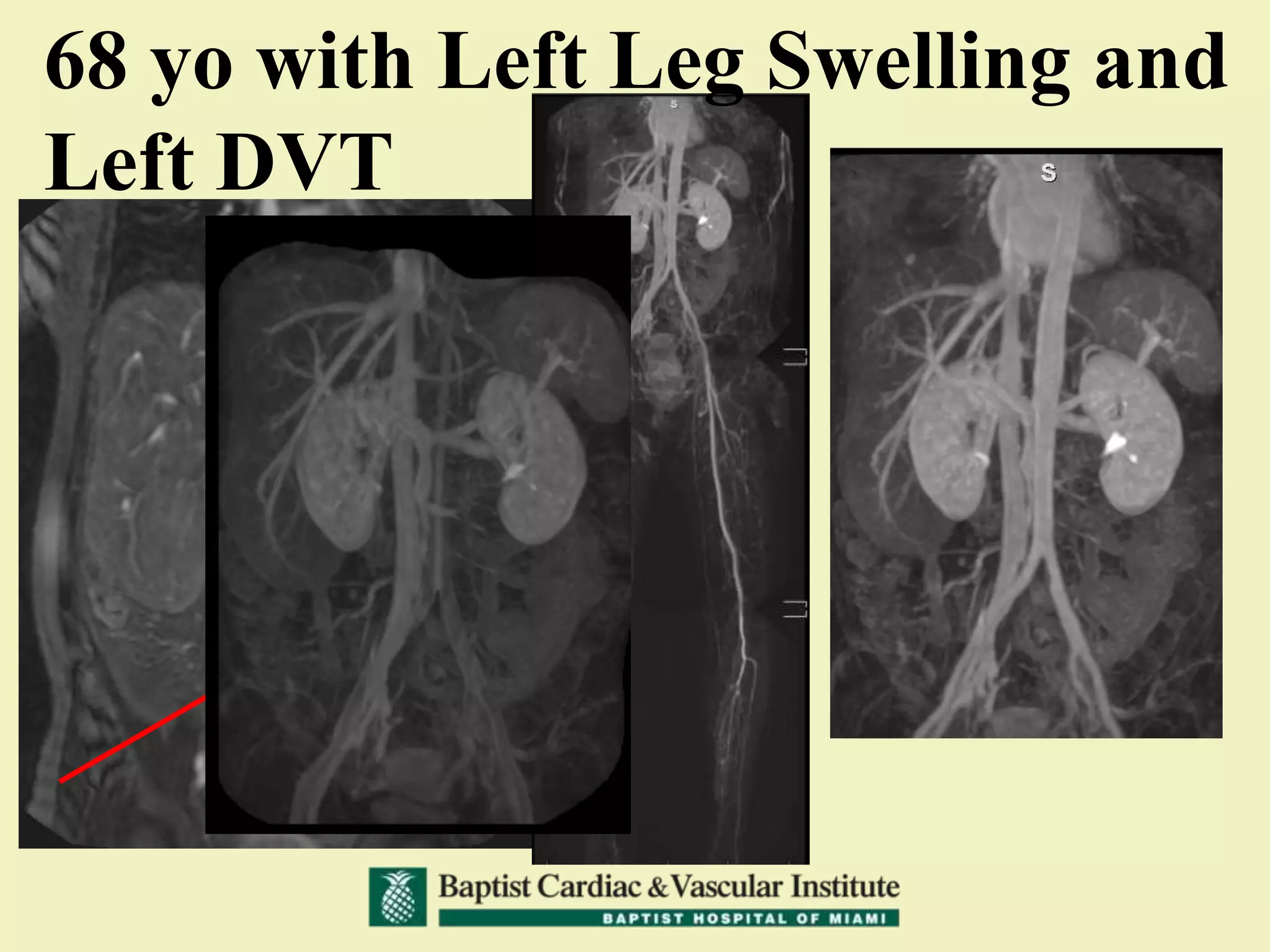
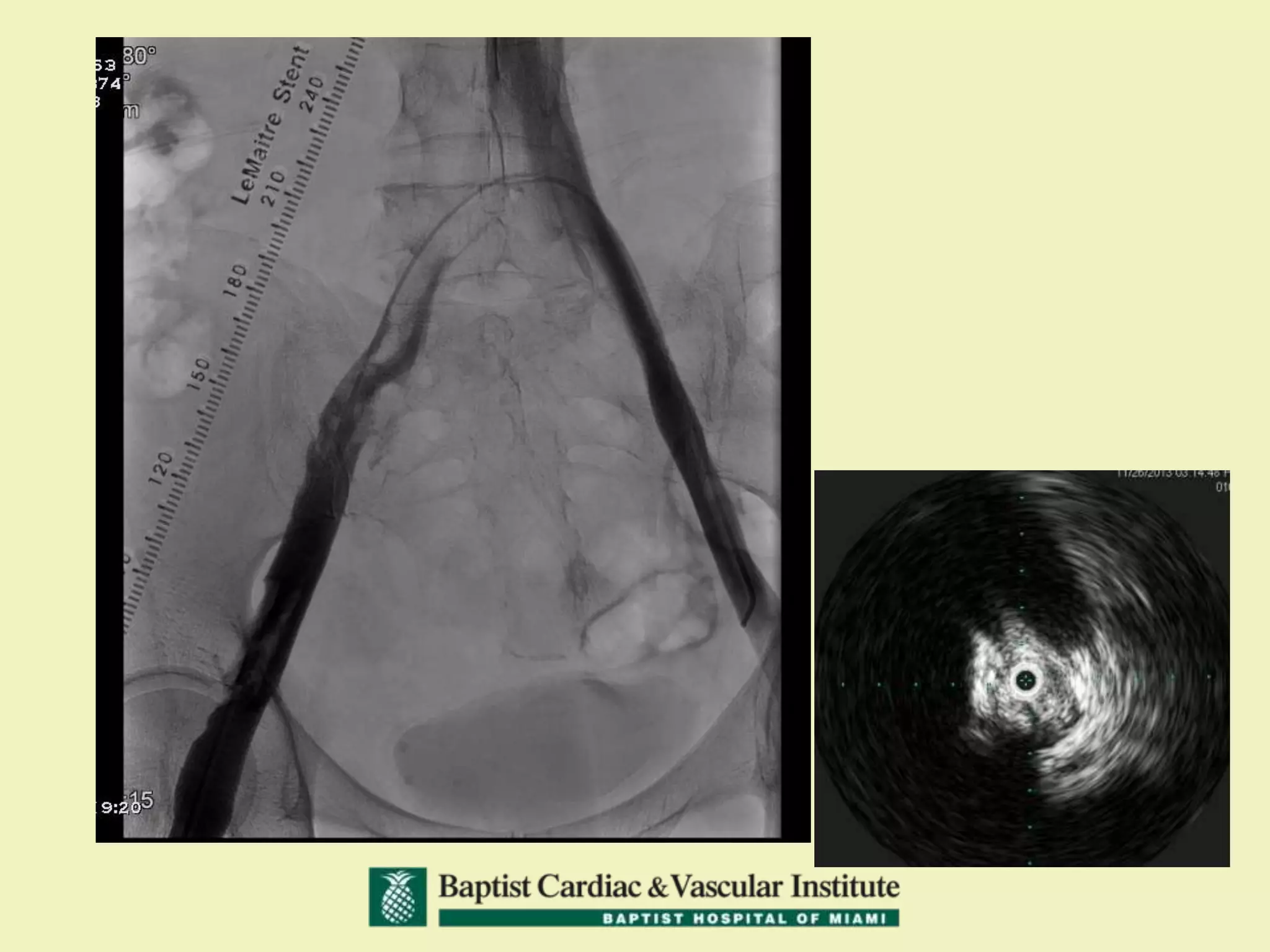
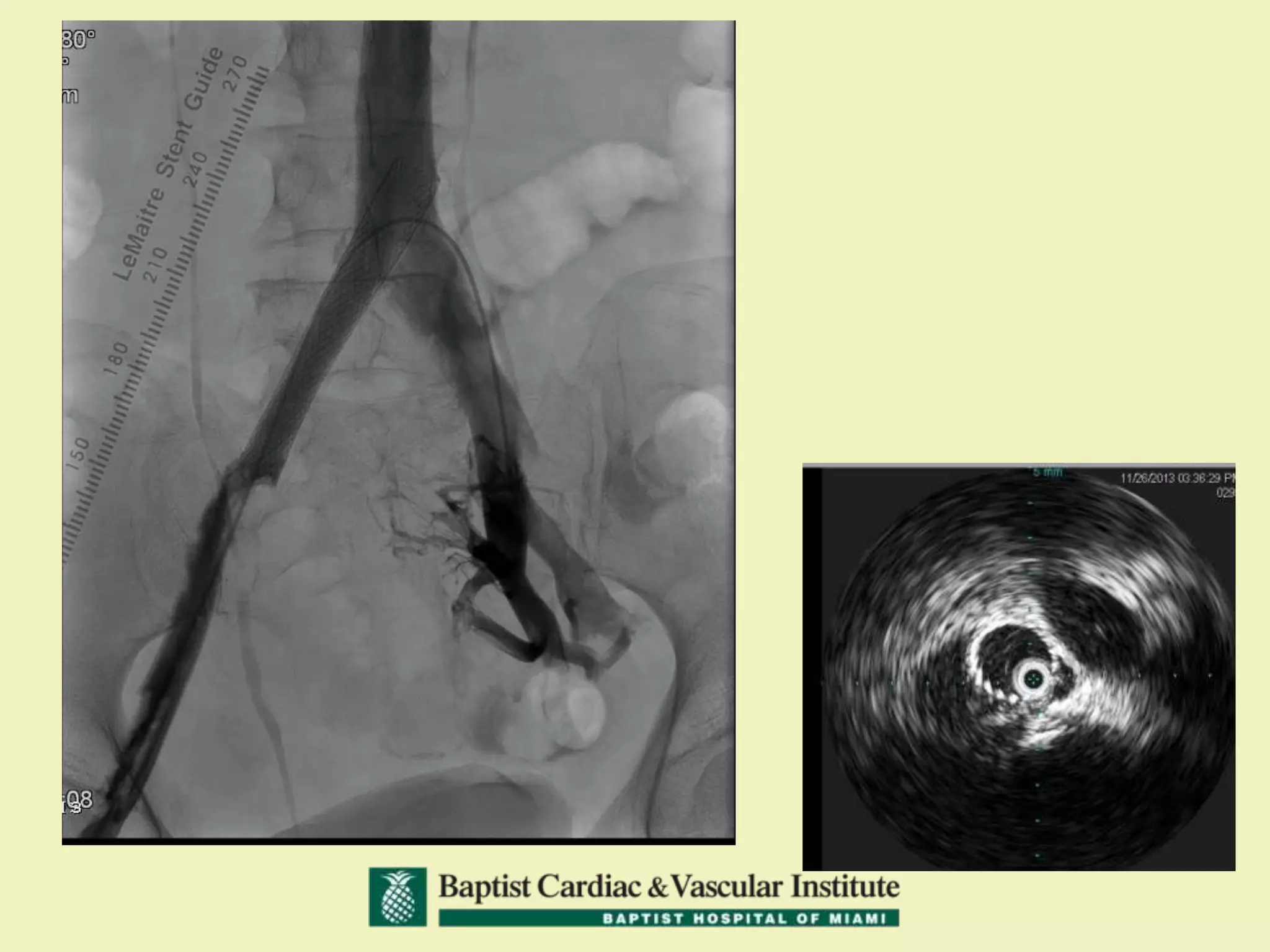
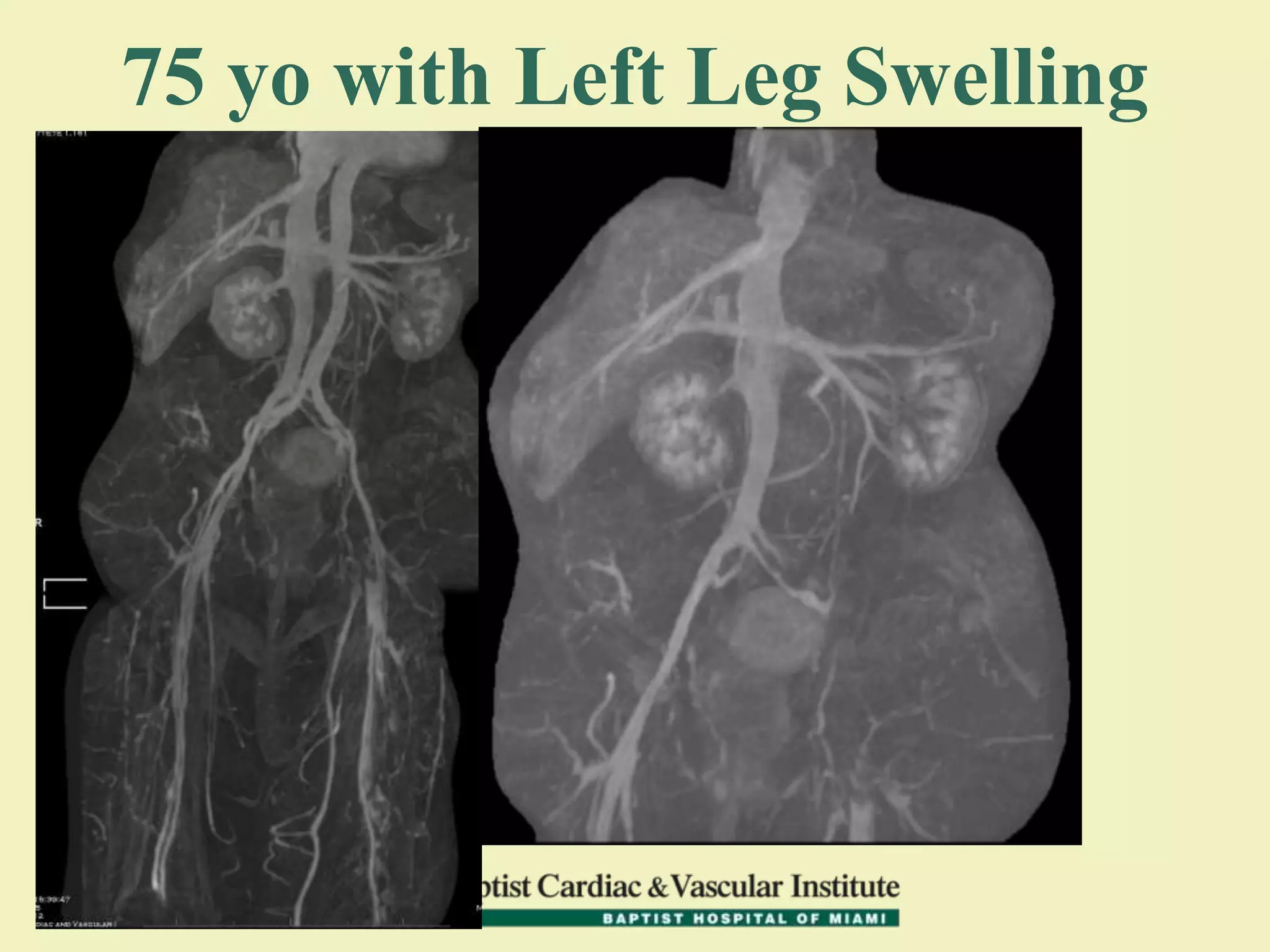
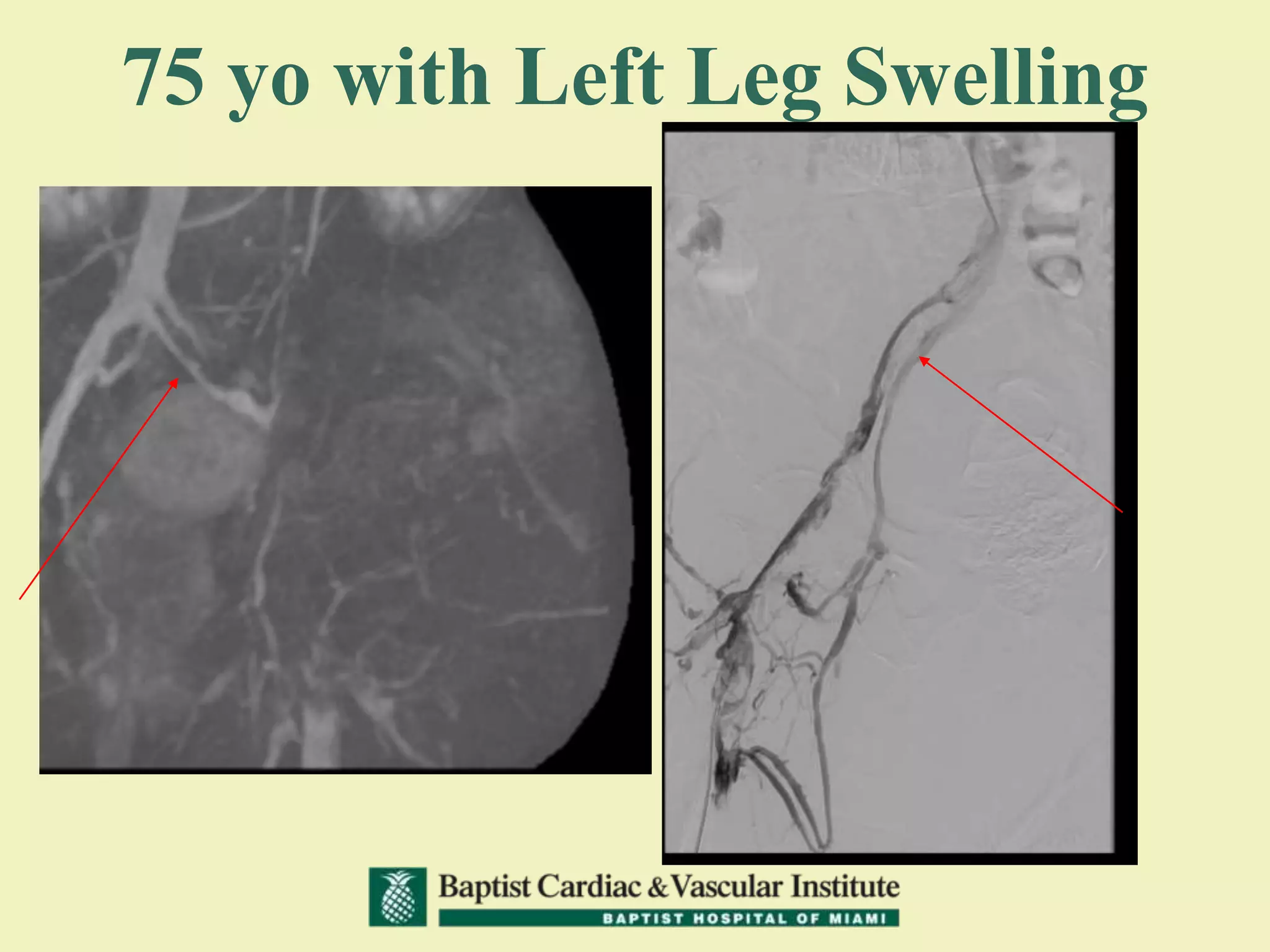
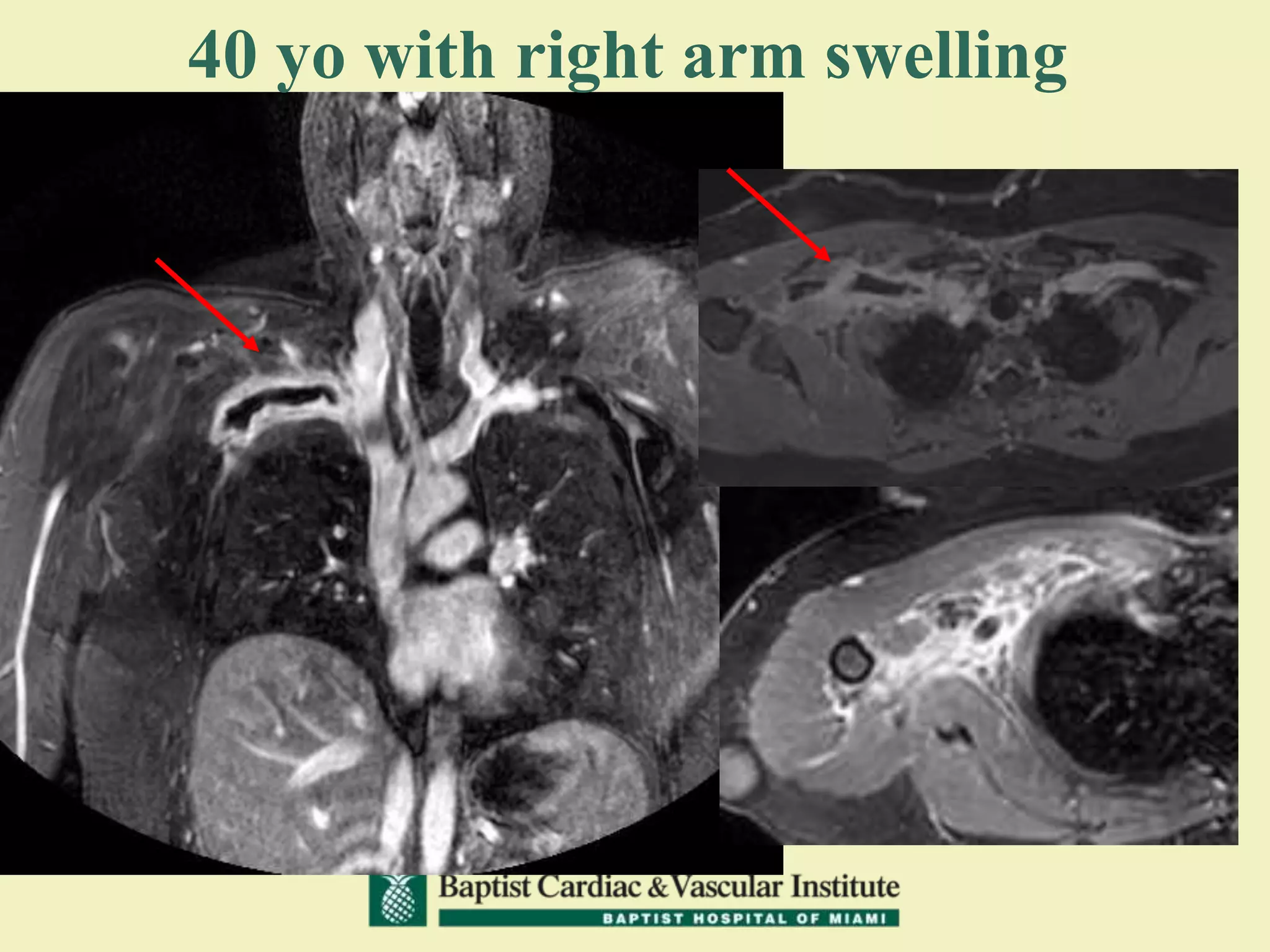
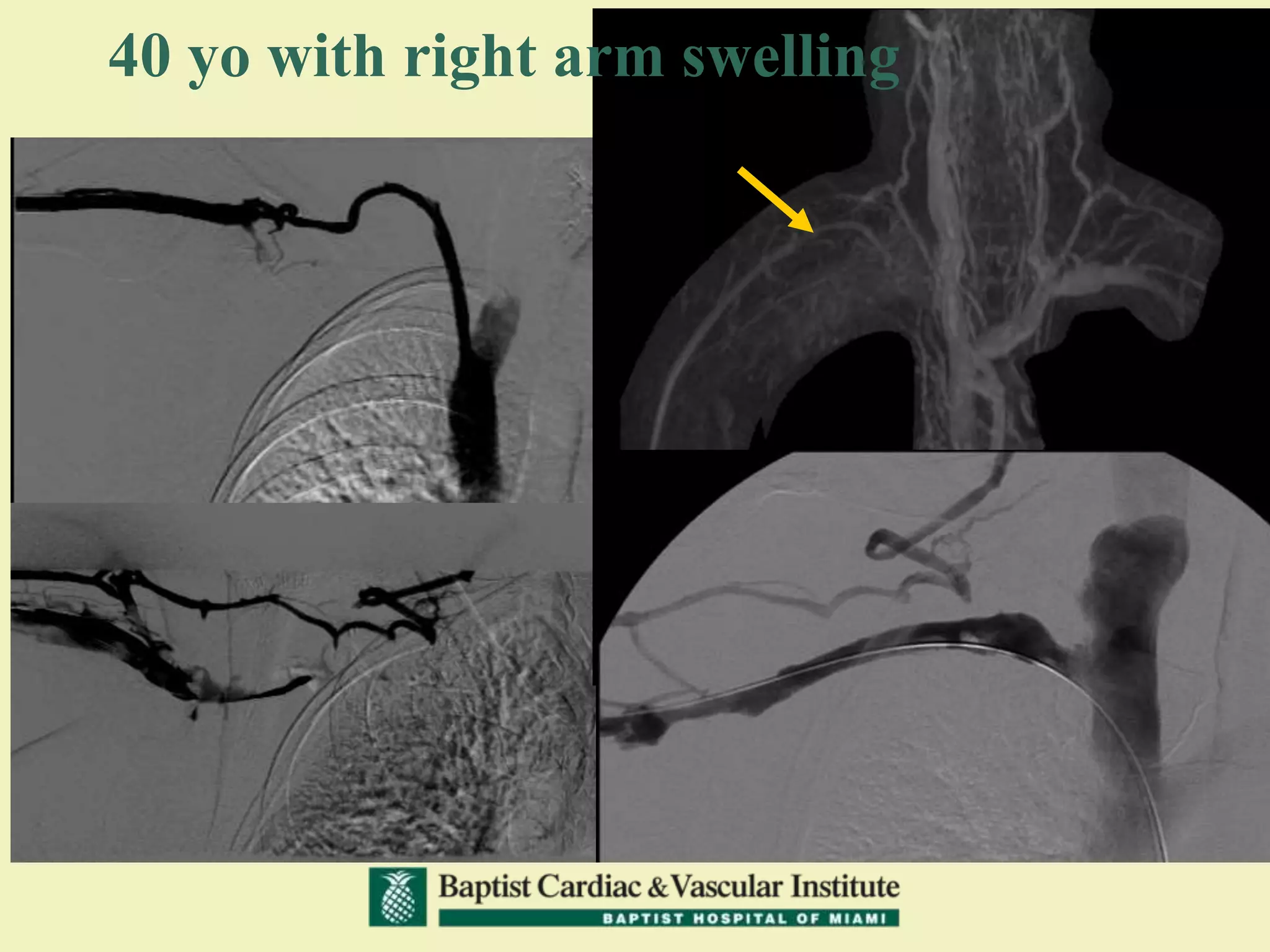
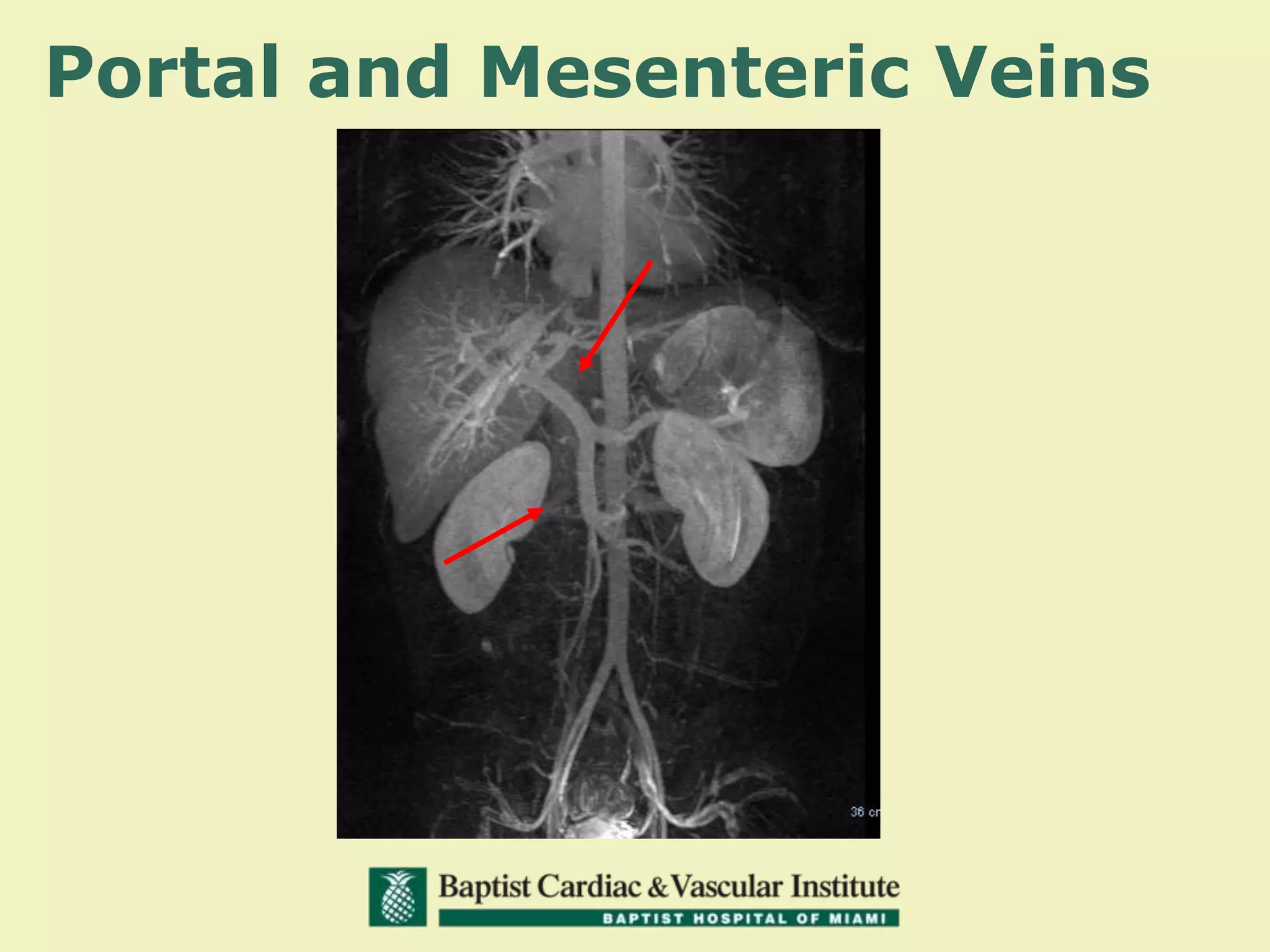
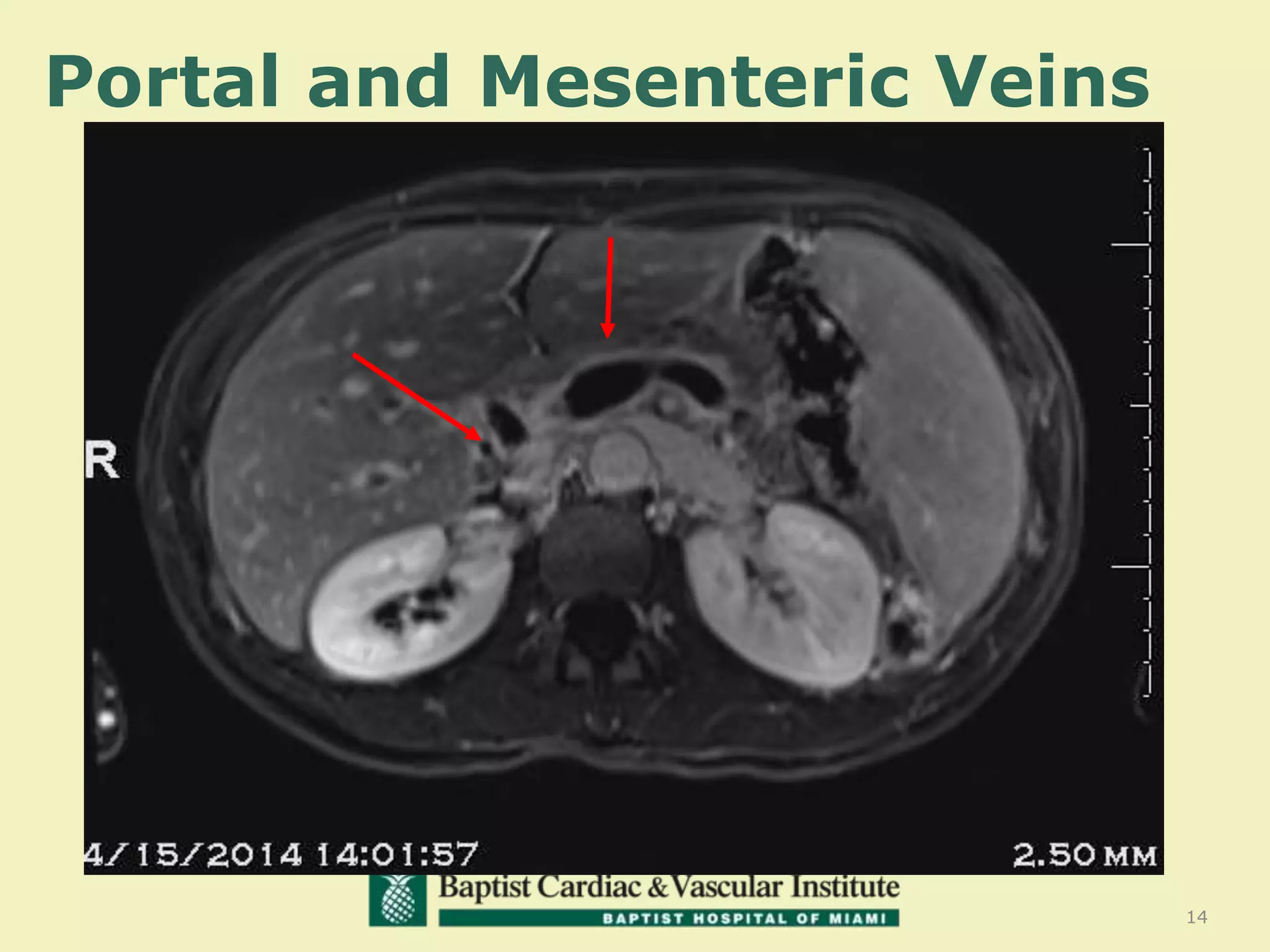
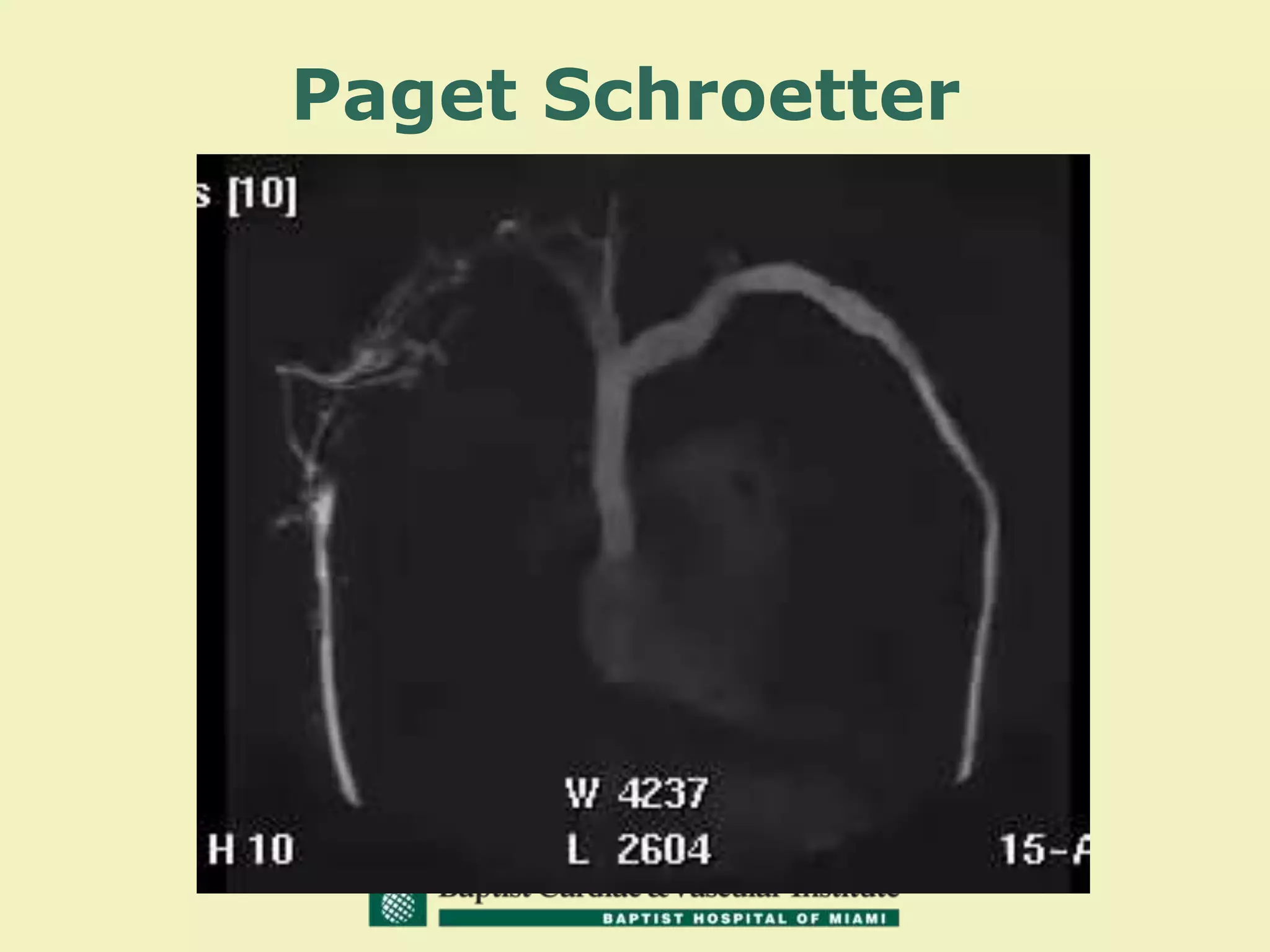
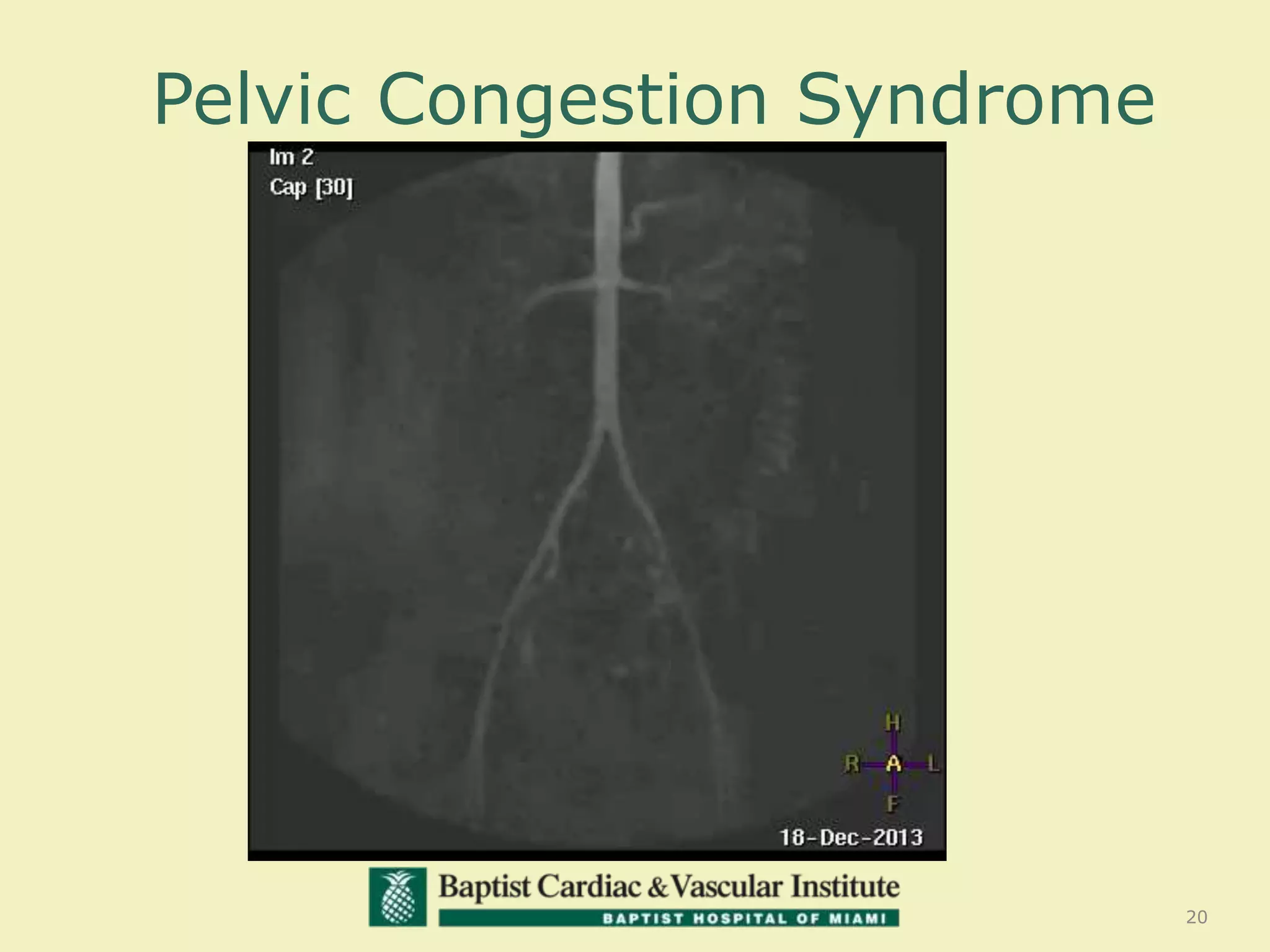
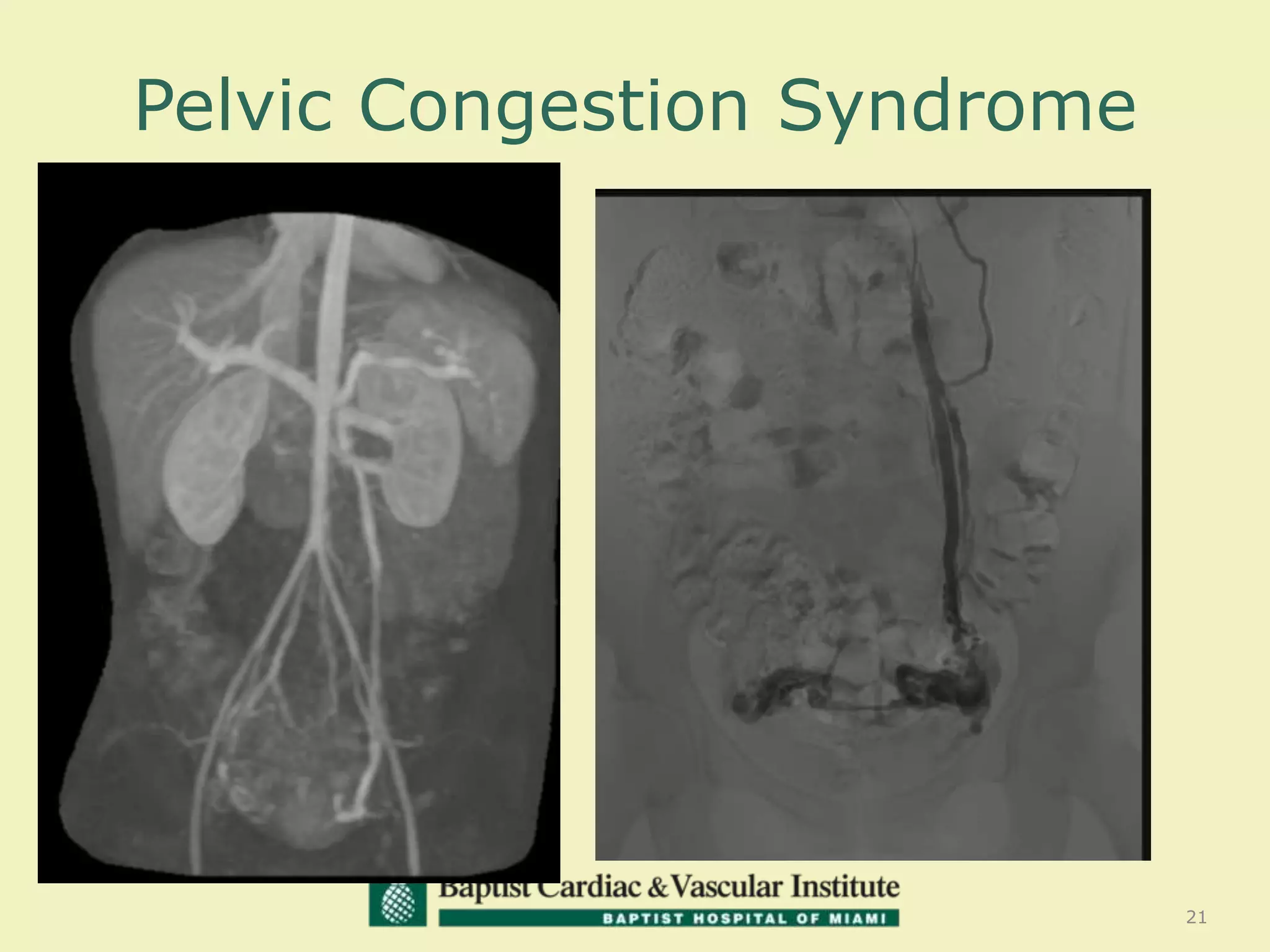
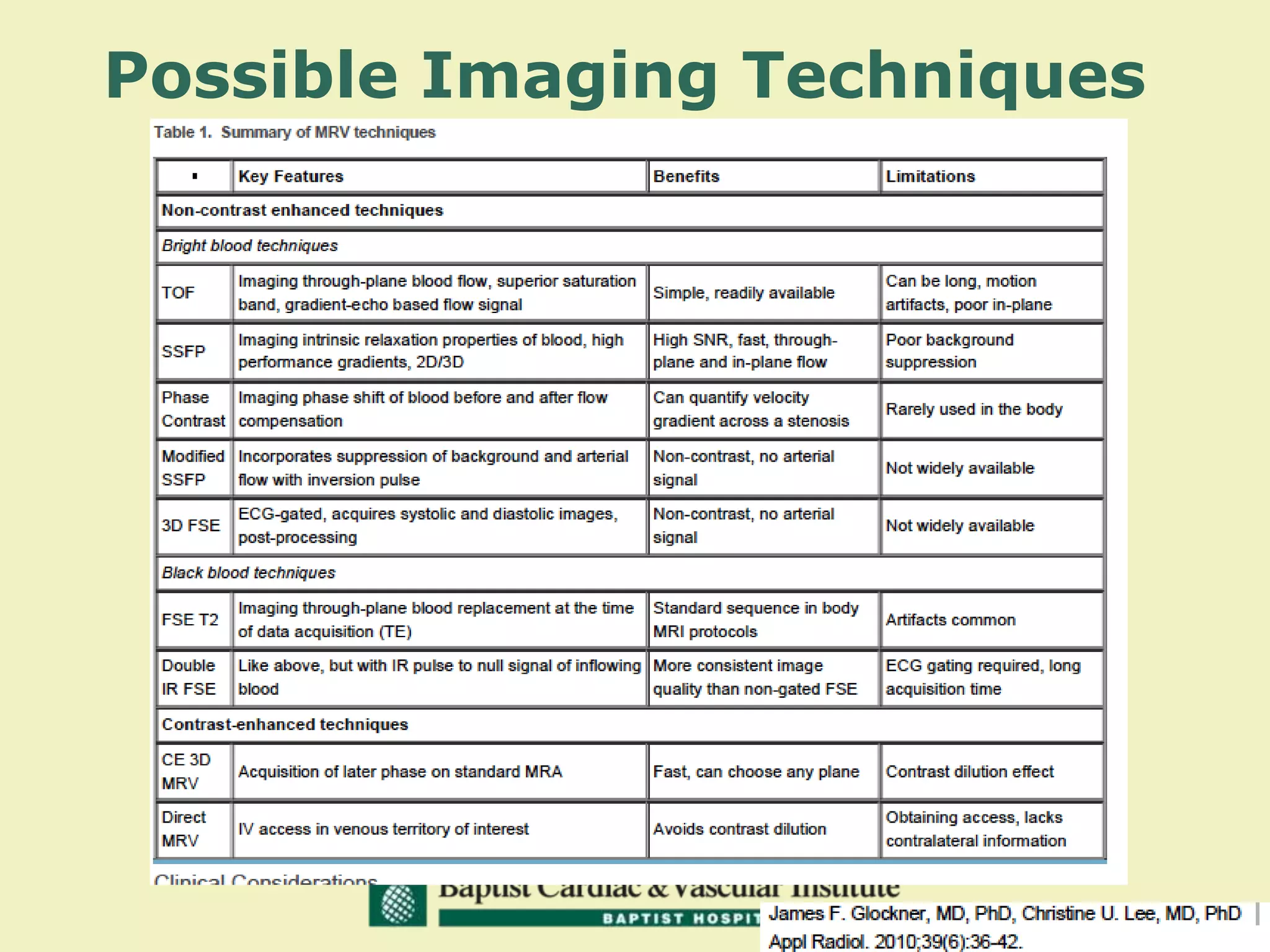
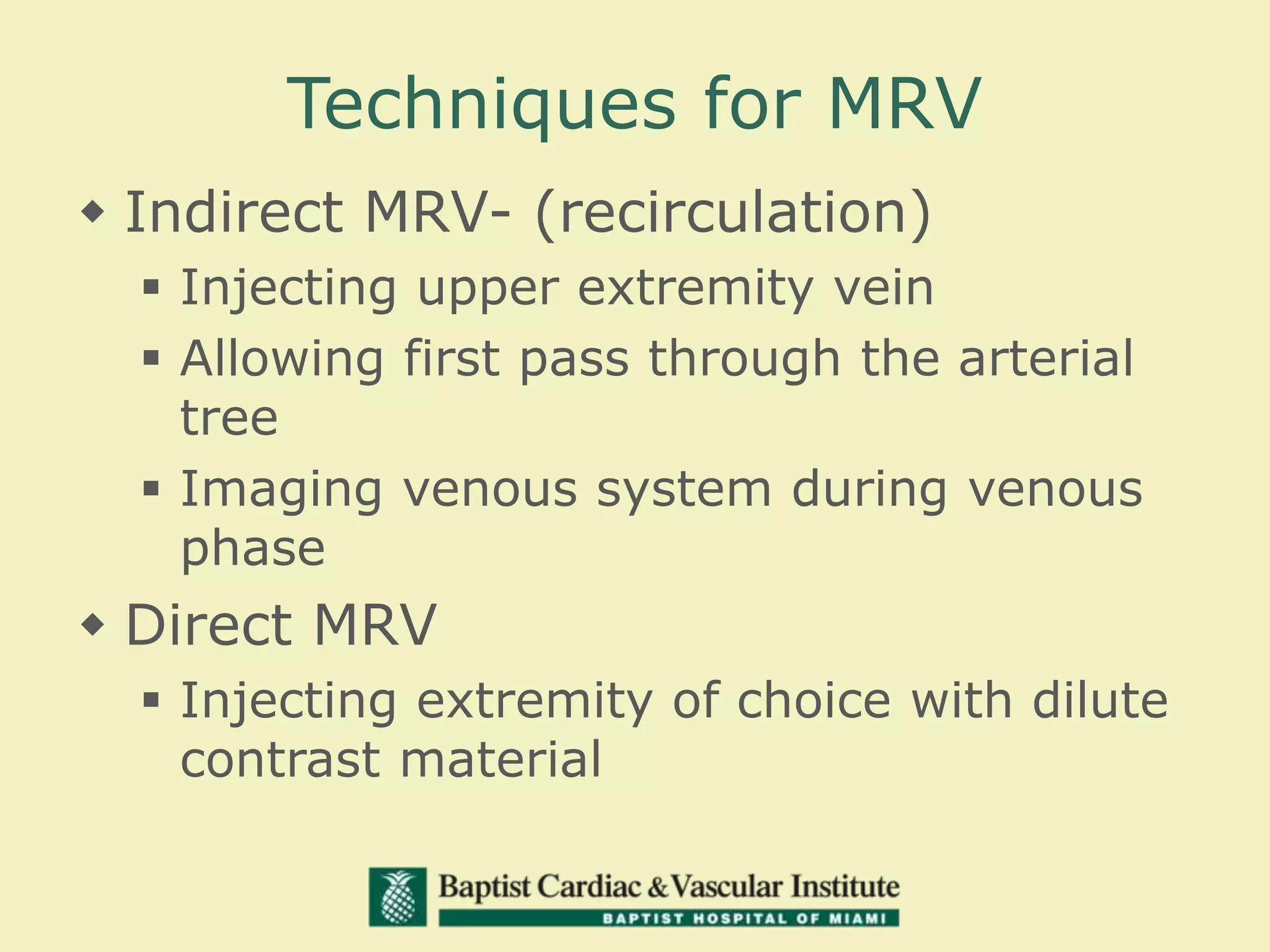
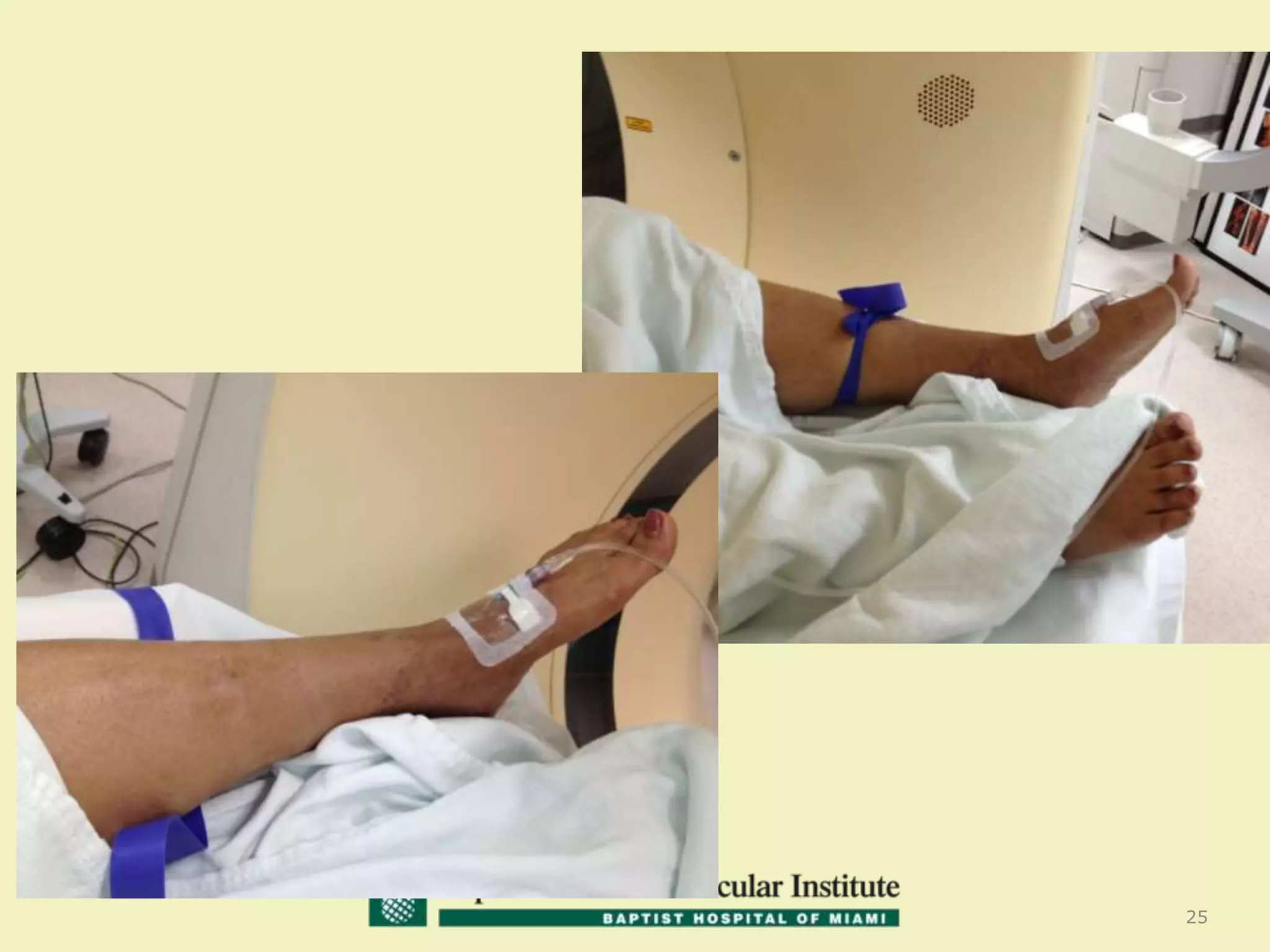
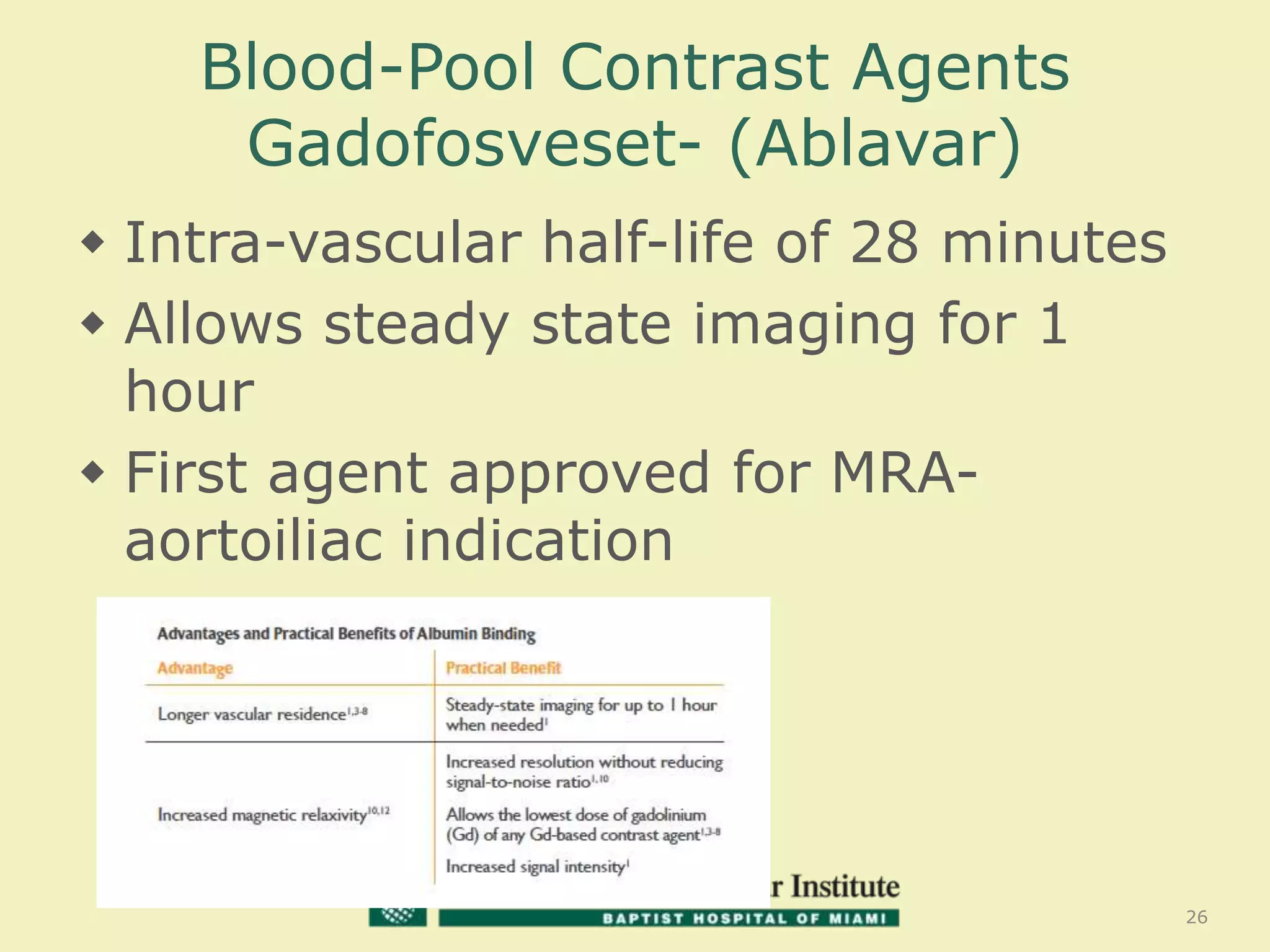
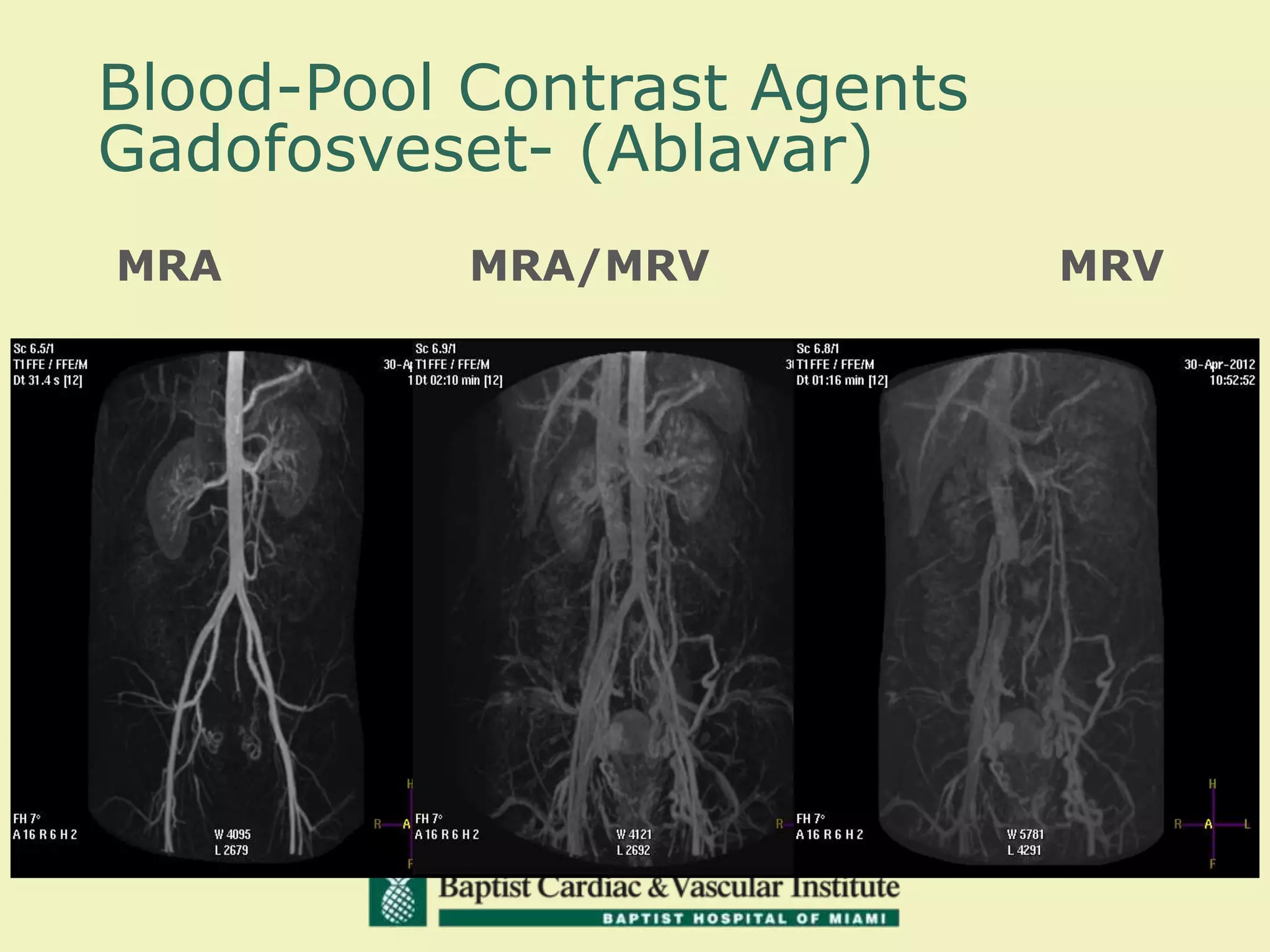
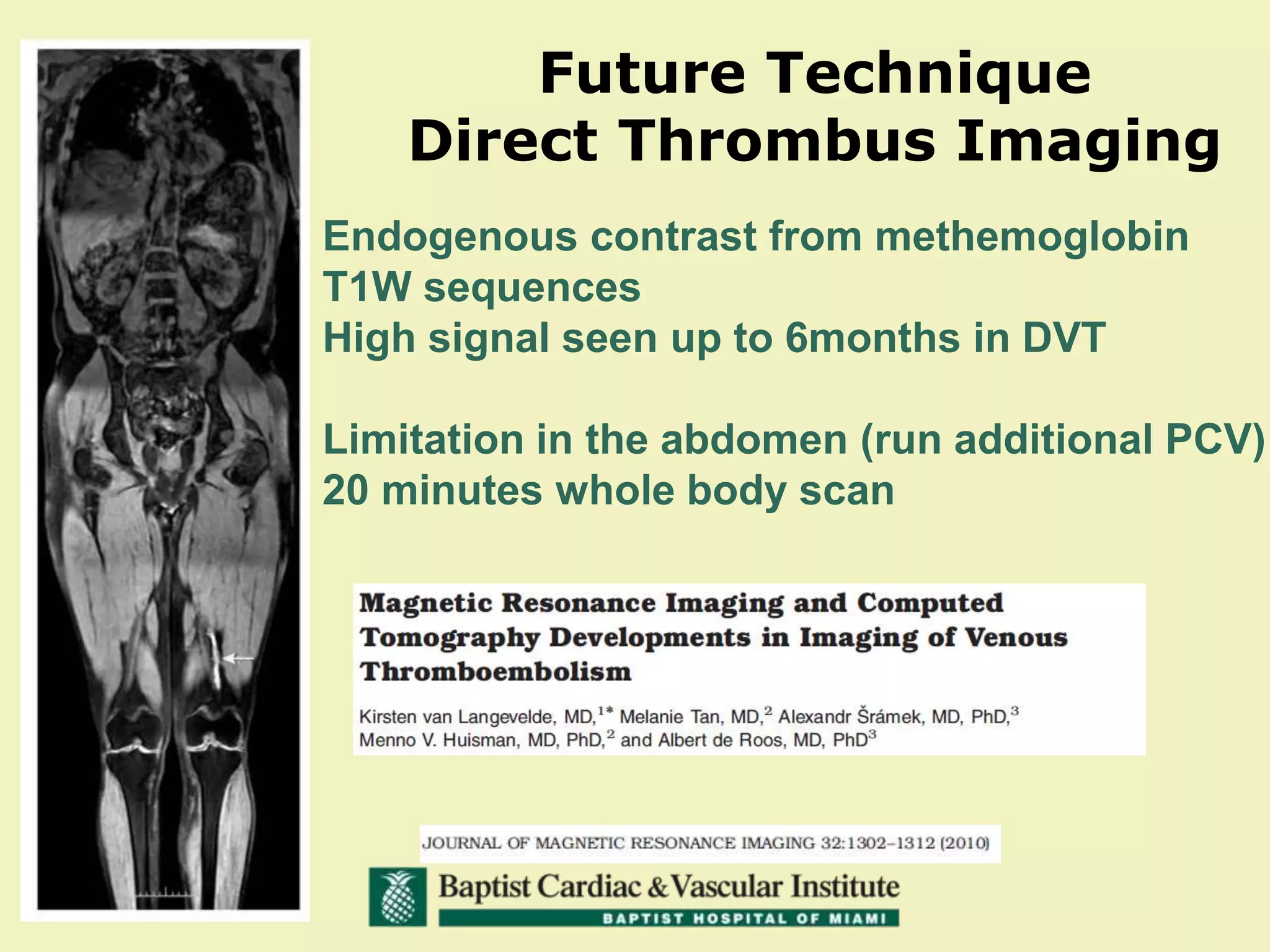
MR venography is used to evaluate central veins for patency and extrinsic compression, providing a radiation-free imaging option with four-dimensional flow evaluation. Its operator dependency arises from varying clinical questions and imaging techniques, with indirect and direct methods used based on patient needs. While MR venography is effective for diagnosing central venous disease, it has limitations in assessing heavy metals and may improve with future advancements in direct thrombus imaging.