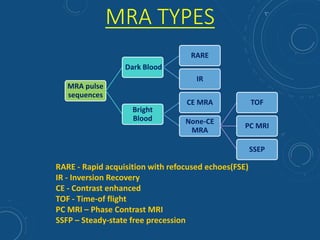
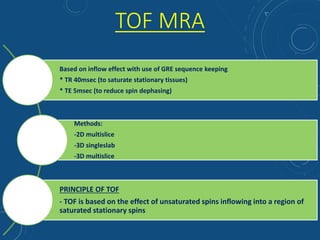
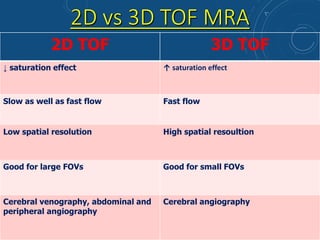
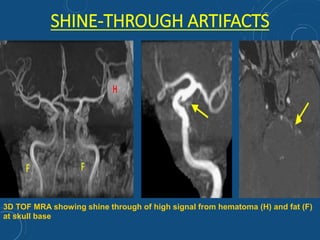
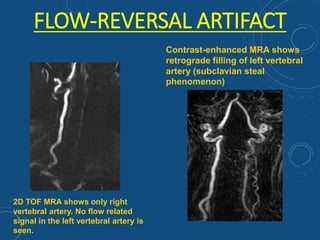
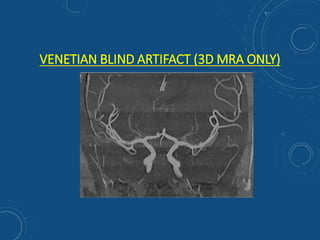
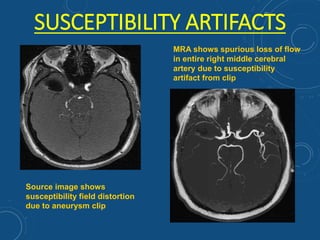
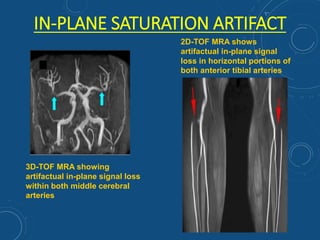
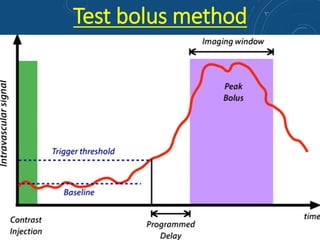
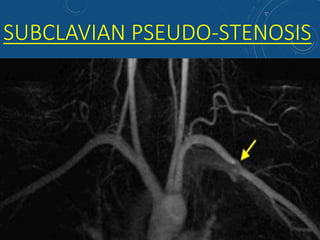
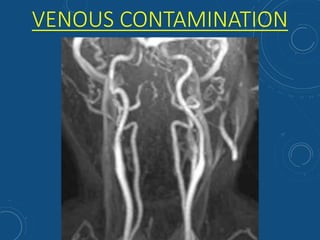
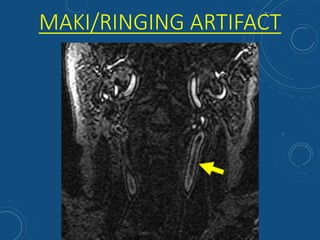
This document discusses MR angiography techniques and vascular abnormalities. It begins by outlining the major vascular systems in the human body. It then describes various vascular abnormalities like stenosis, aneurysms, and arterial venous malformations. The document goes on to explain different MR angiography pulse sequences like TOF, CE MRA, and PC MRI. It provides details on TOF MRA principles and advantages/disadvantages. Common artifacts seen on TOF MRA like shine-through and susceptibility artifacts are also outlined. Finally, the document discusses CE MRA techniques including test bolus timing and advantages/disadvantages compared to TOF MRA.