Embed presentation
Downloaded 34 times




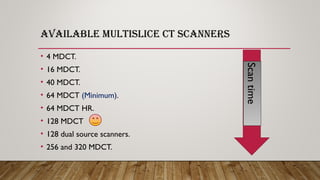




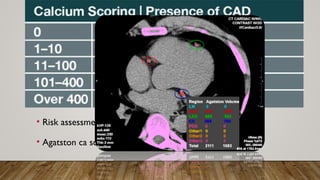



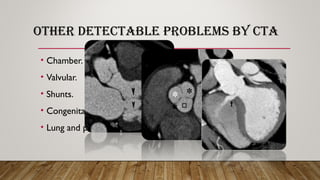



Cardiac CT and coronary CTA can play an important role in diagnosing cardiac patients. Coronary CTA is useful for ruling out obstructive coronary artery disease. Newer multislice CT scanners ranging from 4 to 320 slices allow for faster scanning times and better imaging of the heart. Proper patient preparation including beta blockers, fasting, and controlling heart rate are important for obtaining diagnostic images. Coronary CTA can detect obstructive coronary lesions, evaluate stents and grafts, and perform calcium scoring for risk stratification. It can also detect other cardiac abnormalities.
















