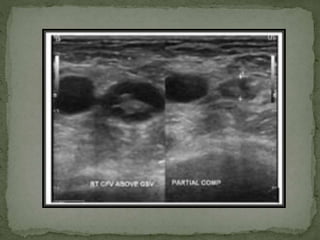
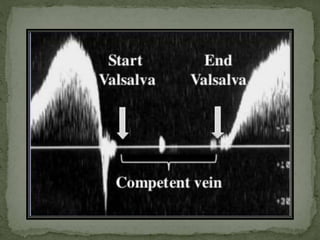
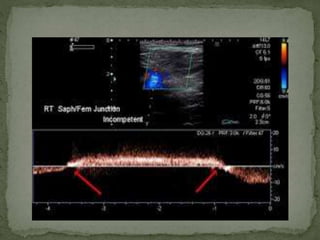
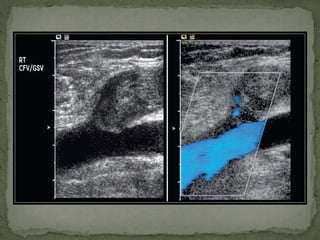
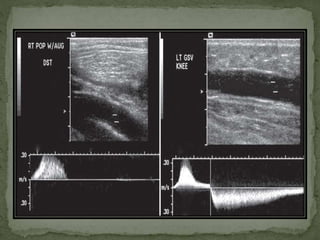
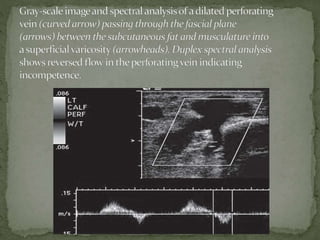
The document extensively discusses various imaging techniques for evaluating venous diseases, emphasizing non-invasive methods like ultrasound (US) which combine both anatomical and physiological information. It describes the applications and limitations of conventional venography, duplex Doppler, and color Doppler, particularly in diagnosing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and related conditions. Additionally, it highlights the importance of proper examination techniques, sensitivity to specific anatomical structures, and the implications of findings in both lower and upper limb venous systems.