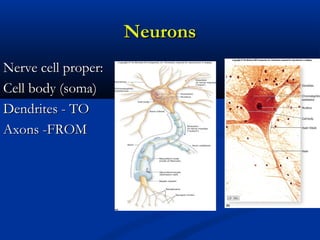
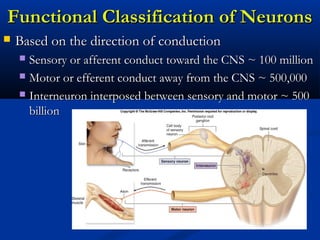
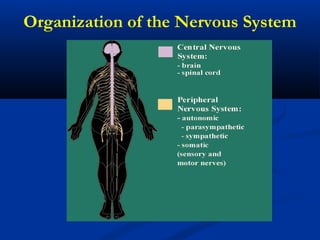
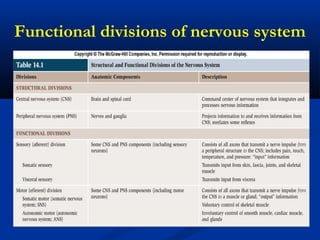
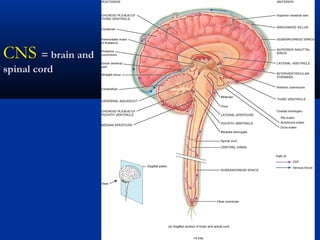
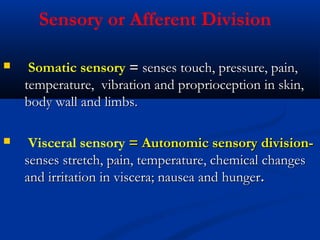
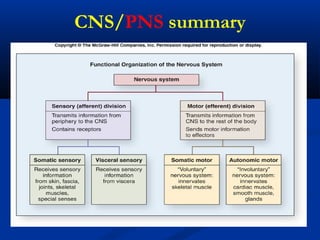
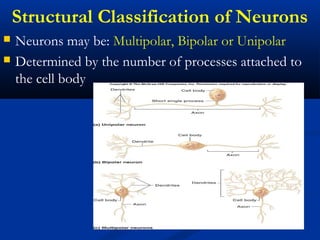
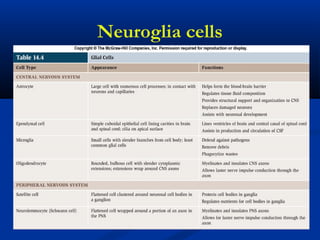
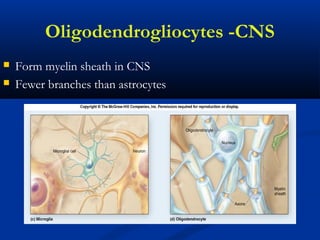
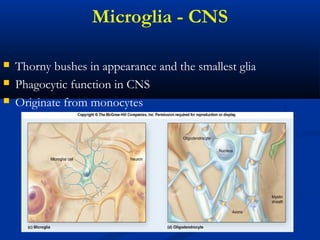
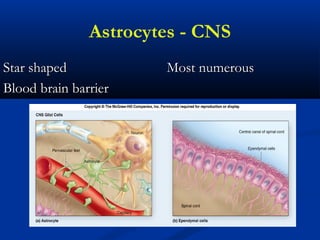
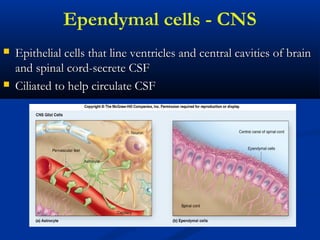
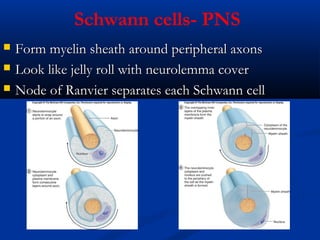
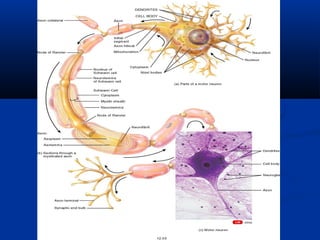
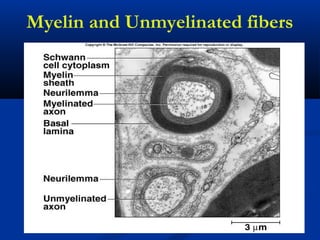
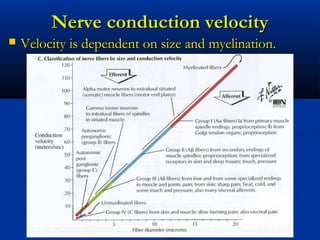
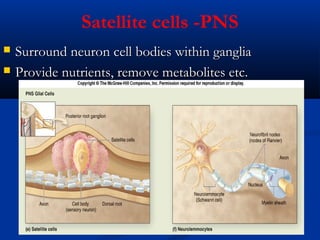
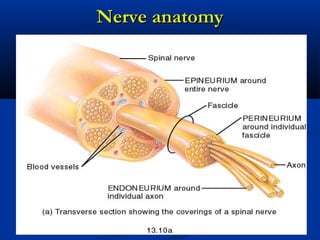
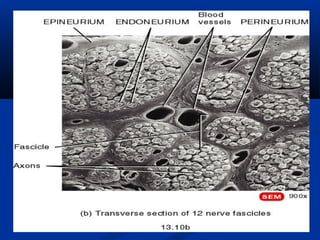
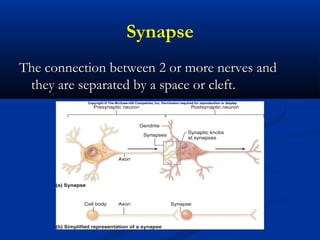
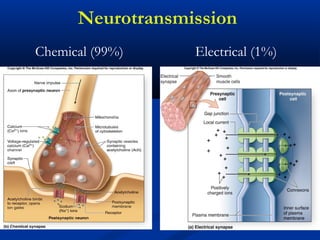
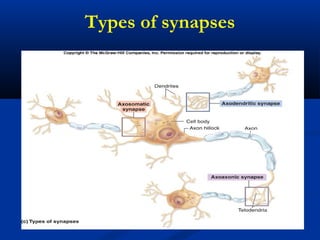
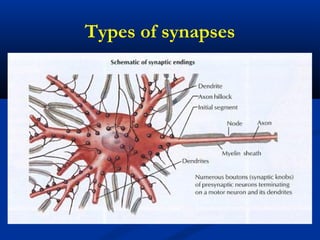
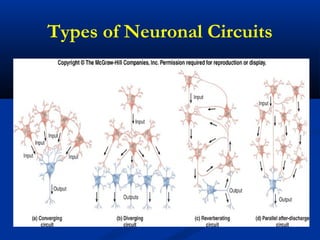
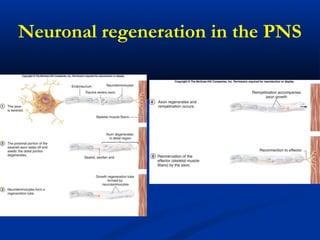
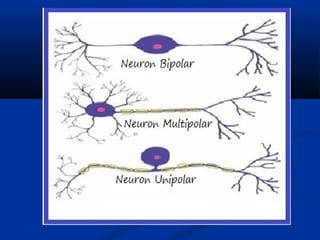
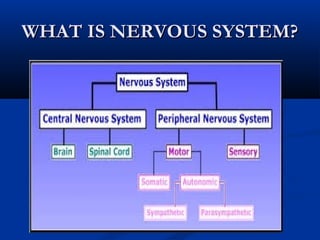
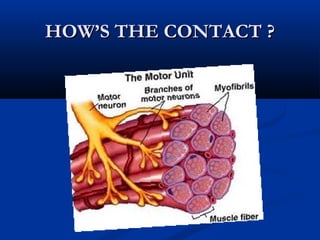
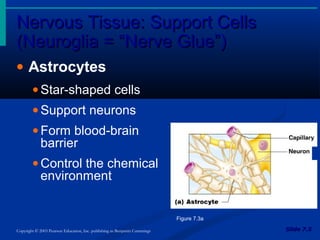
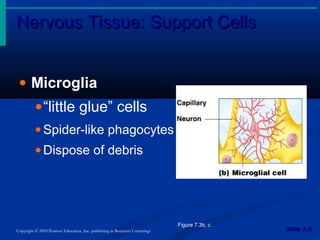
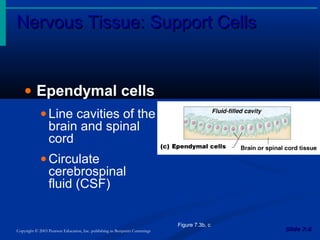
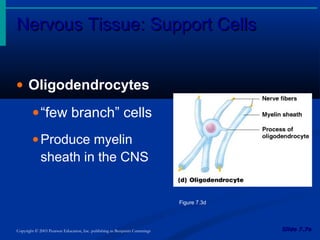
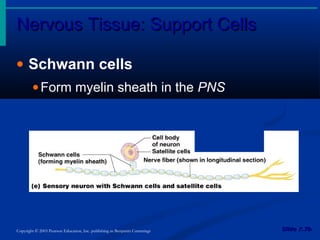
The document discusses the structure and function of the nervous system. It describes how the nervous system is composed of nervous tissue, including neurons and neuroglial cells. Neurons are the conducting cells that send and receive signals, while neuroglial cells provide support and insulation. The document outlines the key cell types, their roles, and organizational structure of the central and peripheral nervous systems.