Embed presentation
Downloaded 669 times






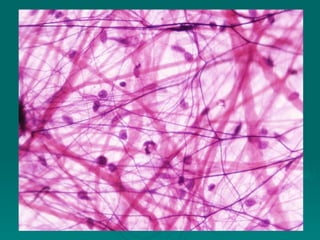

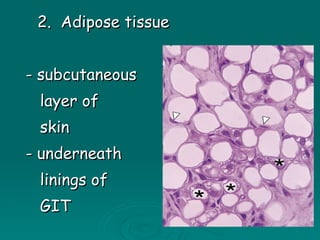
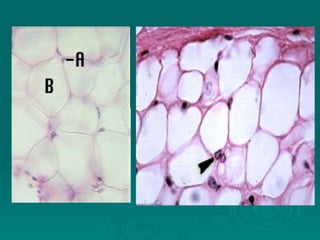

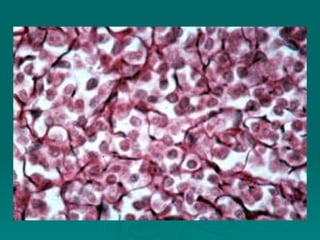
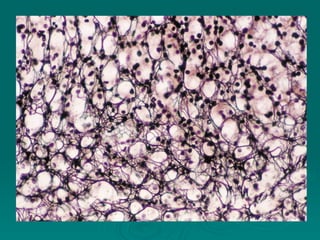

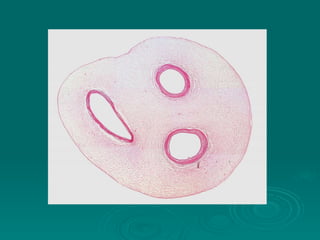
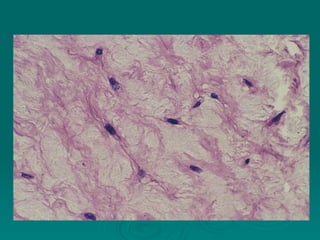
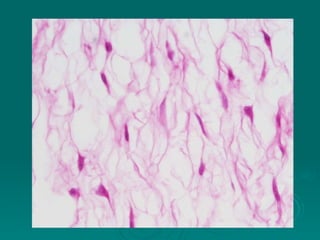
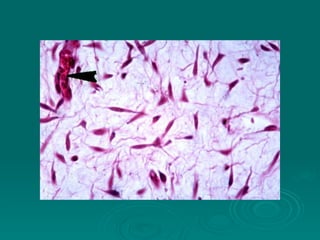

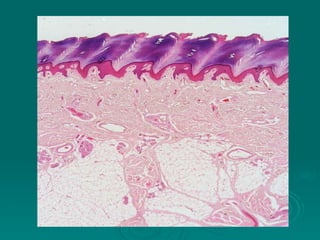
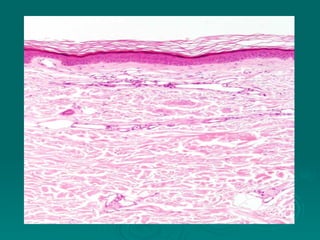
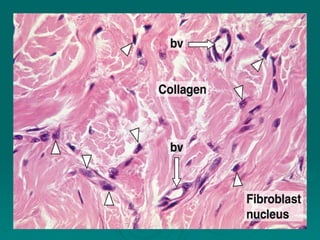
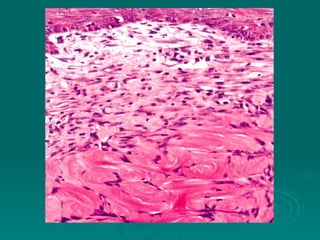
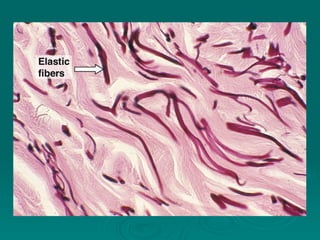

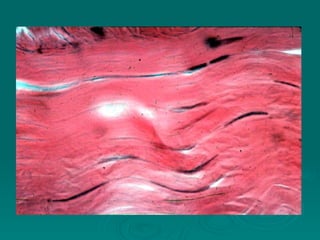
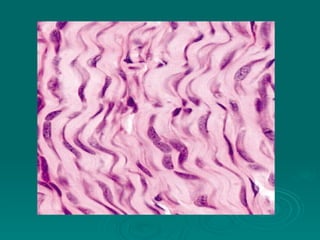

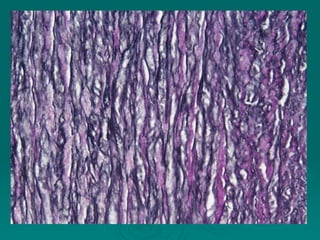
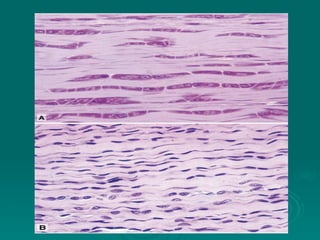
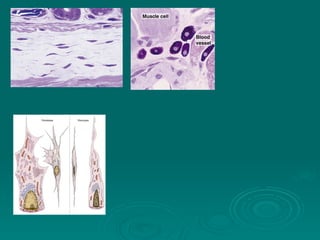

Connective tissues support and bind together other structures throughout the body. They are composed of connective tissue cells, ground substance, and fibers. Connective tissues have few cells separated by an abundant intercellular substance containing fibers. Their main functions are to bind tissues, provide mechanical support, store fat and minerals, allow for metabolite exchange, and aid in repair and healing. Connective tissues are classified as connective tissue proper, which includes loose and dense connective tissues, and specialized connective tissues like cartilage, bone, and blood.































