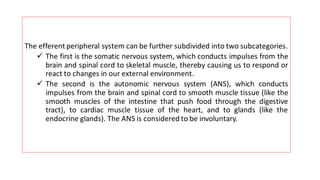
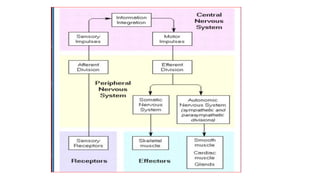
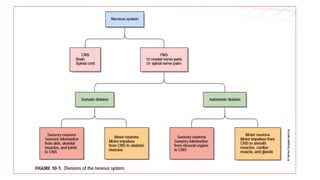
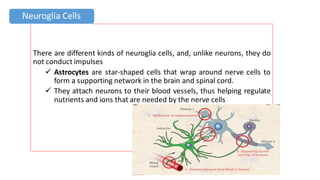
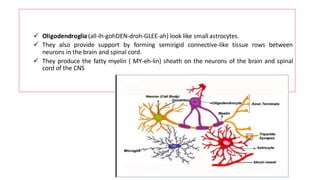
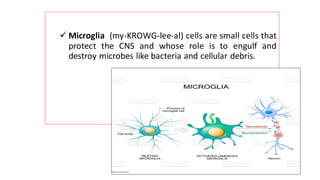
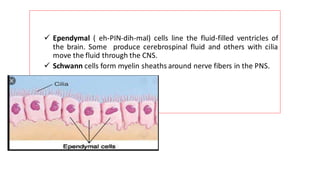
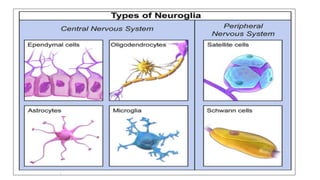
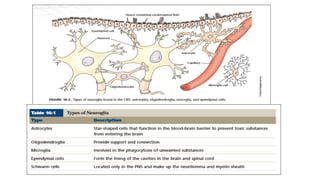
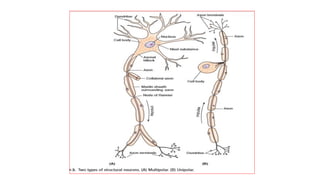
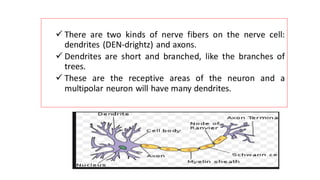
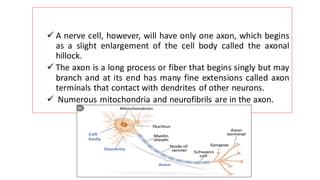
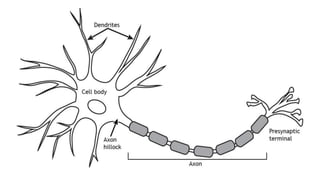
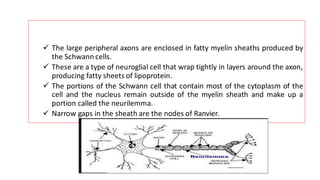
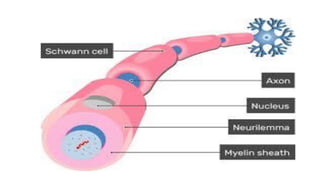
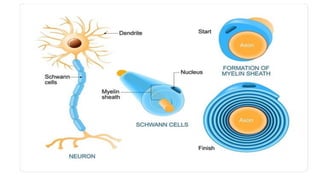
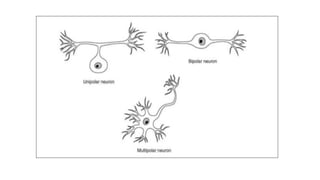
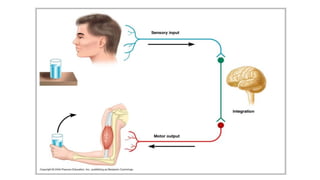
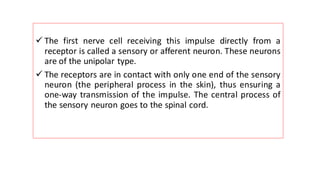
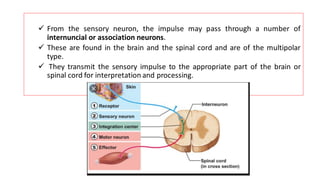
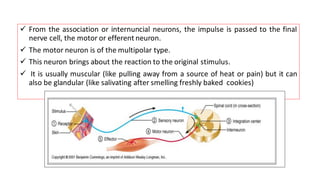
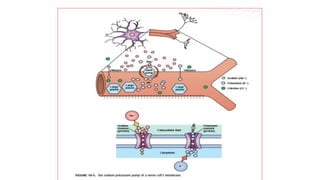
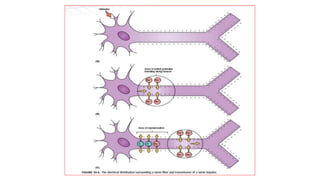
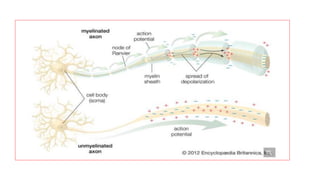
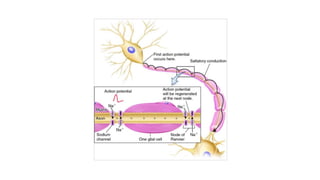
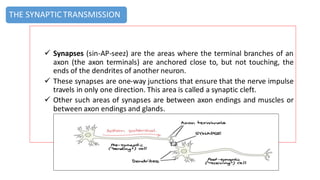
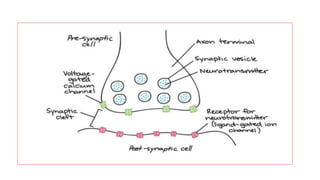
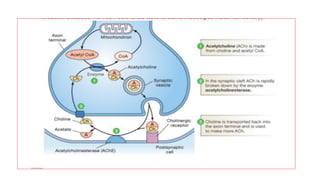
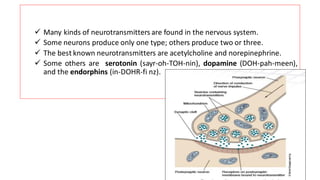
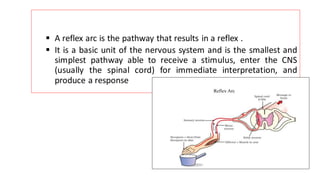
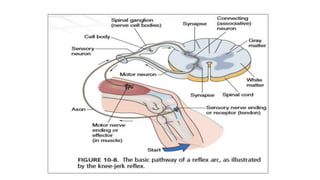
The nervous system serves as the body's control center and communication network, directing organ functions and interpreting external stimuli through the central (CNS) and peripheral nervous systems (PNS). The PNS includes sensory neurons (afferent) that convey information to the CNS and motor neurons (efferent) that relay responses to muscles and glands, with subdivisions including the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. Neurons transmit impulses via electrical changes and neurotransmitters at synapses, which facilitate communication between neurons and execute reflex actions impacting response times to stimuli.