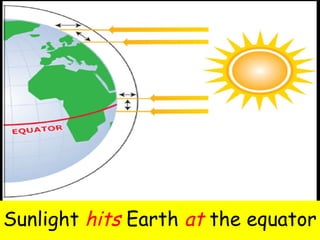
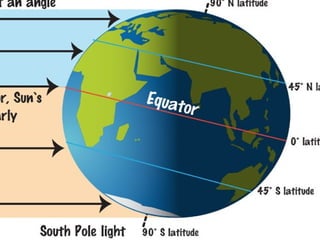
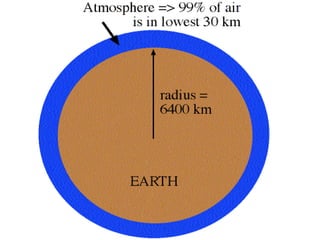
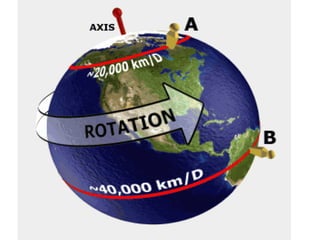
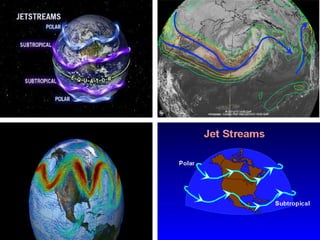
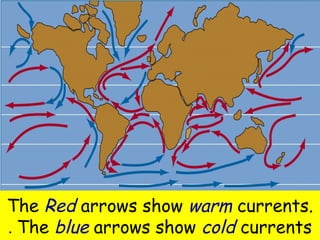
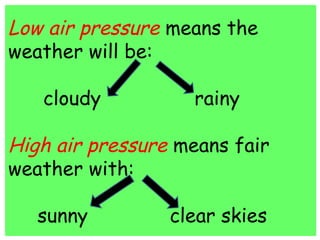
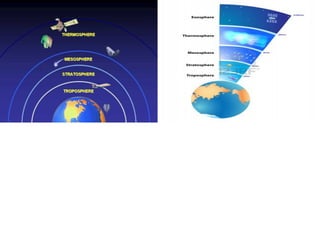
This document discusses weather and climate. It defines weather as the current conditions of the atmosphere at a specific time and place, while climate is the pattern of weather conditions over many years. The document outlines several factors that affect climate, such as sunlight, oceans, mountains, and altitude. It also describes tools that scientists use to measure and study weather conditions like temperature, wind speed and direction, humidity, air pressure, and rainfall.