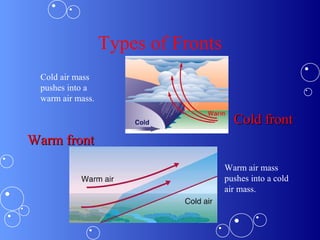
This document summarizes different weather phenomena and tools used to study weather. It describes how temperature, wind, and precipitation are measured using instruments like a thermometer, anemometer, and rain gauge. It also explains different types of clouds, air masses, fronts, storms like hurricanes and tornadoes. Key weather terms are defined, such as humidity, high and low pressure systems, and how meteorologists use barometers and study changes in air pressure to predict weather patterns and conditions.