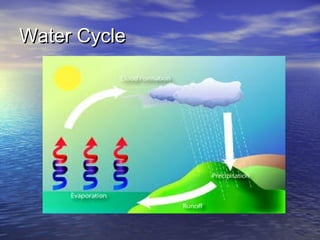
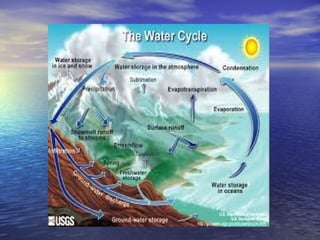
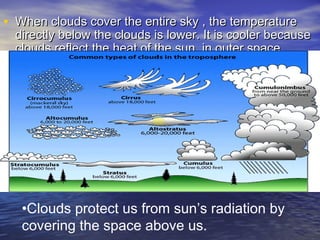
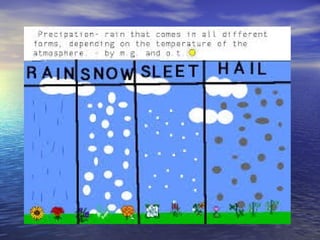
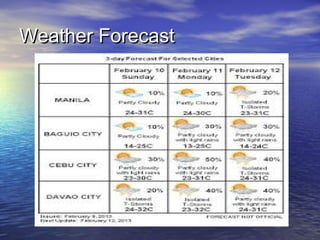
The document discusses various factors that affect weather, including cloudiness and precipitation. It describes different types of clouds and how they indicate upcoming weather conditions. Instruments for measuring and observing weather are also outlined, such as rain gauges and weather stations. Weather forecasting is important to be prepared for changing conditions.