This document provides information about weather and climate through several sections:
1) It defines weather as the short-term atmospheric conditions including temperature, precipitation, wind etc. that change frequently. Weather is reported through daily forecasts.
2) Climate is defined as the pattern of weather in a place over a long period (30 years) and influences the wildlife and vegetation. It depends on the typical temperature and precipitation.
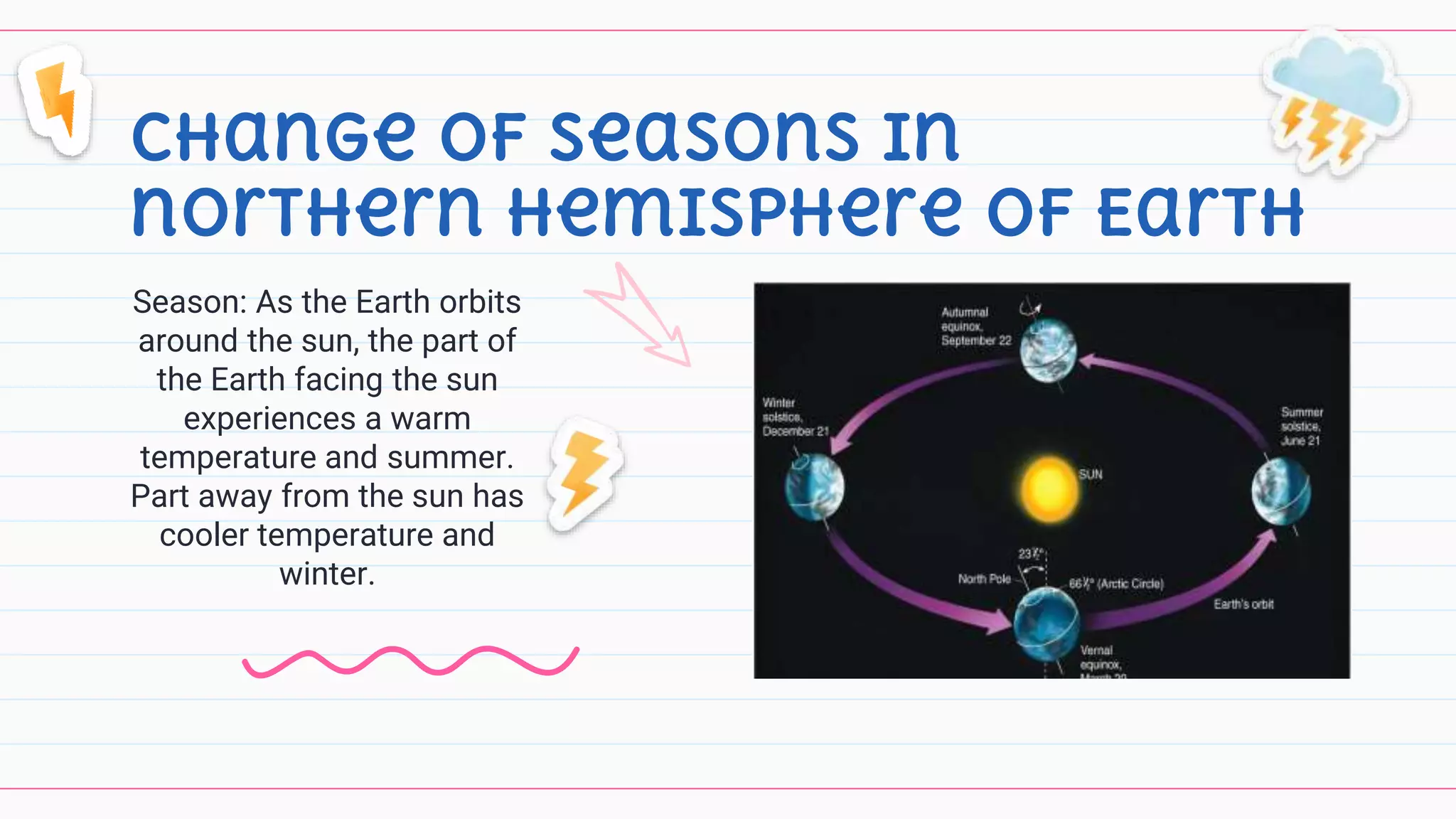
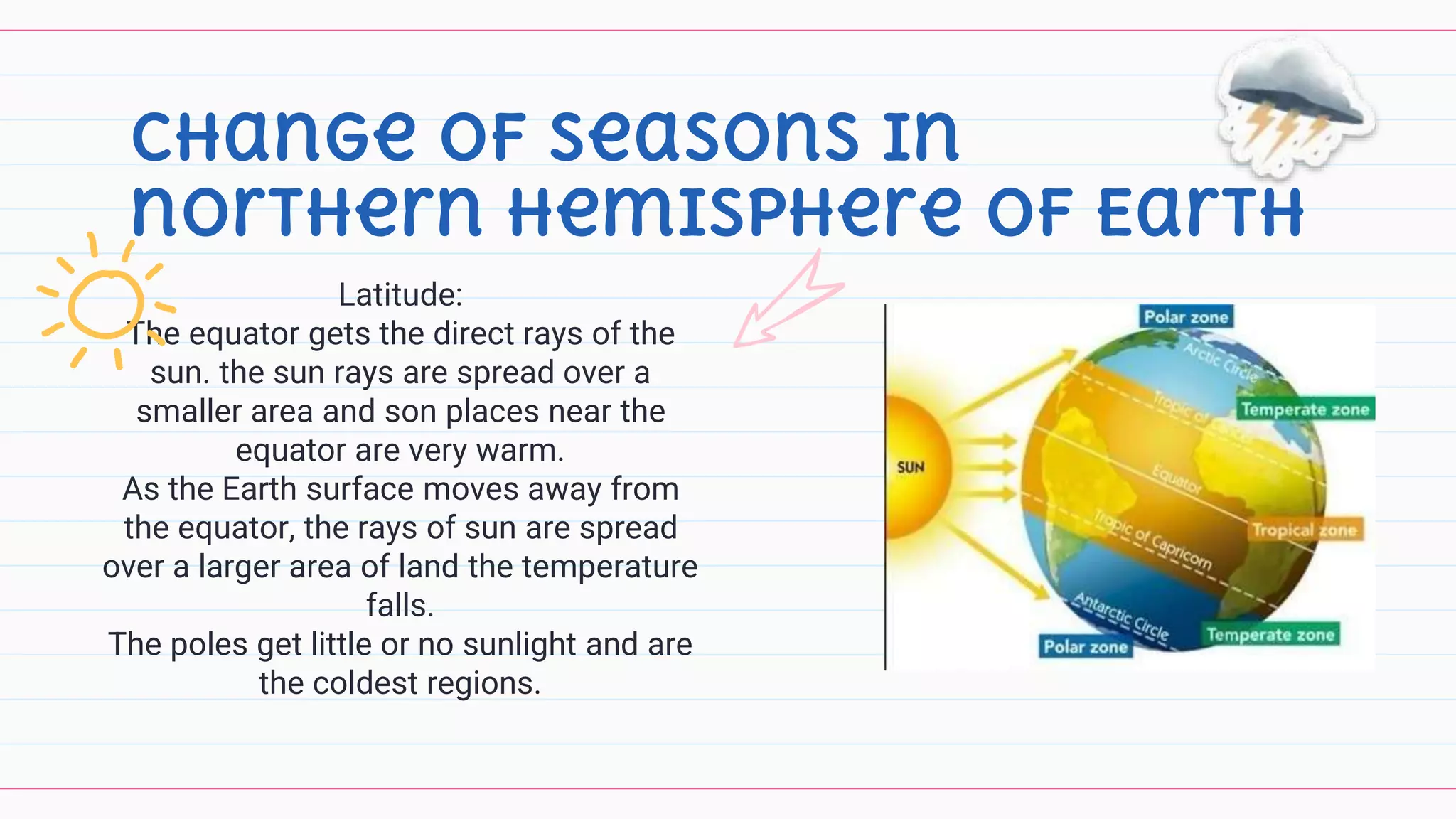
3) Key factors that influence climate are identified as seasons, latitude, altitude, distance from large bodies of water. Seasonal changes are caused by the earth's orbit around the sun. Latitudinal changes influence temperature based on proximity to the equator.