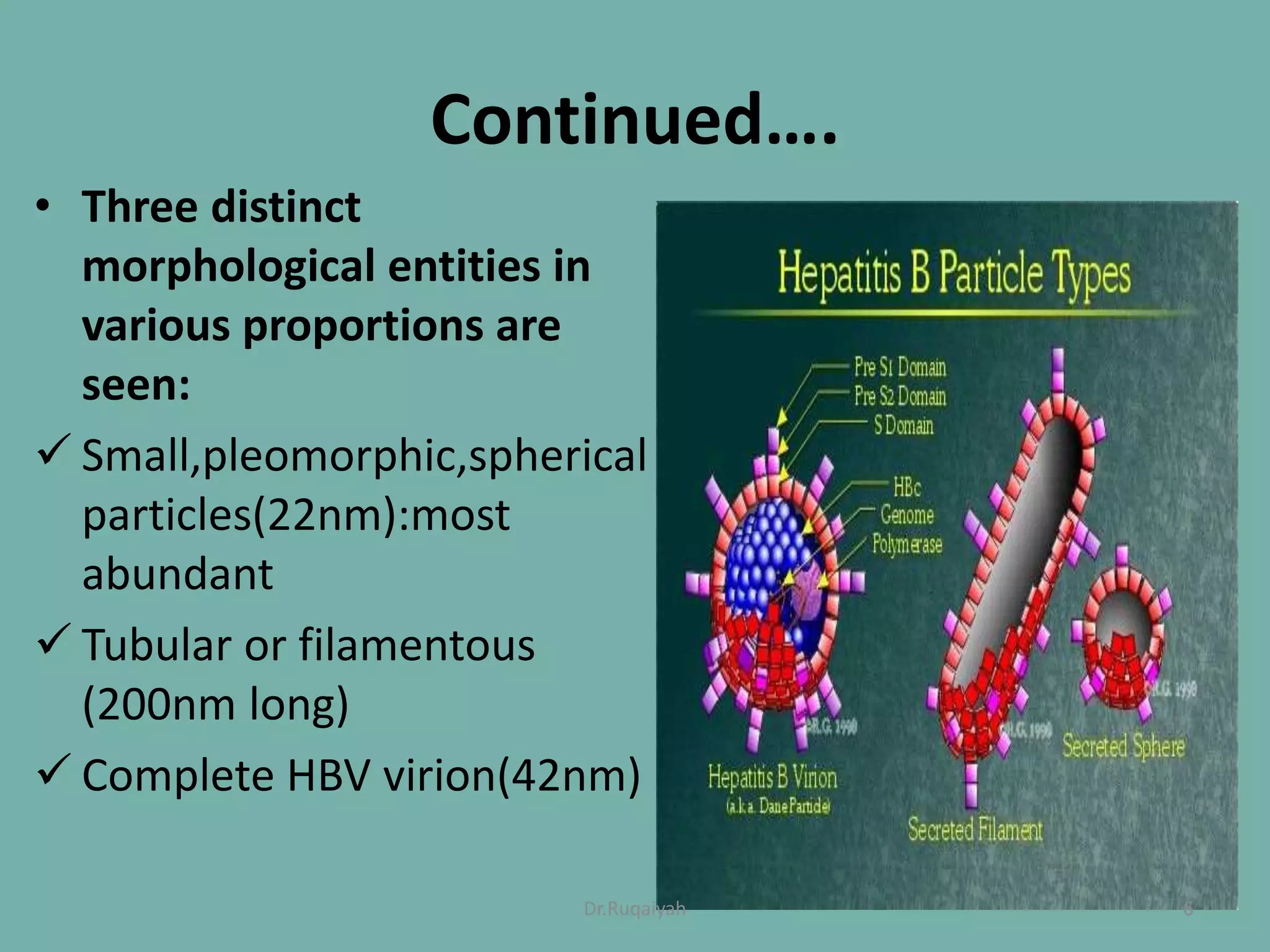
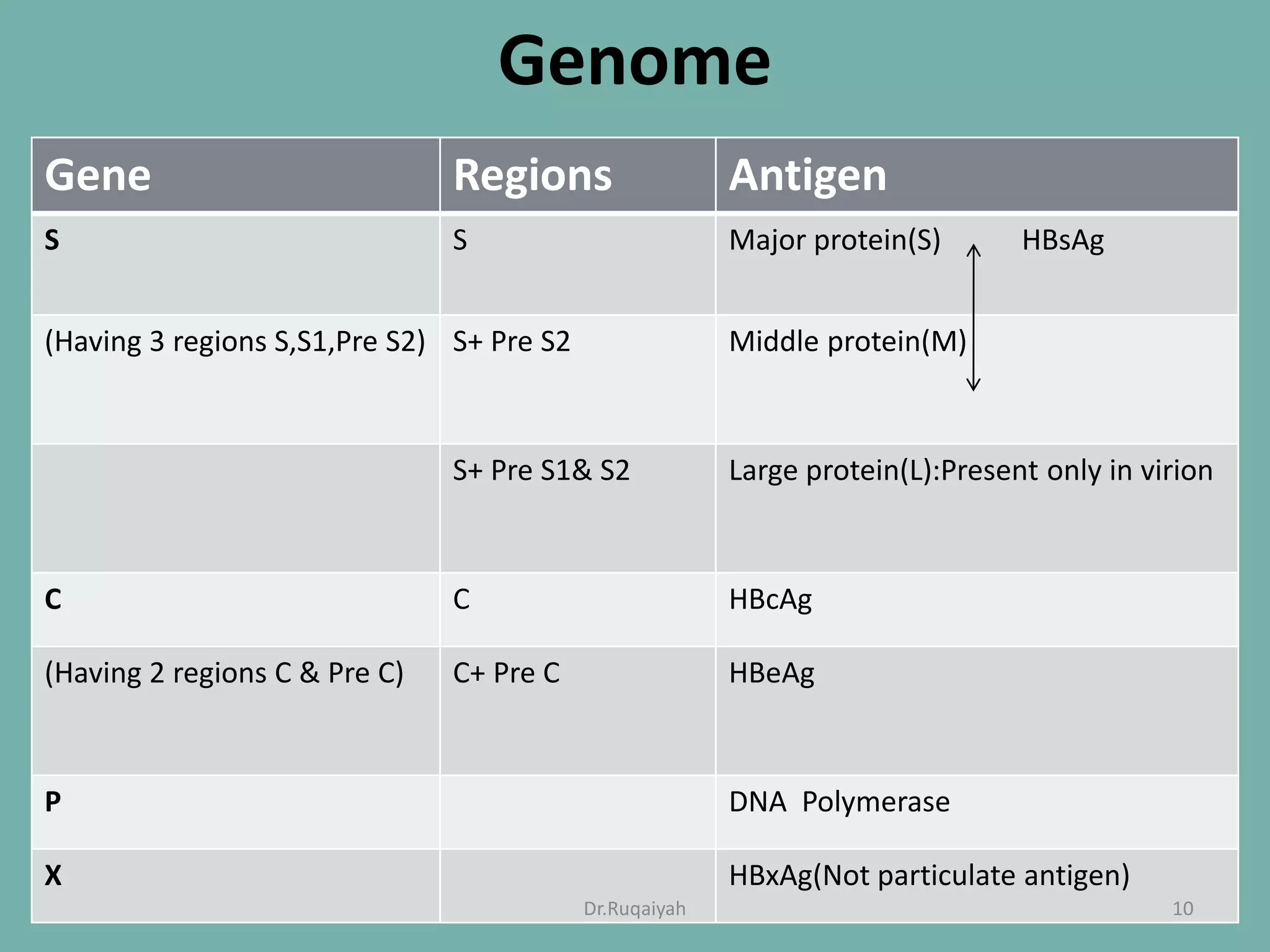
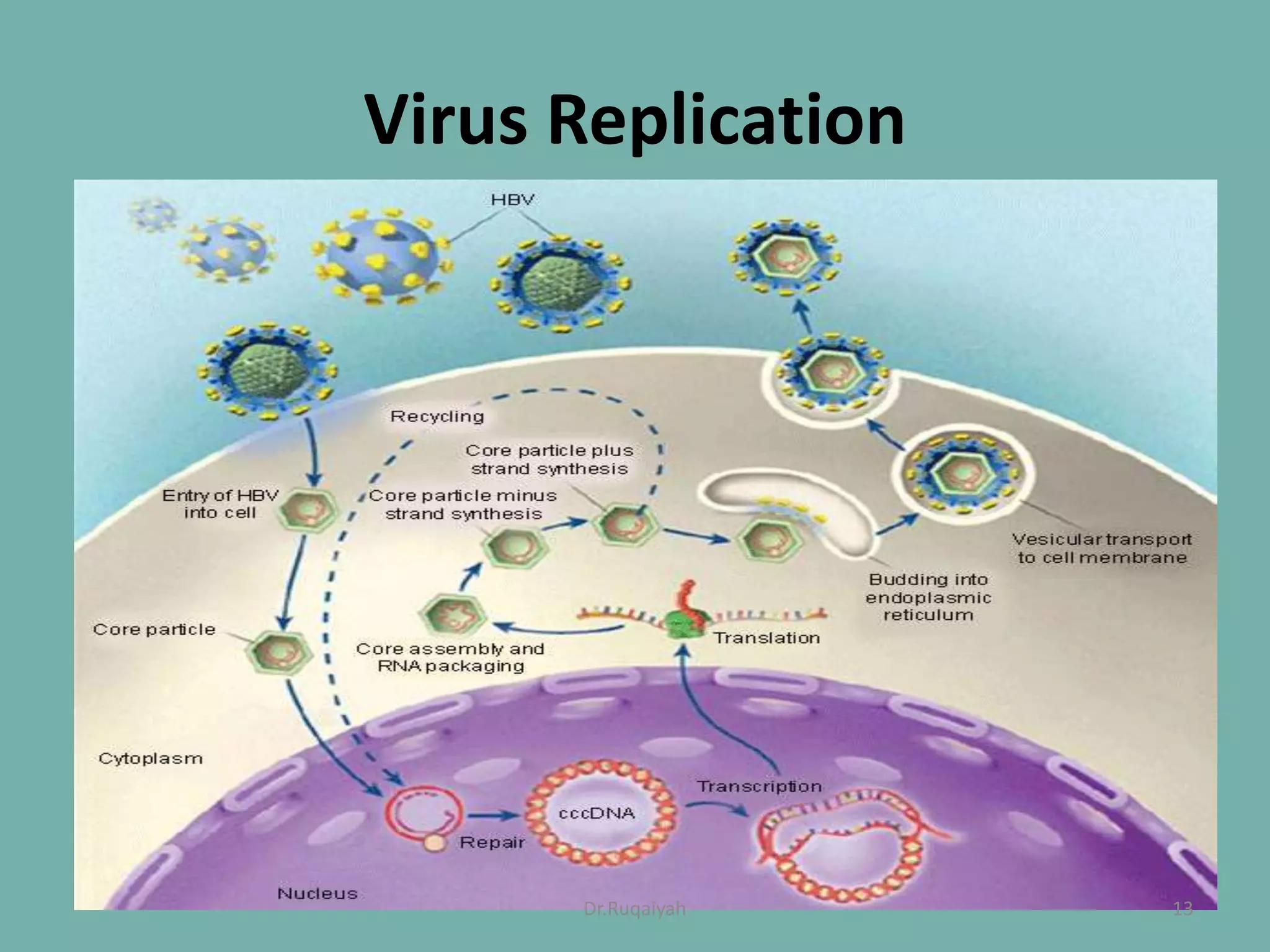
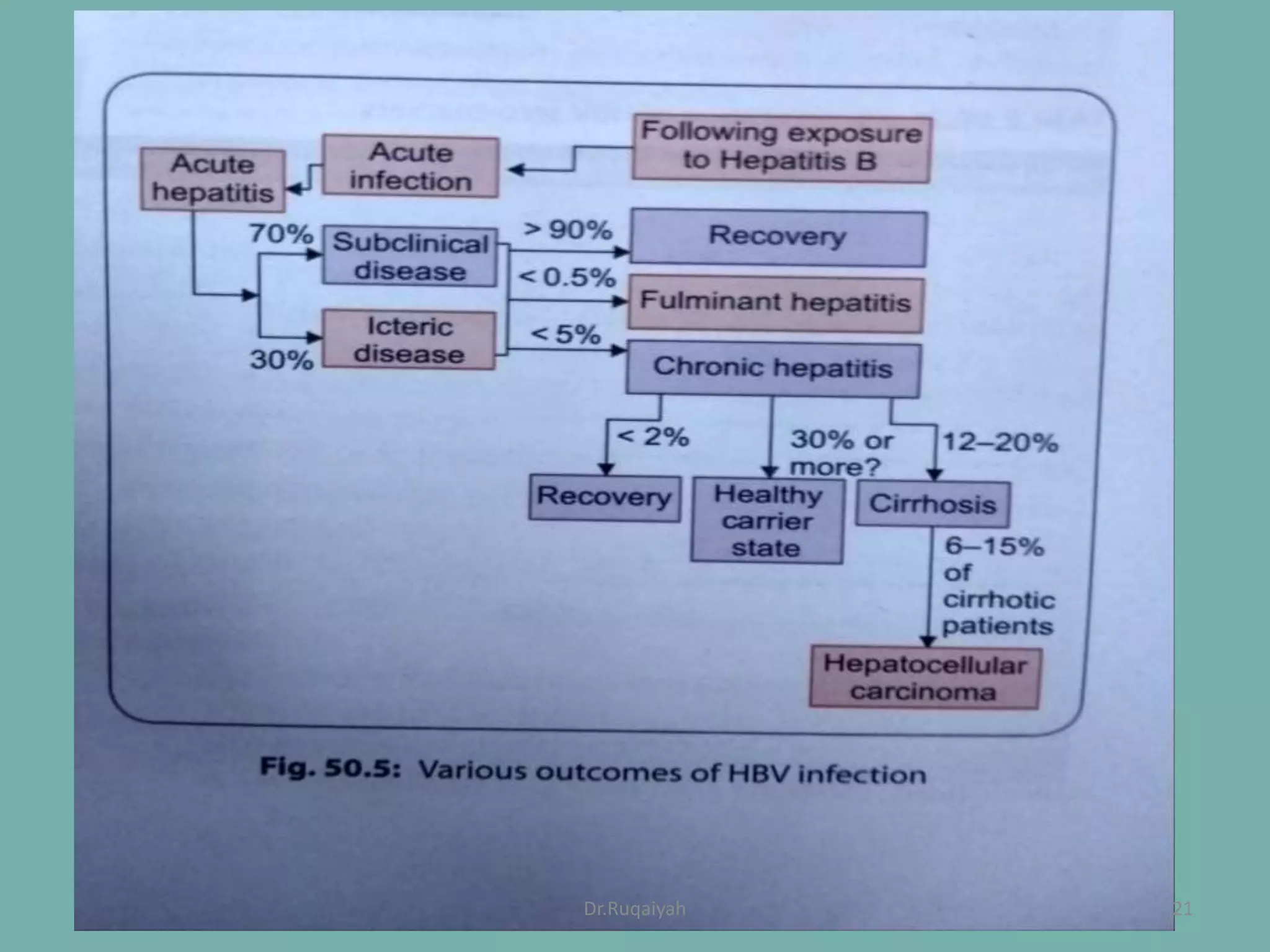
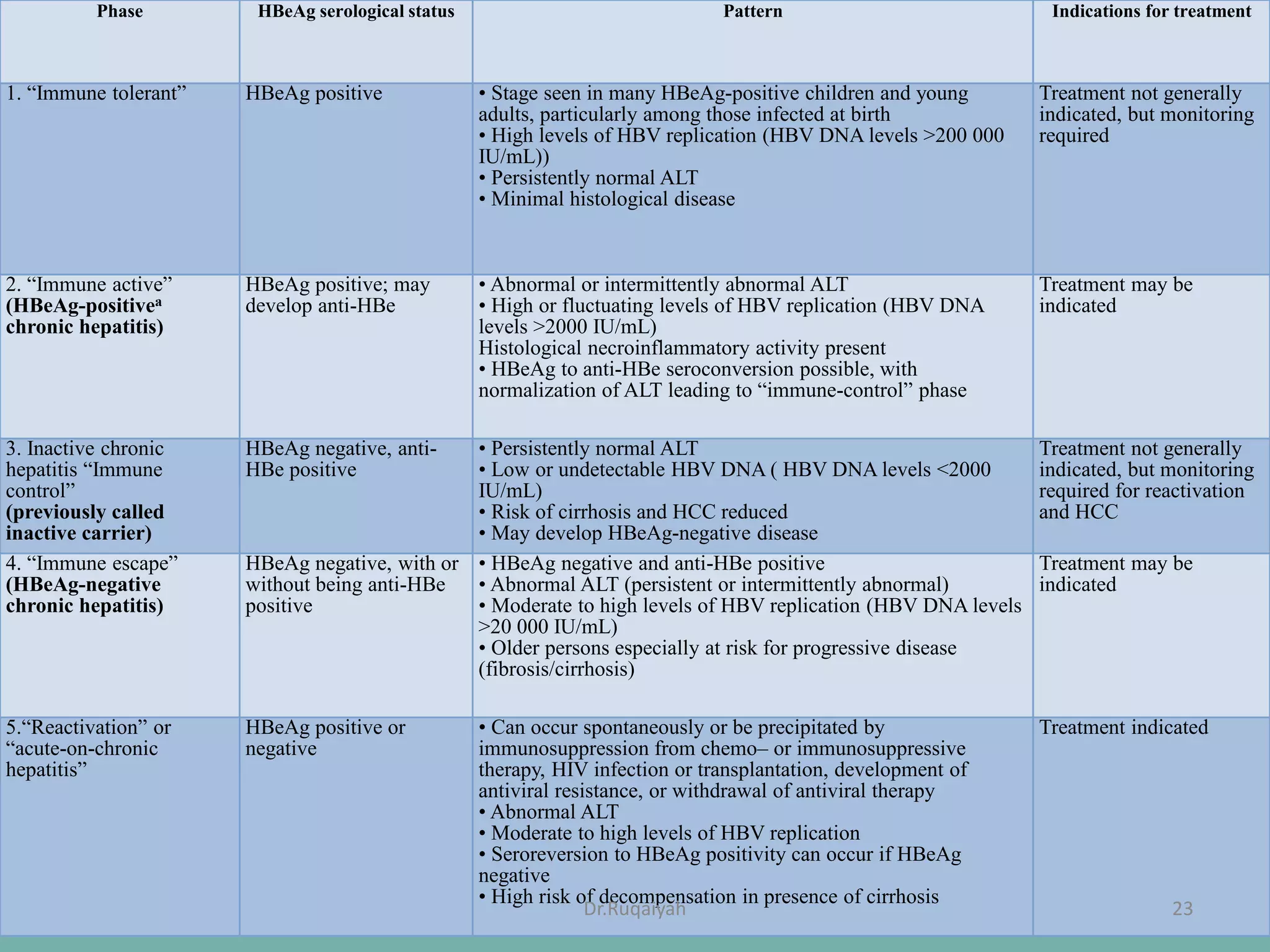
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that affects the liver and can become chronic. It was first described in the 5th century and major developments in understanding the virus occurred between the 1940s-1970s with the identification of antigens and viral particles. The virus is classified taxonomically and has an overlapping genome encoding various antigens. It exists in different morphological forms and has multiple genotypes and serotypes. Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood or bodily fluids and has various stages from acute to chronic infection. Diagnosis involves detecting antigens, antibodies, and viral DNA through serological and molecular tests. Vaccination and antiviral treatment can help prevent and manage the disease.