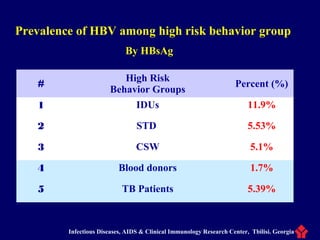
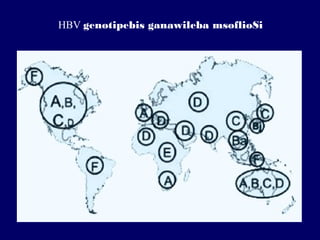
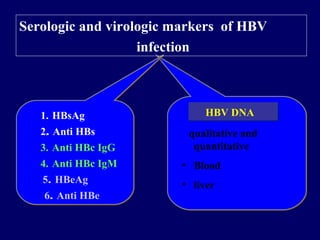
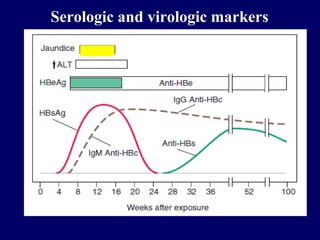
The document discusses hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis B. It provides definitions and details about the epidemiology, transmission, clinical manifestations, pathogenesis, and serologic and virologic markers of HBV infection. Some key points include:
- HBV is a viral infection of the liver that affects around 2 billion people worldwide and causes over 1 million deaths annually.
- It is transmitted through contact with infectious blood or body fluids from an infected person.
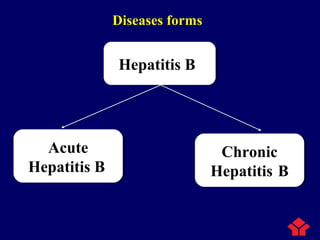
- Clinical manifestations range from an acute self-limiting illness to chronic lifelong infection associated with cirrhosis and liver cancer.
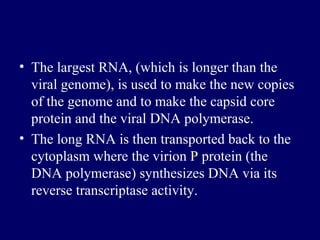
- HBV pathogenesis involves the virus gaining entry into liver cells and using the host cell machinery to replicate. The host immune