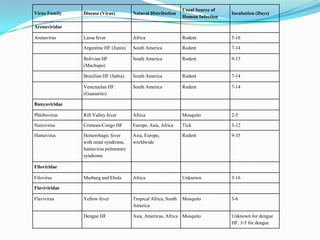
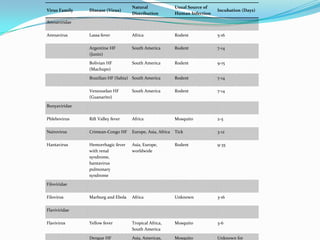
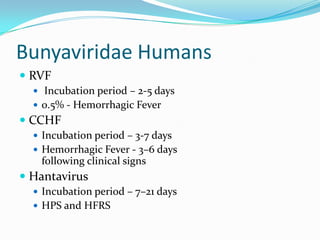
Viral hemorrhagic fevers are caused by RNA viruses from several families including Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Filoviridae, and Flaviviridae. They cause severe illness characterized by fever and bleeding and can be lethal. Transmission varies between rodents, ticks, and mosquitoes depending on the virus. Symptoms typically appear 2-16 days after exposure and include fever, malaise, and bleeding from various orifices. Treatment is largely supportive though ribavirin may be effective for some viruses. Strict isolation of patients and notification of authorities is required.