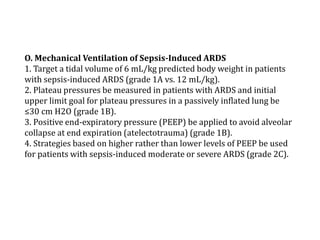
Sepsis is defined as infection plus systemic manifestations of infection. Severe sepsis is defined as sepsis with organ dysfunction or tissue hypoperfusion. Initial resuscitation goals include maintaining a central venous pressure of 8-12 mmHg, mean arterial pressure of at least 65 mmHg, urine output of 0.5 mL/kg/hr, and oxygen saturation of 70% or higher. Effective intravenous antimicrobials should be administered within one hour of recognizing sepsis or septic shock. Source control and infection prevention are also important aspects of treatment.




















![4. Not using antithrombin for the treatment of severe sepsis and
septic shock (grade 1B).
5. In patients with severe sepsis, administer platelets
prophylactically when counts are <10,000/mm3 (10 x 109/L) in
the absence of apparent bleeding. We suggest prophylactic
platelet transfusion when counts are < 20,000/mm3 (20 x
109/L) if the patient has a significant risk of bleeding. Higher
platelet counts (≥50,000/mm3 [50 x 109/L]) are advised for
active bleeding, surgery, or invasive procedures (grade 2D).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sepsisguidelines-140915135541-phpapp02/85/Sepsis-guidelines-2013-22-320.jpg)