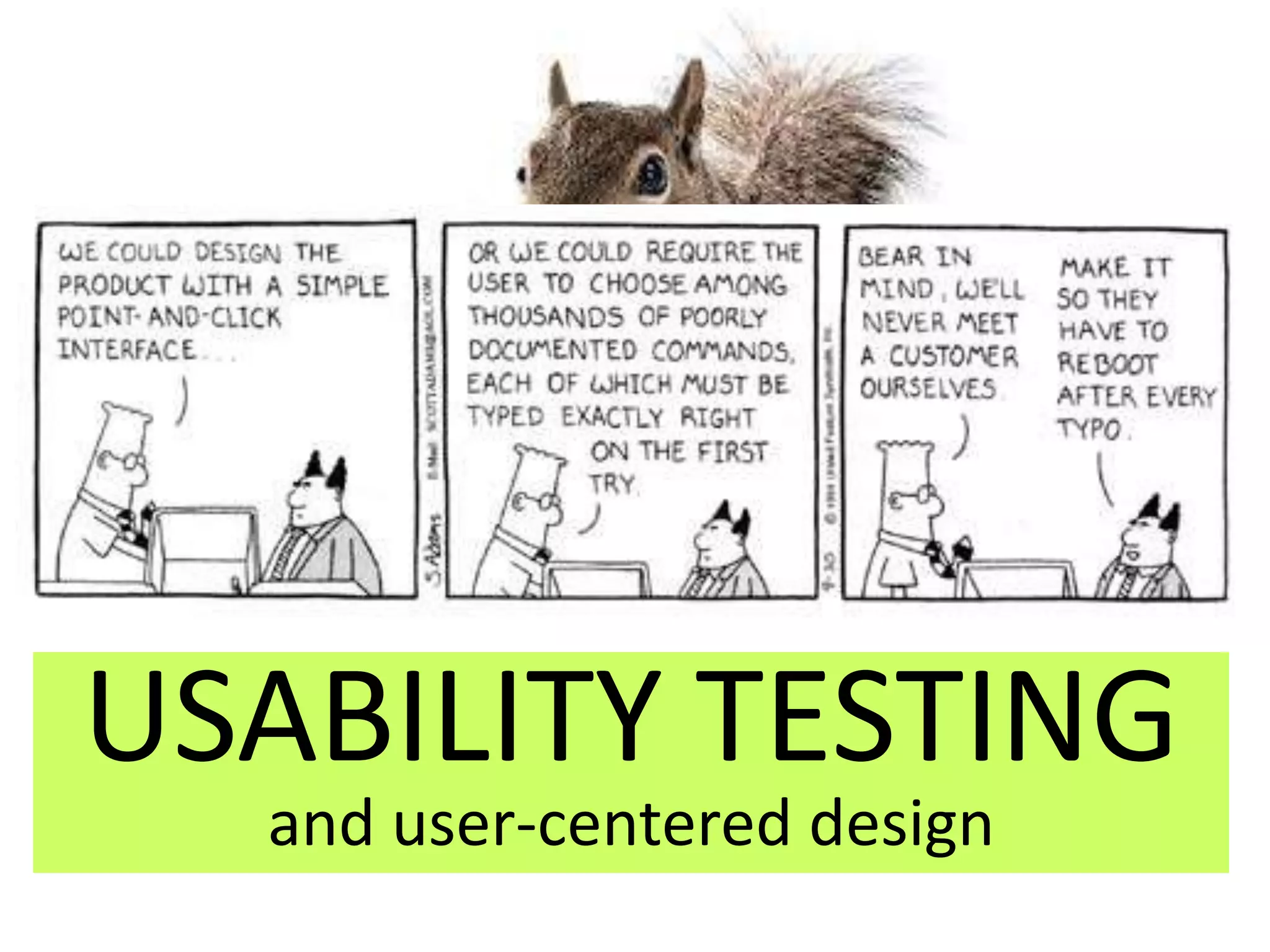
This document discusses usability testing and user-centered design. It defines user-centered design as considering end users' needs in all stages of the design process. It then describes usability testing as a way to determine if the assumptions made during design were correct. It lists characteristics of usable products and potential difficulties in usability testing for software/websites. Finally, it outlines the main steps to conduct a cognitive walkthrough usability test, including choosing products, identifying users, designing tasks, collecting data, and reporting results.