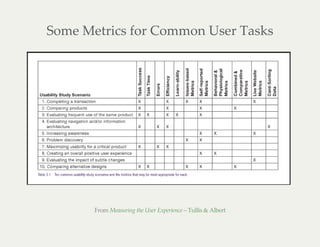
This document provides an overview of usability testing and highlights from its history. It discusses why usability testing is important and how even simple, qualitative testing can identify major usability issues. Examples of usability metrics like effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction are given. The document then describes how to plan and conduct DIY usability tests with only a few participants through defining goals, tasks, recruiting testing and debriefing. It also discusses testing accessibility, mobile usability, and using tools like prototyping and A/B testing.