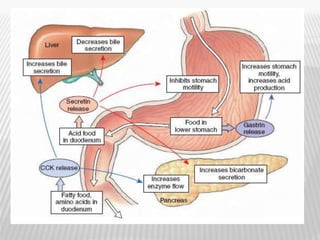
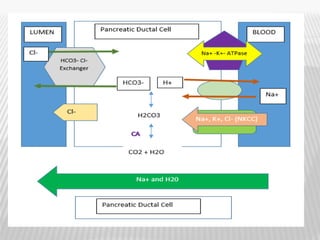
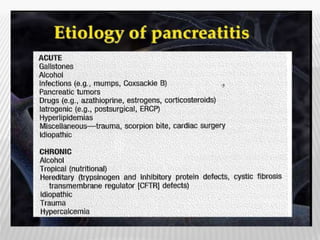
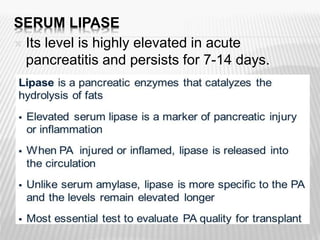
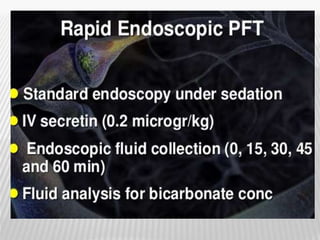
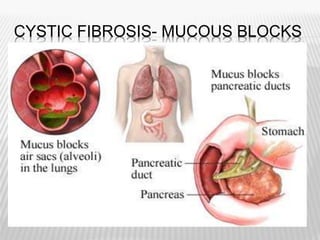
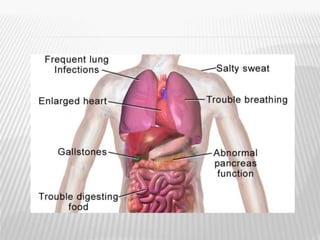
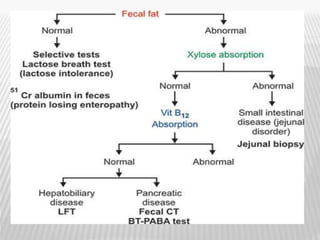
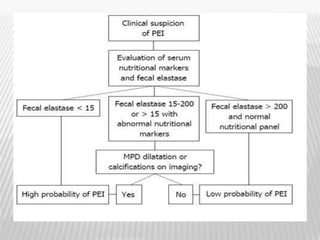
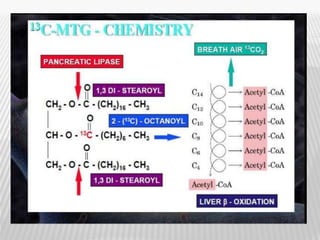
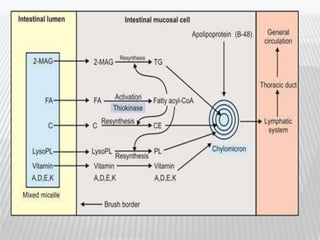
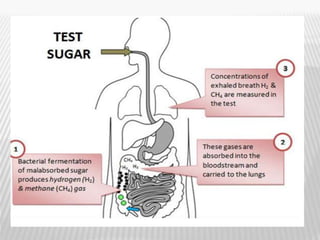
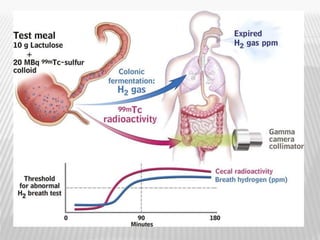
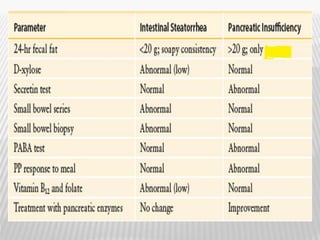
The document outlines various tests for assessing pancreatic and intestinal functions, detailing the exocrine and endocrine roles of the pancreas, along with specific pancreatic enzyme levels and their implications in conditions like acute pancreatitis. It also discusses the function and testing of the small intestine, the diagnostic relevance of various tests for malabsorption and intestinal diseases, and the role of tumor markers in conditions like pancreatic carcinoma and carcinoid syndrome. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for understanding both pancreatic and intestinal function tests in clinical practice.