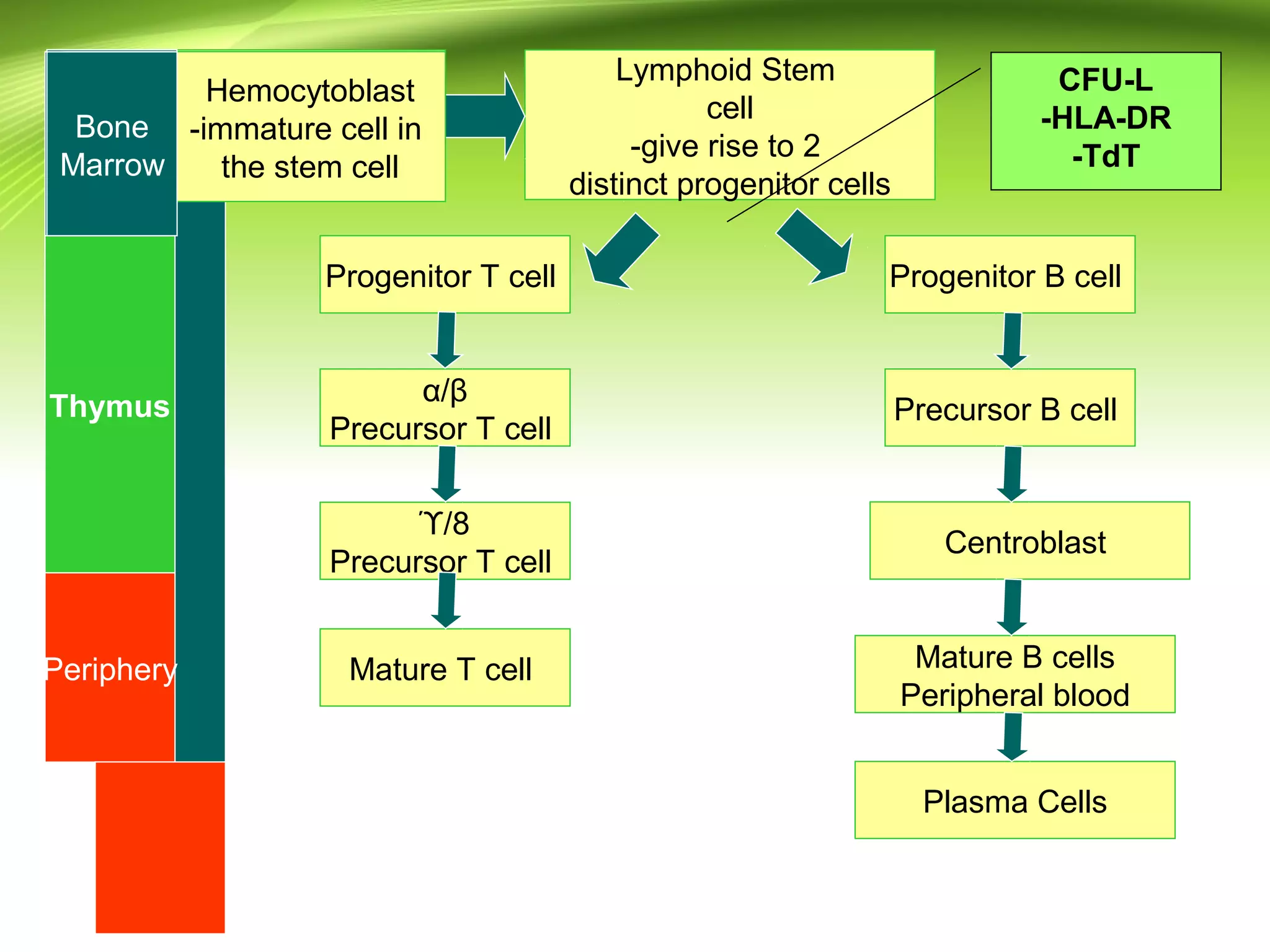
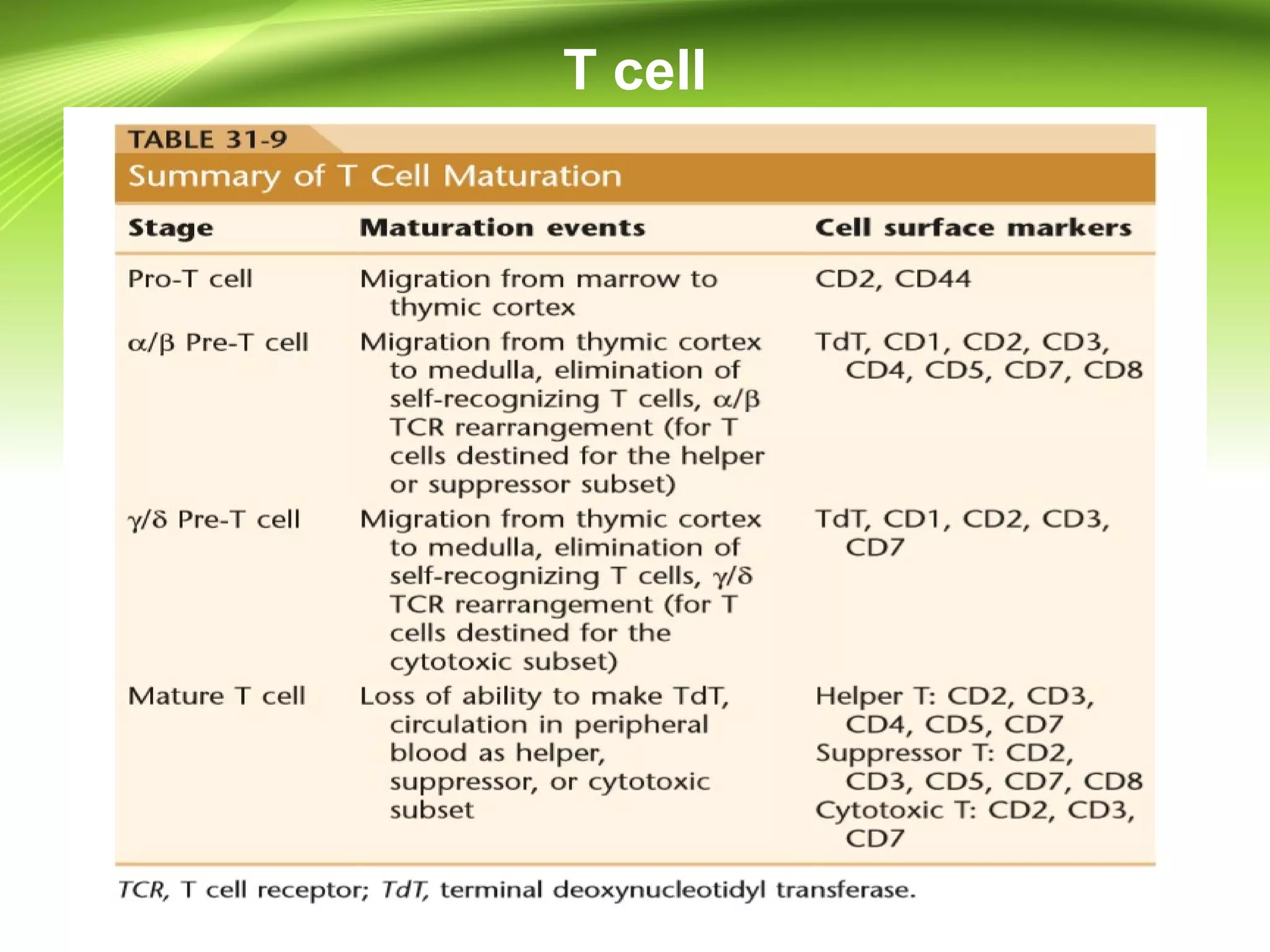
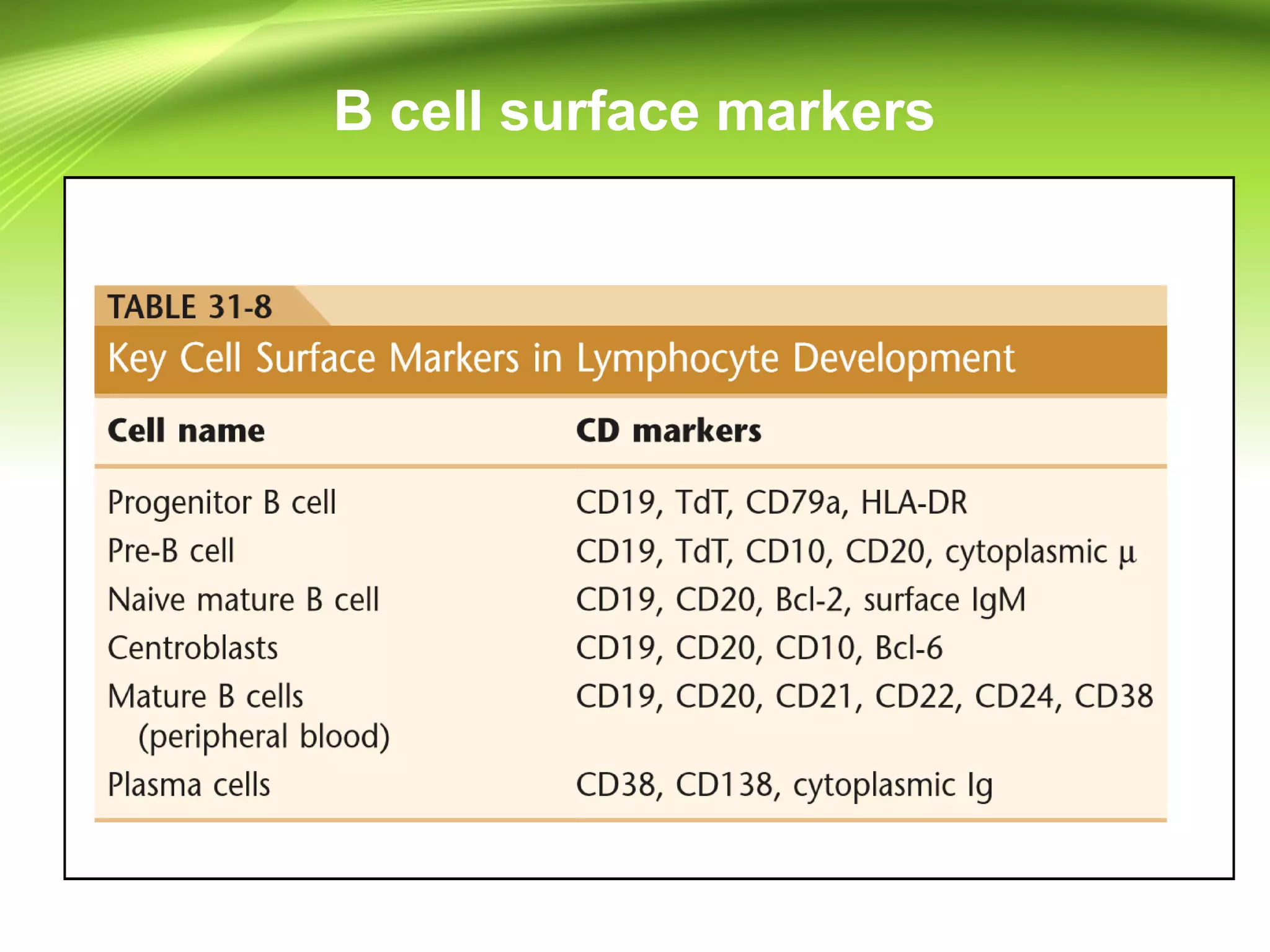
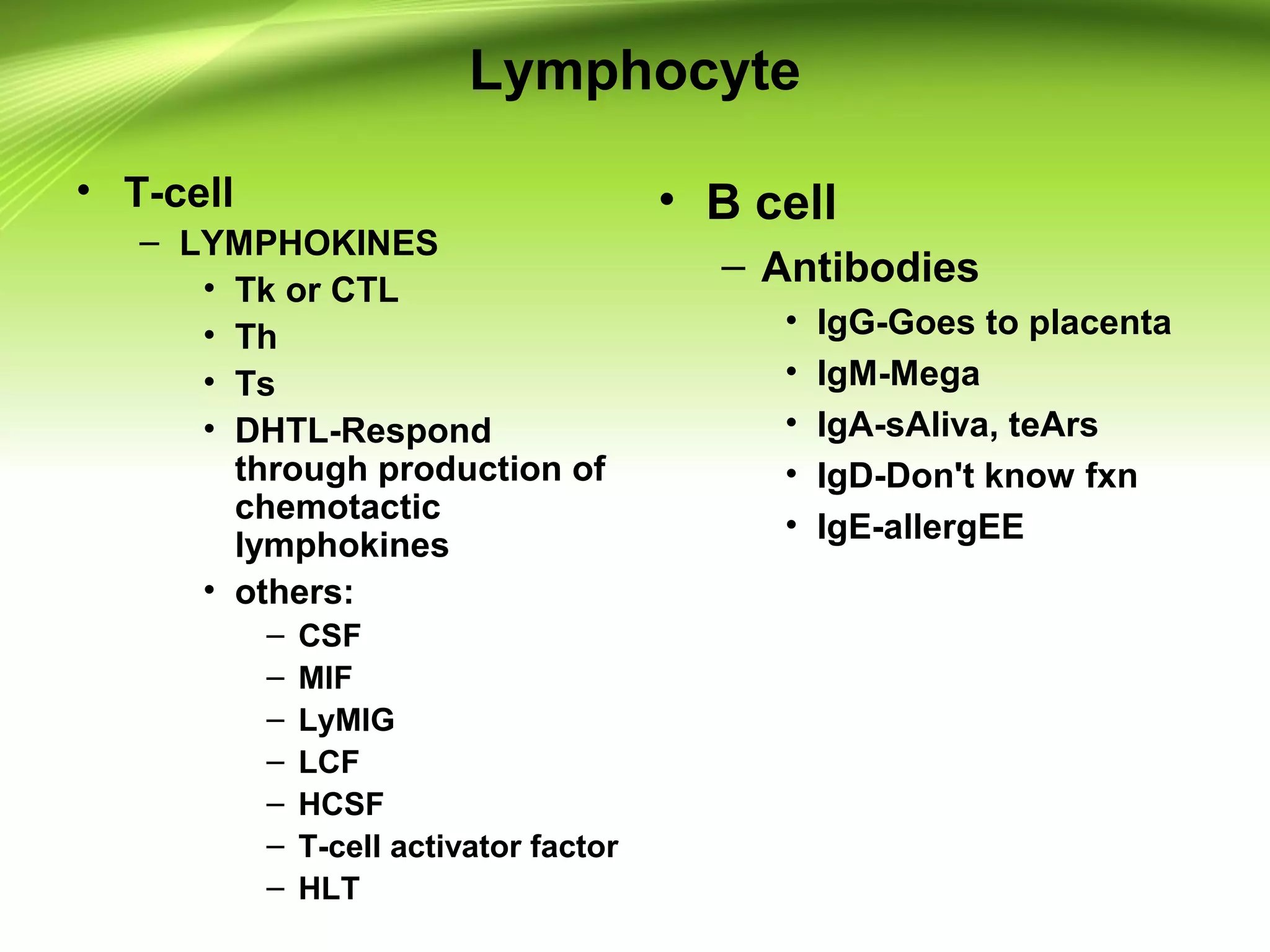
Lymphocytes develop and mature through distinct stages in primary and secondary lymphoid tissues. In primary tissues like the bone marrow and thymus, lymphocyte progenitors undergo lineage commitment and maturation. A small percentage then migrate to secondary tissues like lymph nodes and spleen where antigen stimulation drives proliferation. T cells mature in the thymus while B cells mature in the bone marrow, undergoing gene rearrangement and expressing specific surface markers at different stages to eventually produce mature, circulating T and B cells. Lymphocytes recirculate between lymphoid tissues throughout the body and have varying life spans, with the majority lasting 4 years but some up to 20 years.