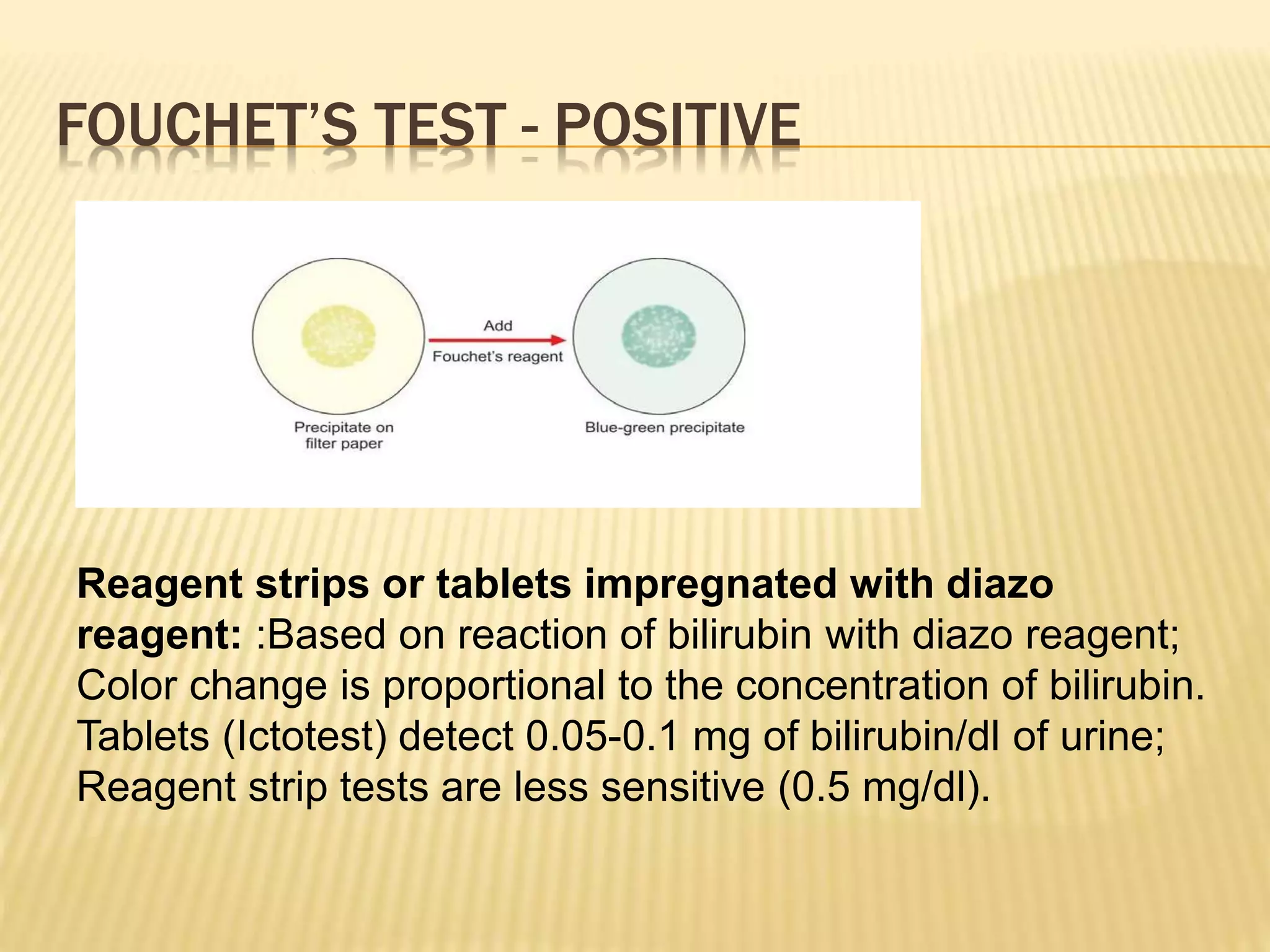
The document outlines the significance of urine examination in diagnosing renal and urinary tract diseases, detailing various urine characteristics such as color, odor, turbidity, pH, and specific gravity. It discusses abnormal constituents found in urine, including glucose, proteins, ketones, bilirubin, and urobilinogen, along with their clinical implications and associated conditions. Additionally, the document highlights the importance of microscopic examination to identify casts, cells, and other elements that signify potential health issues.