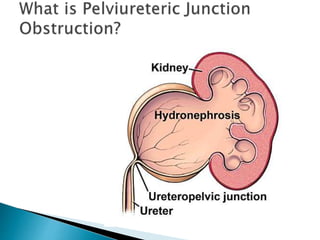
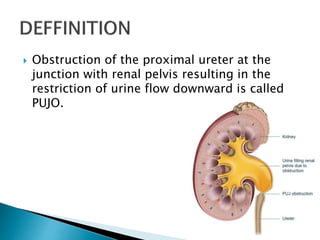
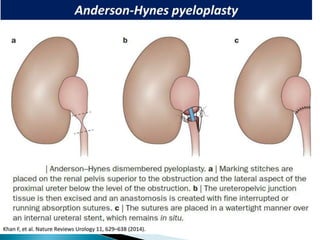
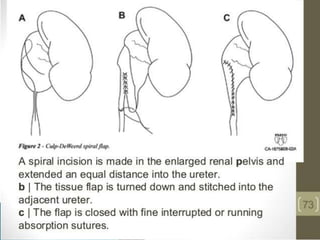
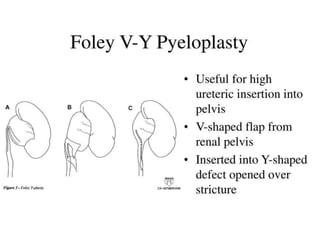
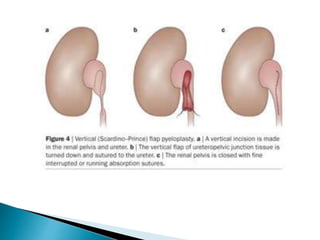
PUJO is an obstruction of the proximal ureter at the junction with the renal pelvis. It is most common in childhood, affecting 1 in 1000 children, with boys more commonly affected than girls. Presentation includes flank pain, flank mass, nausea, vomiting, recurrent UTIs, and hematuria. Diagnosis involves blood tests, urine tests, ultrasounds, CT scans, nuclear scans, and retrograde pyelography. Treatment depends on symptoms and impairment - watchful waiting may be sufficient, but surgery like pyeloplasty is often needed and has a high success rate of 90-95%.