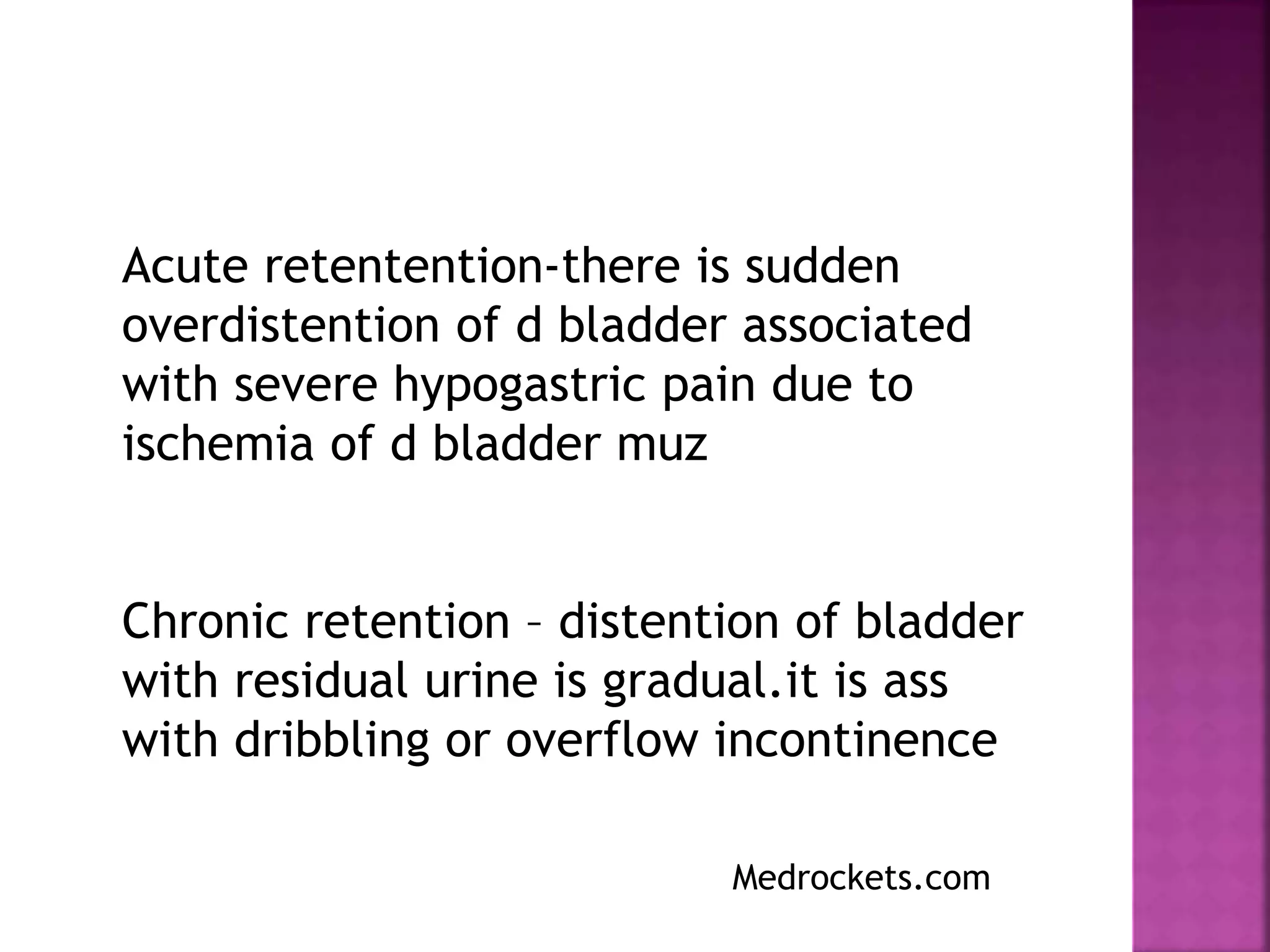
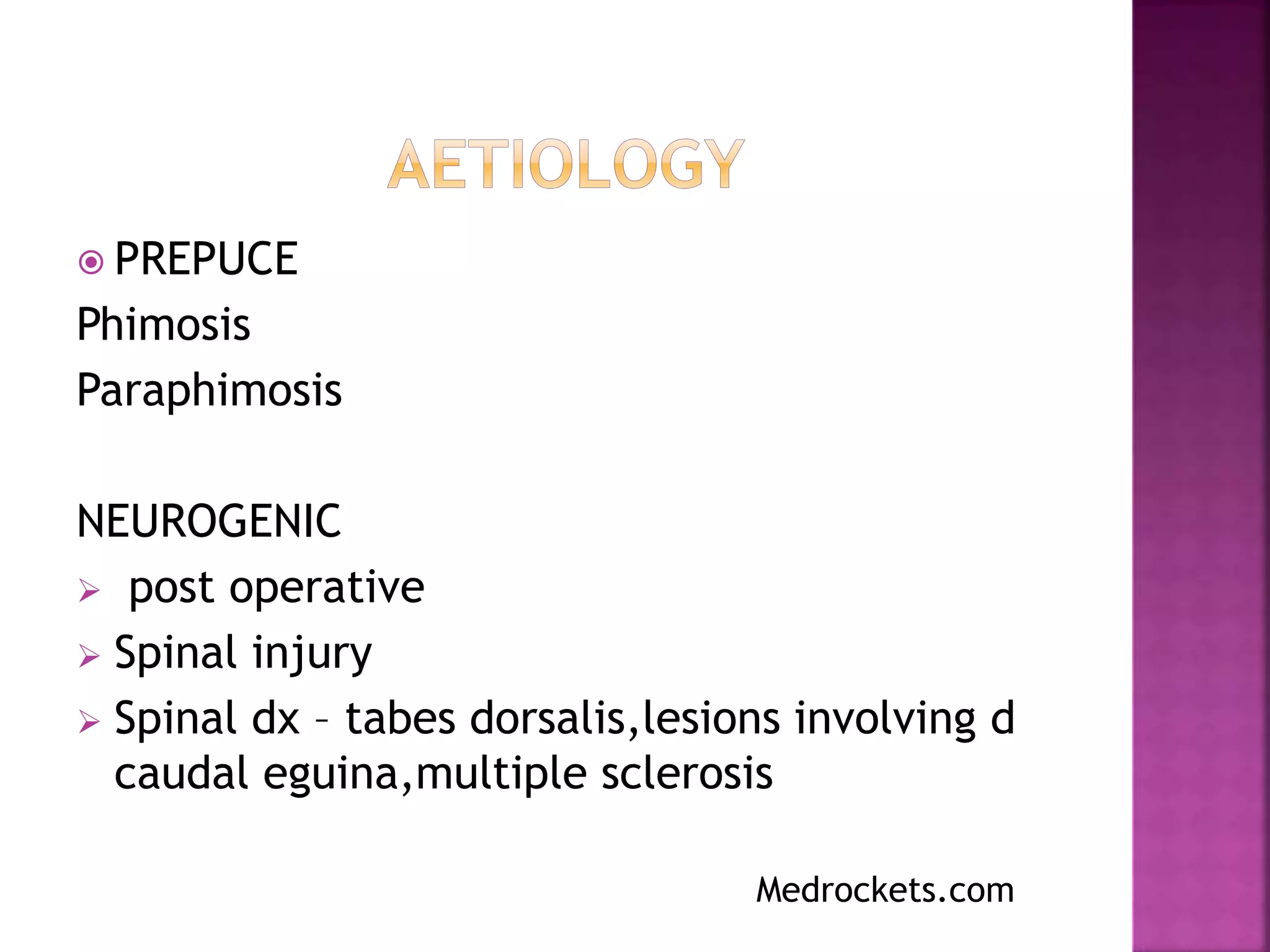
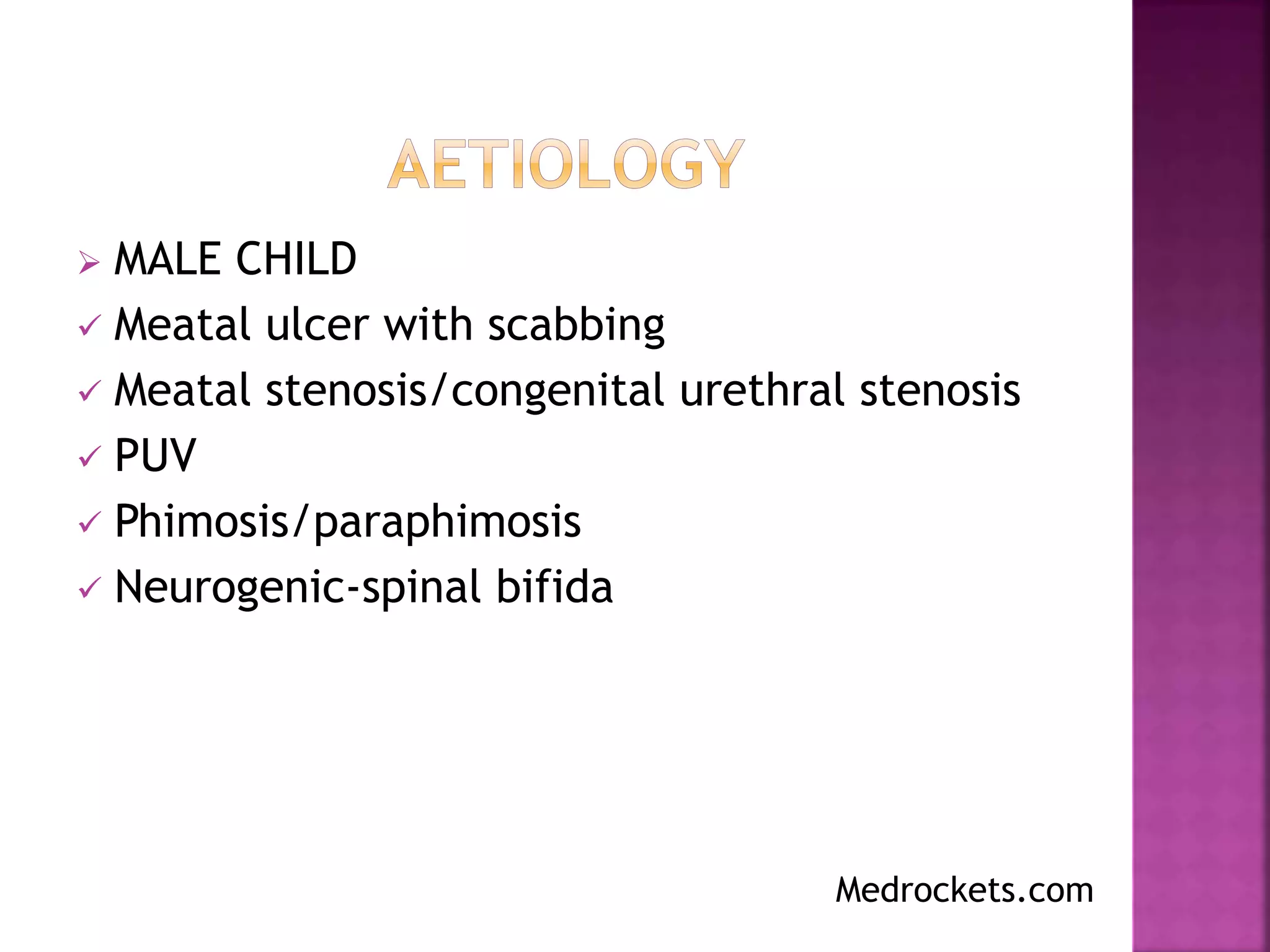
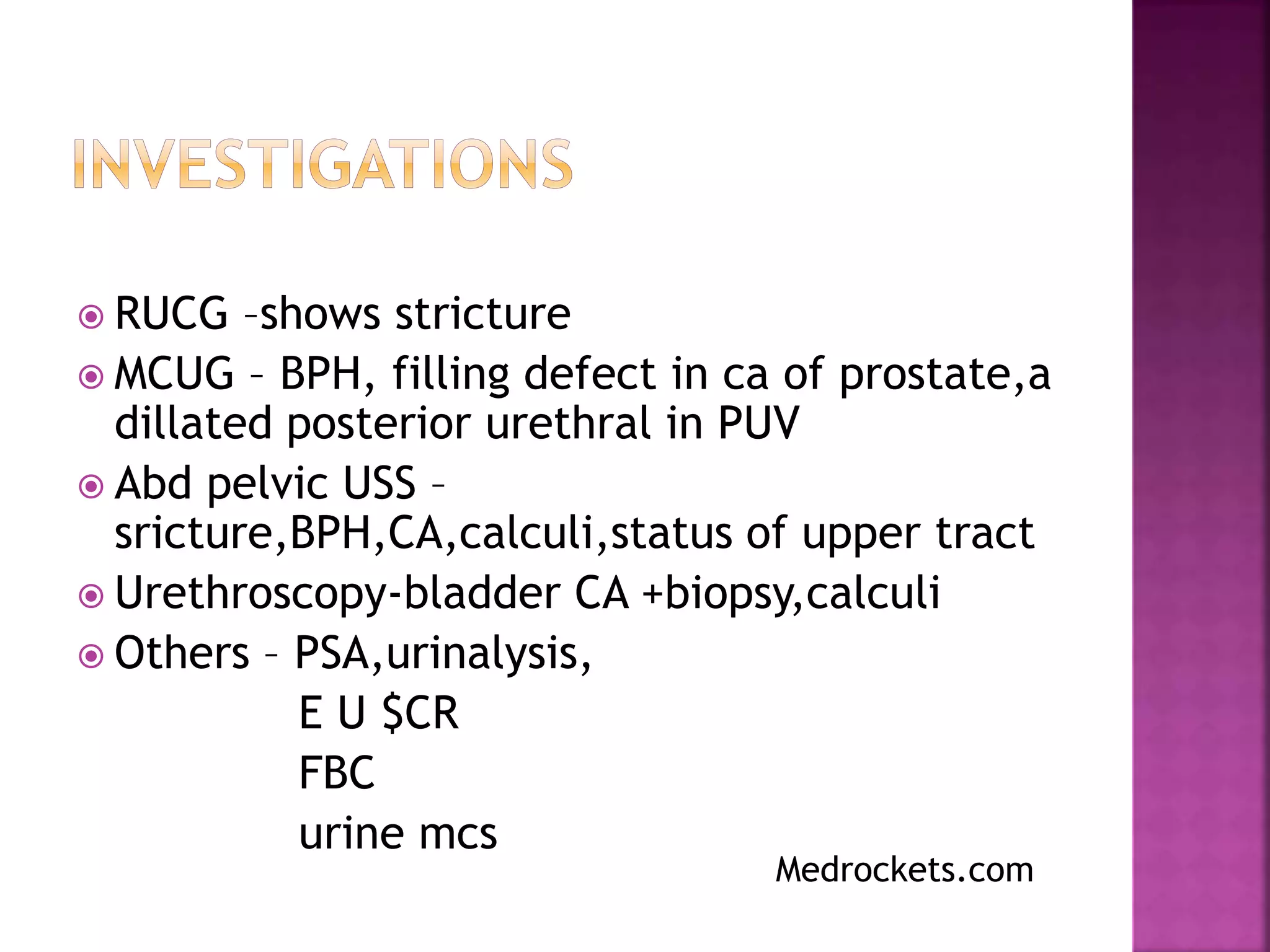
This document discusses urinary retention, including its types, causes, clinical features, investigations, management, and prognosis. Urinary retention is defined as the inability to void despite bladder distention. It can be acute, chronic, or acute-on-chronic. Common causes in males include benign prostatic hyperplasia and urethral stricture. Clinical features depend on whether retention is acute or chronic. Initial management involves relieving the obstruction through catheterization. Long-term management depends on identifying and treating the underlying cause. Complications can include bladder and kidney damage if not properly treated.