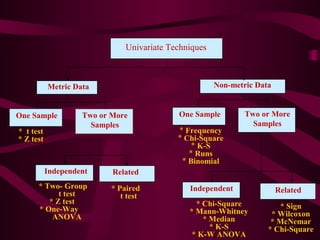
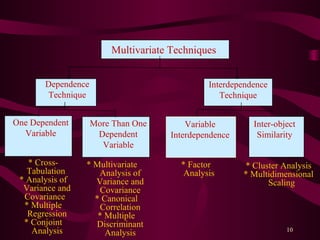
This document discusses factors that influence the selection of data analysis strategies and provides a classification of statistical techniques. It notes that the previous research steps, known data characteristics, statistical technique properties, and researcher background all impact strategy selection. Statistical techniques can be univariate, analyzing single variables, or multivariate, analyzing relationships between multiple variables simultaneously. Multivariate techniques are further classified as dependence techniques, with identifiable dependent and independent variables, or interdependence techniques examining whole variable sets. The document provides examples of common univariate and multivariate techniques.