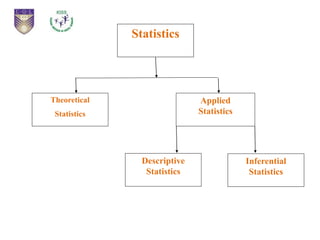
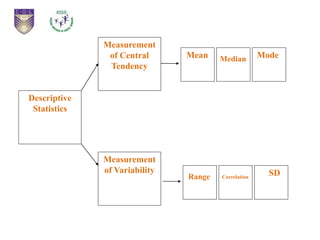
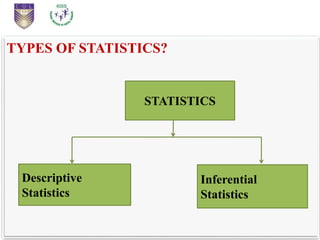
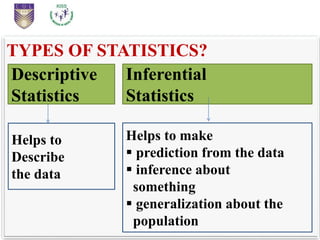
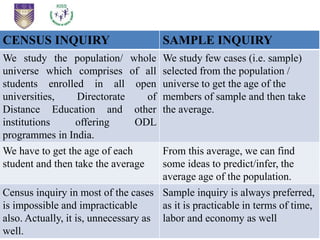
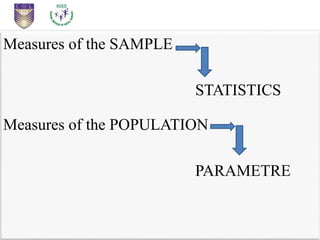
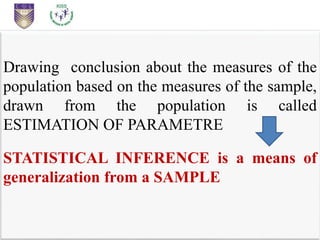
This document provides an introduction to statistical inference. It defines statistics as dealing with collecting, analyzing, and presenting data. The purpose of statistics is to make accurate conclusions or predictions about a population based on a sample. There are two main types of statistics: descriptive statistics, which describes data, and inferential statistics, which helps make predictions and generalizations from data. Statistical inference involves analyzing sample data and making conclusions about the population using statistical techniques, as it is impractical to study entire populations. The key concepts of population, sample, parameters, statistics, and sampling distribution are introduced.