1. The immune system protects the body from infection and disease through two branches - the innate and adaptive immune systems.
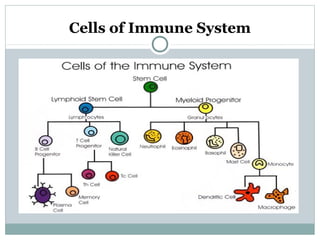
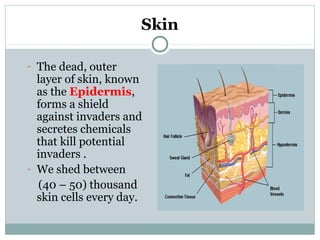
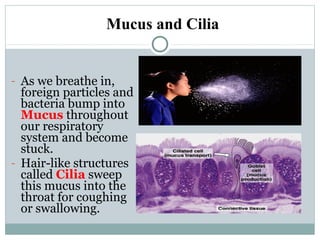
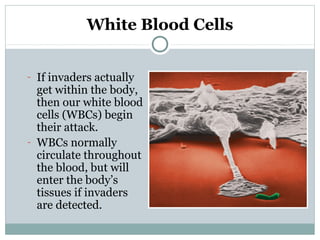
2. The innate immune system provides immediate defenses like white blood cells and barriers of the skin. The adaptive immune system mounts specialized defenses like antibodies and memory cells.
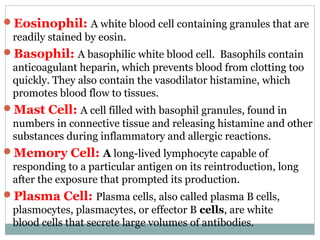
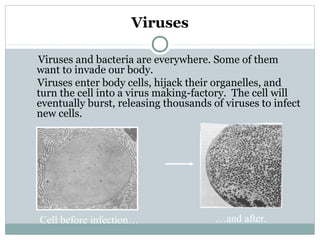
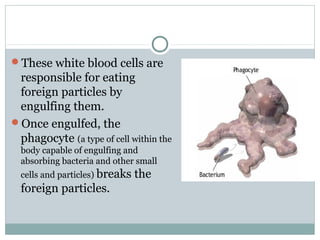
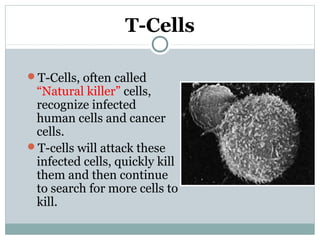
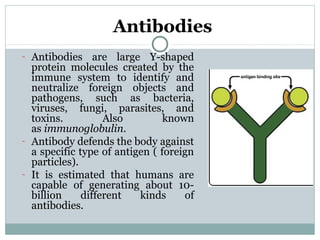
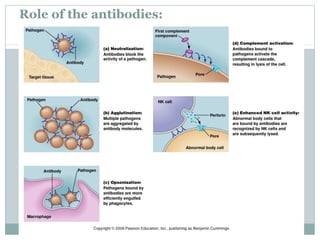
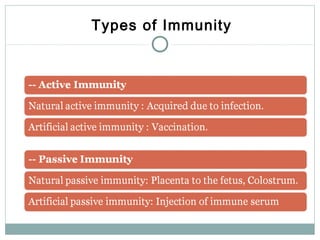
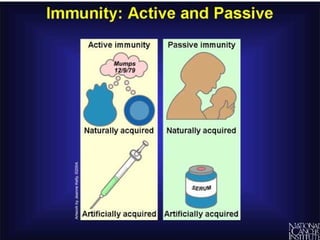
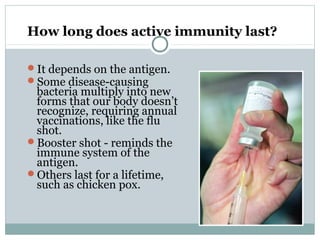
3. When pathogens breach these defenses, the body responds through inflammation, antibodies, and specialized immune cells like phagocytes, natural killer cells, and T cells that destroy infected cells. Immunity can be active from exposure or passive from antibodies transferred from mother to child.