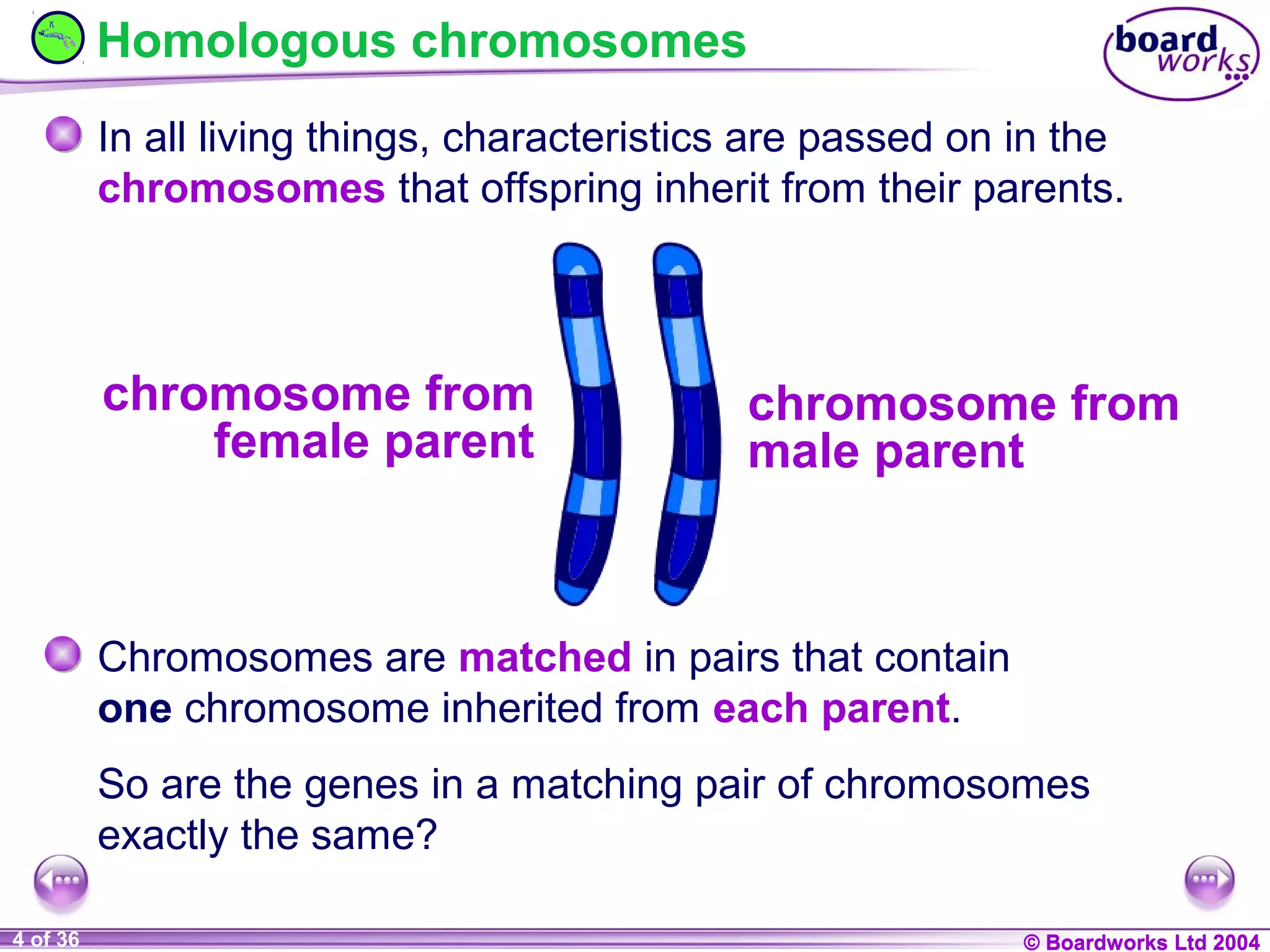
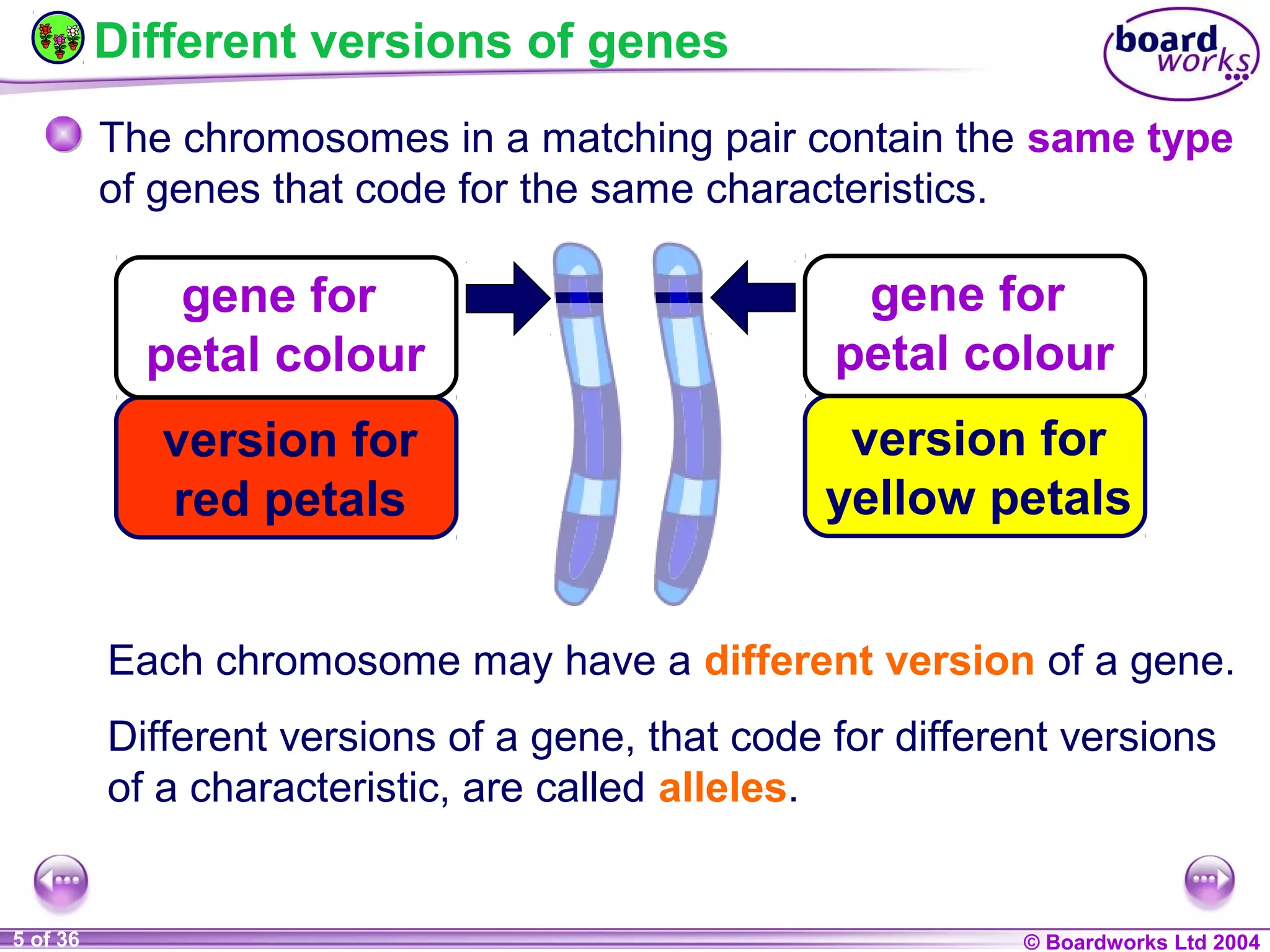
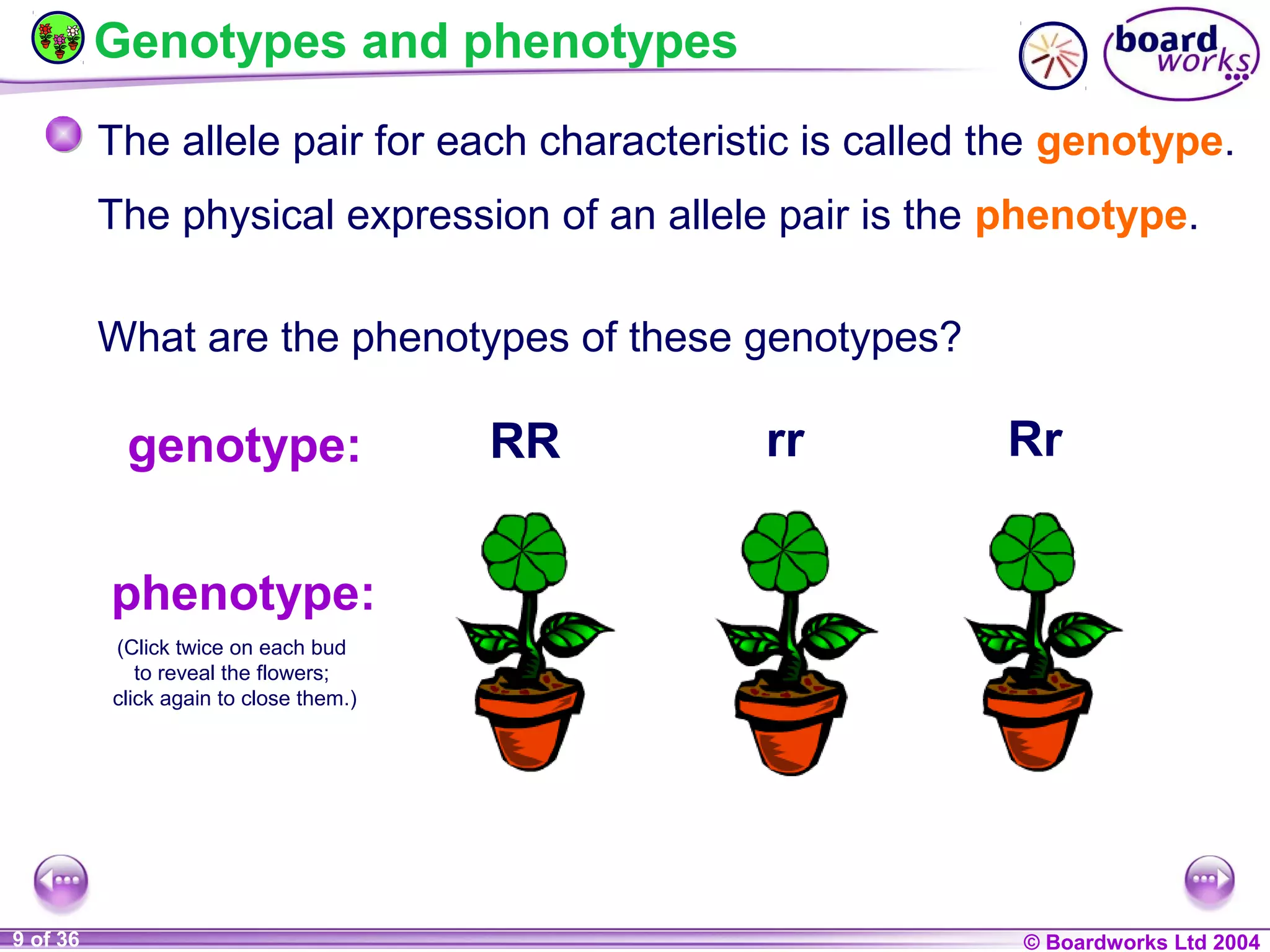
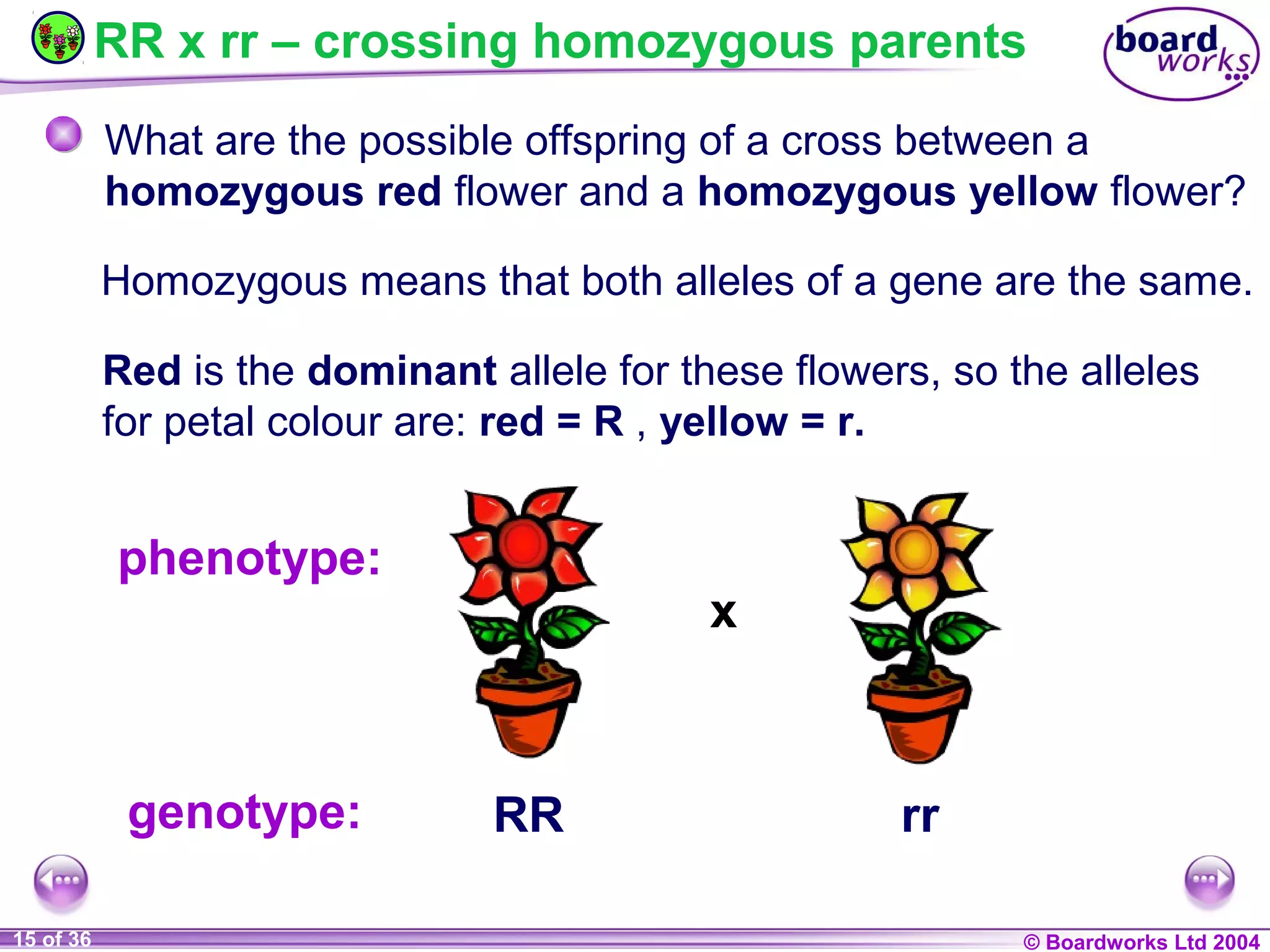
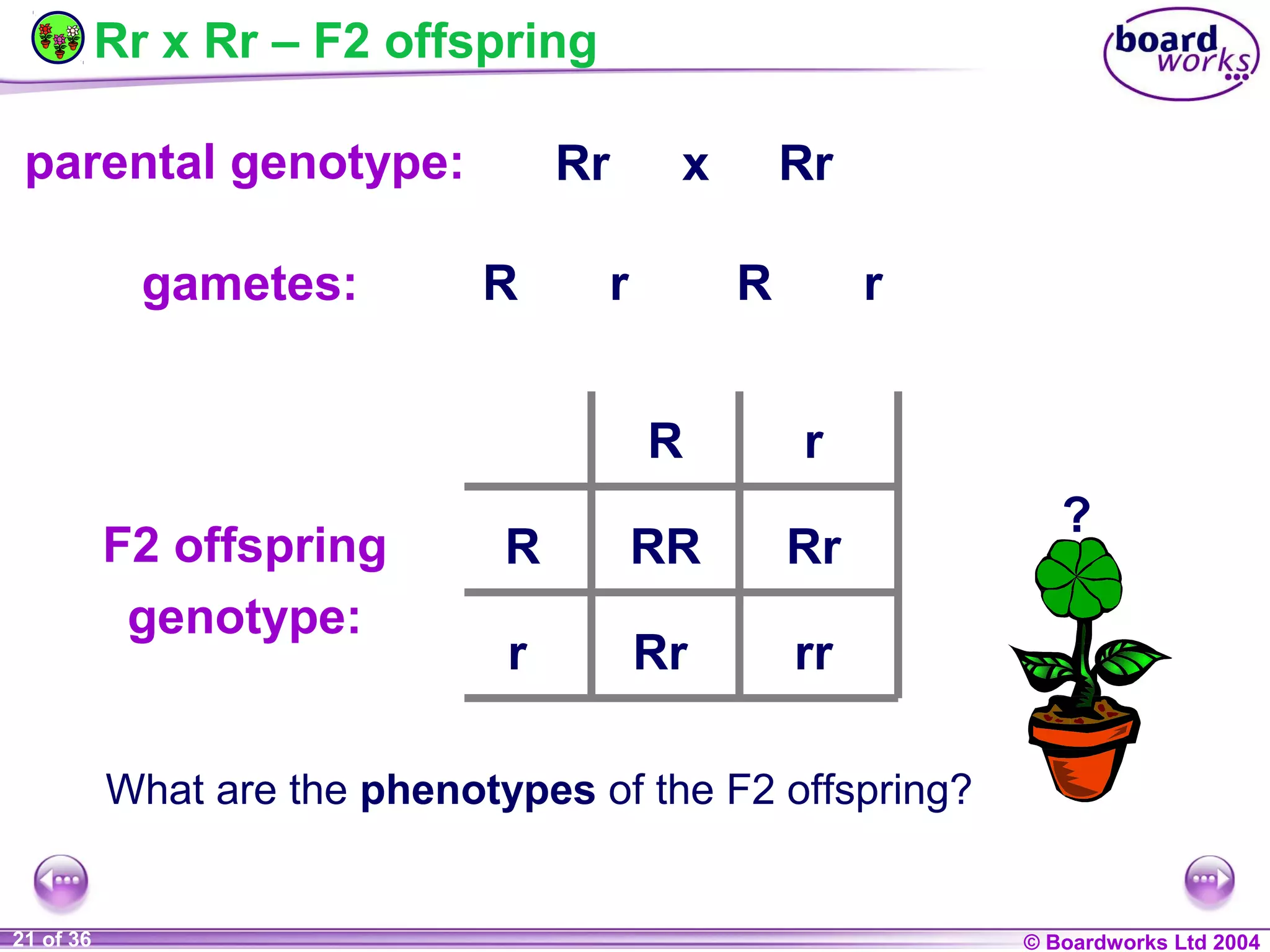
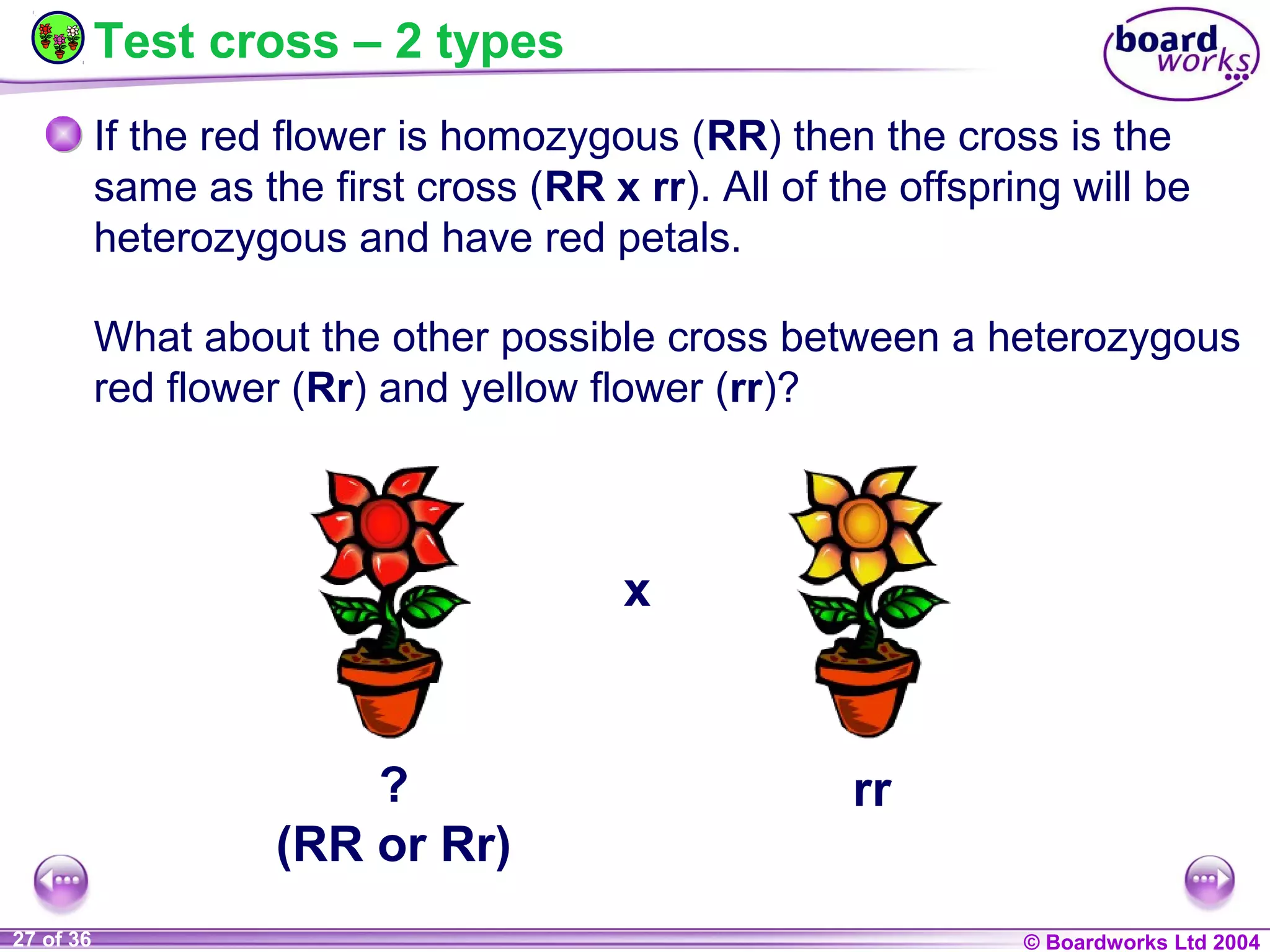
This document discusses genetic inheritance and provides examples using flower petal color. It defines key genetic terms like genes, alleles, homozygous, heterozygous, dominant, and recessive. It also explains genetic crosses like homozygous crosses which result in heterozygous offspring, heterozygous crosses which result in a 3:1 ratio, and test crosses which can determine if a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous. The document notes that in co-dominance, neither allele is recessive to the other and both are expressed in offspring.