This document provides an overview of testicular cancer, including:
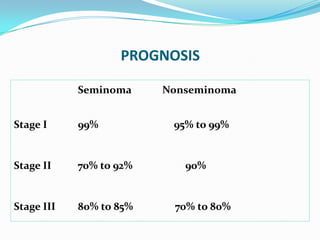
1. Testicular cancer most commonly affects men aged 20-40 and is the most common cancer in that age group. It has very good survival rates due to effective diagnostic techniques, tumor markers, and multimodal treatments.
2. Risk factors include cryptorchidism, Klinefelter syndrome, trauma, and genetic factors. Cryptorchidism increases risk by 14-48 times.
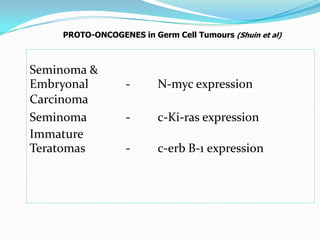
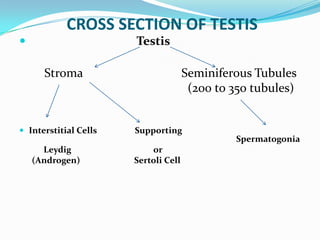
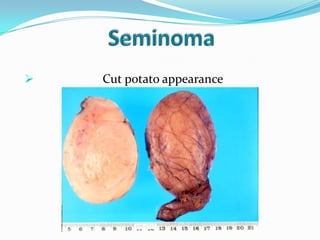
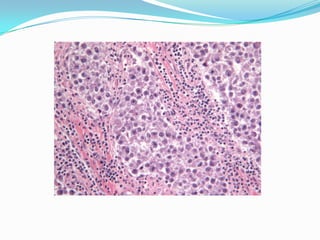
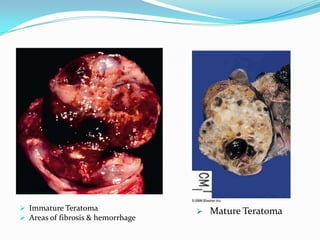
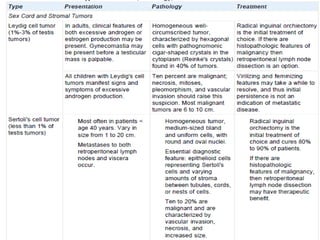
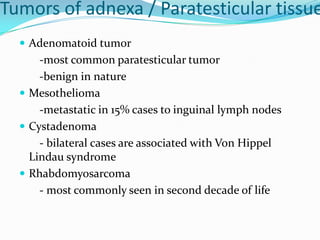
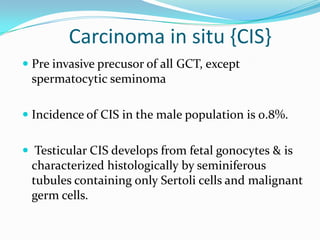
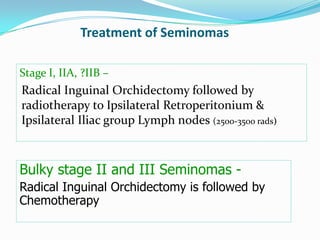
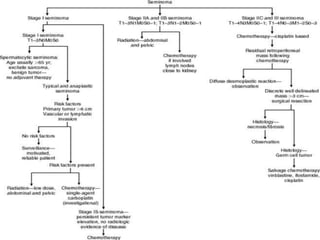
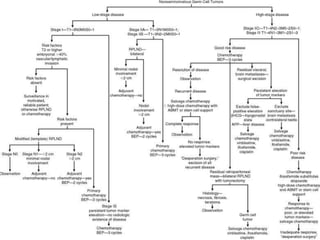
3. Types include seminomas, embryonal carcinomas, teratomas, and others. Seminomas and non-seminomas are treated differently.
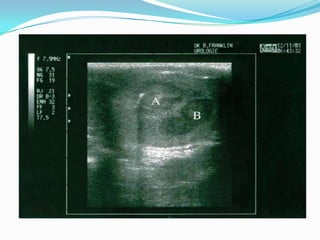
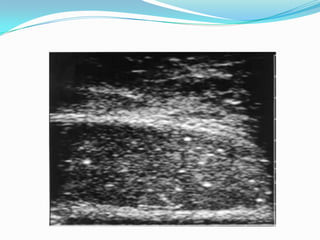
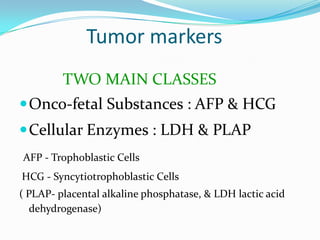
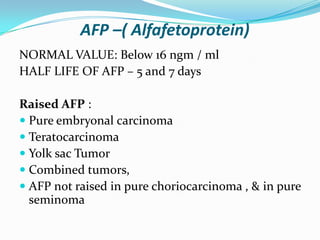
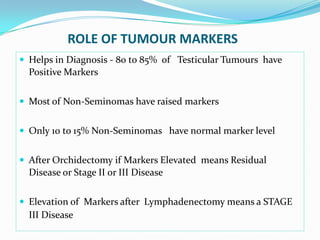
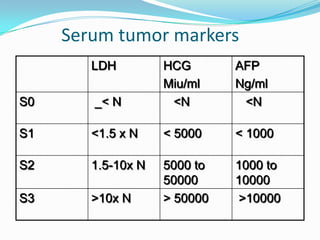
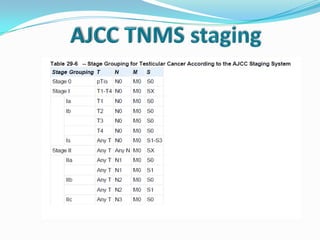
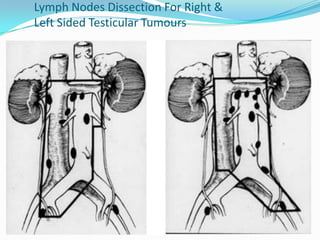
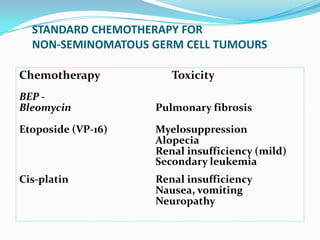
4. Diagnosis involves physical exam, ultrasound, tumor markers like AFP and H