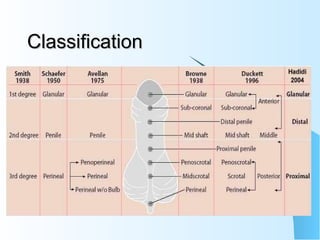
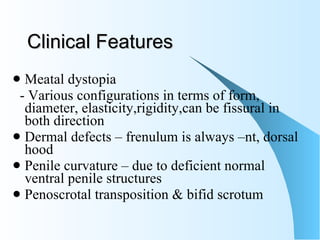
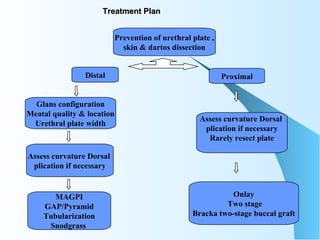
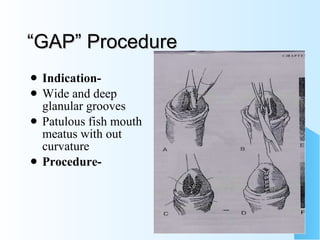
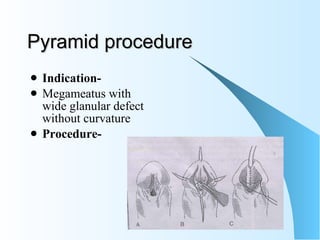
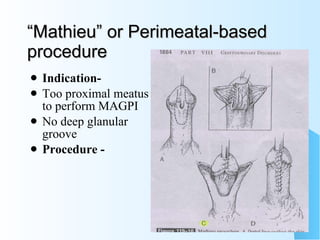
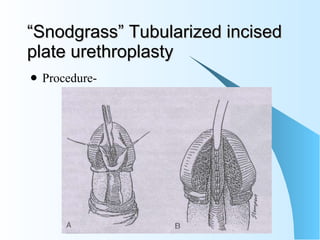
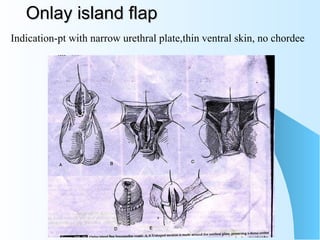
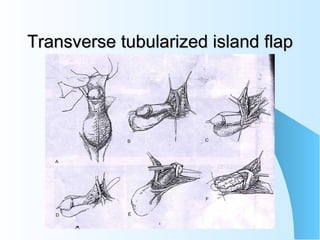
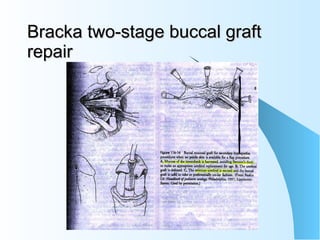
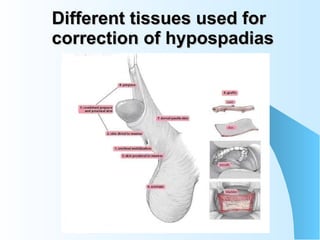
This document discusses hypospadias, a congenital anomaly where the urethra opens on the underside of the penis instead of at the tip. It covers the embryology, risk factors, classifications, clinical features, and various surgical treatment options for hypospadias repair. The goals of treatment are to position the urethral meatus at the tip of the penis, correct any penile curvature, and provide adequate skin coverage. Complications can include meatal stenosis, fistula formation, infection, and procedure failure. Careful patient selection and appropriate surgical technique are emphasized to achieve the best outcomes.