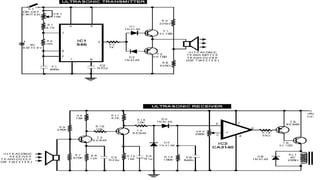
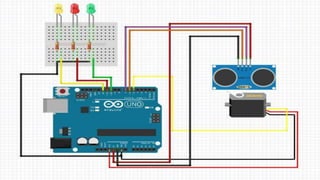
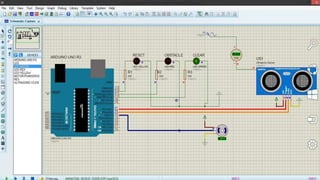
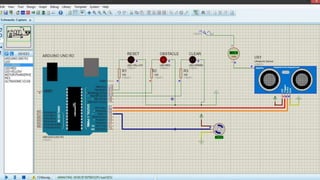
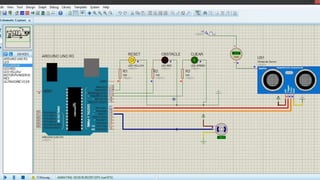
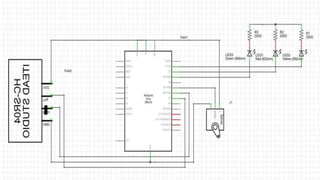
Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves to measure distance. They have a transmitter that sends out ultrasonic pulses and a receiver that listens for the echo when the pulse bounces off an object. By measuring the time it takes for the echo to return, the sensor can calculate the distance to the object. Some applications of ultrasonic sensors include monitoring water levels in tanks, proximity detection in cars to trigger warnings or braking, and more. The document discusses the working principle, circuit diagram, and applications of ultrasonic sensors.