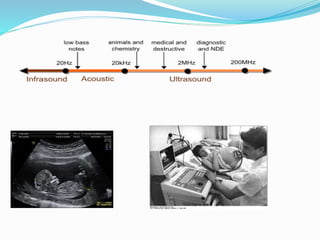
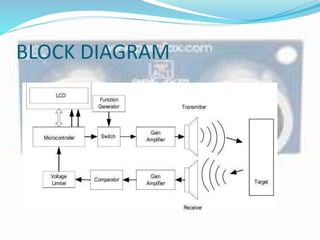
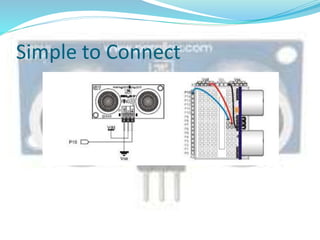
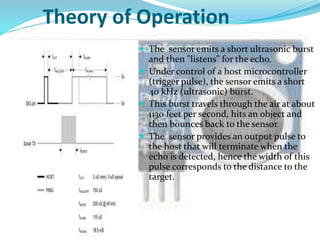
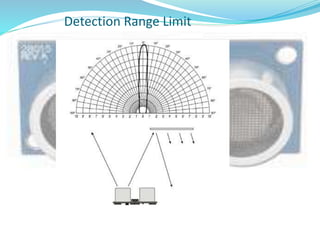
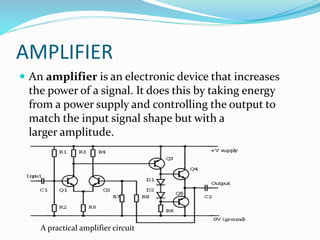
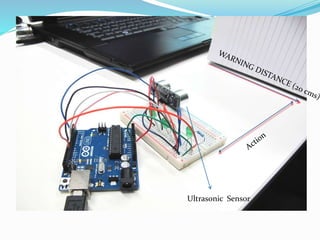
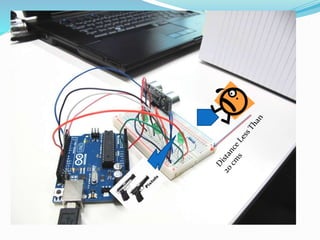
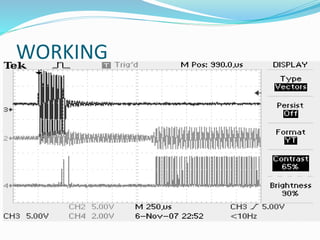
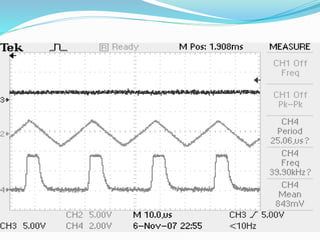
This document discusses the working of an ultrasonic sensor security system. It contains sections on the history of ultrasound, how ultrasonic sensors work, and the key components of an ultrasonic sensor system including the transmitting unit, receiver unit, and microcontroller. The transmitting unit sends out ultrasonic pulses and the receiver unit detects echoes which are used by the microcontroller to calculate the distance to objects. Potential applications are discussed like intruder alarms, automatic doors, and parking assistance.