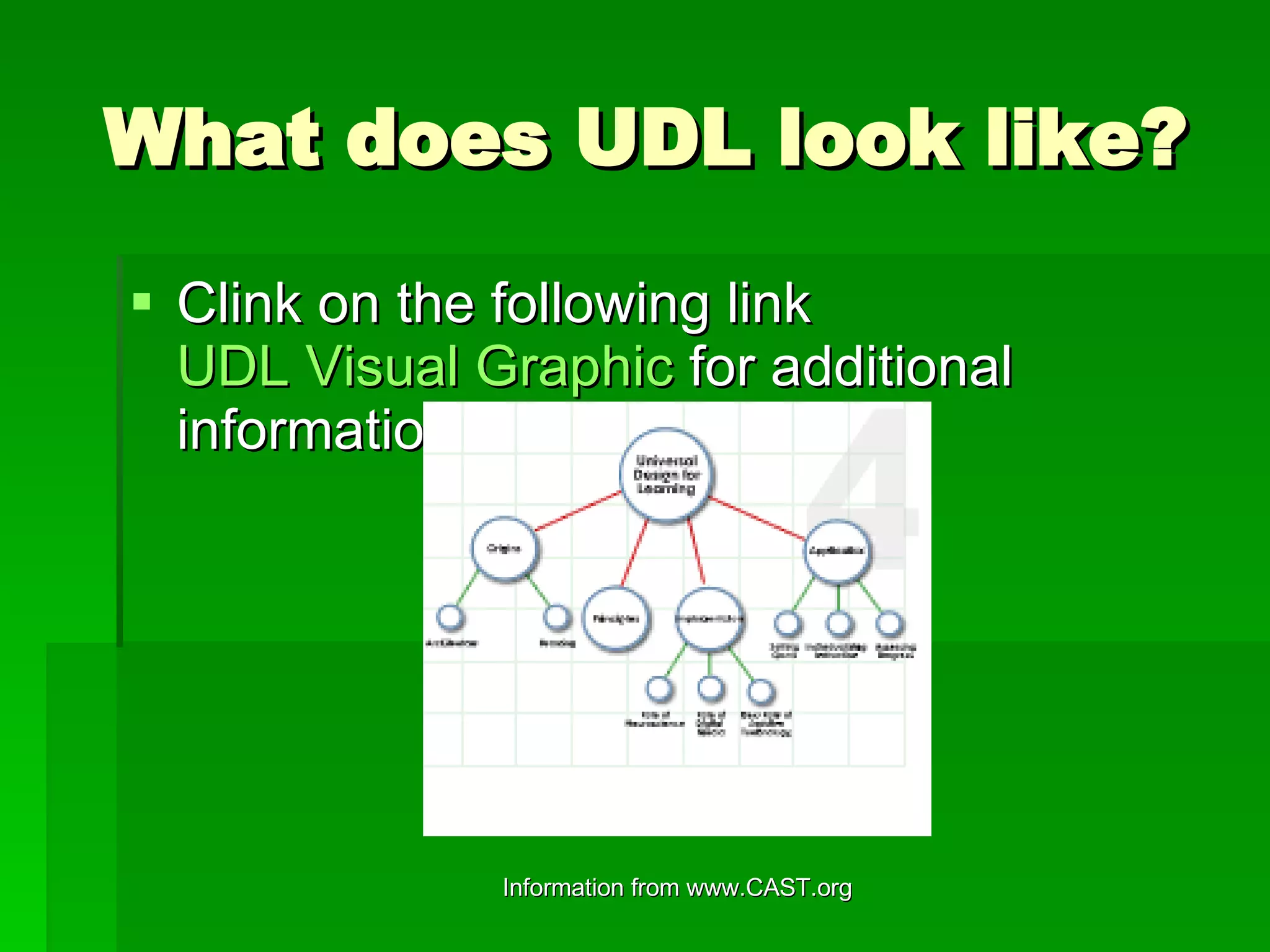
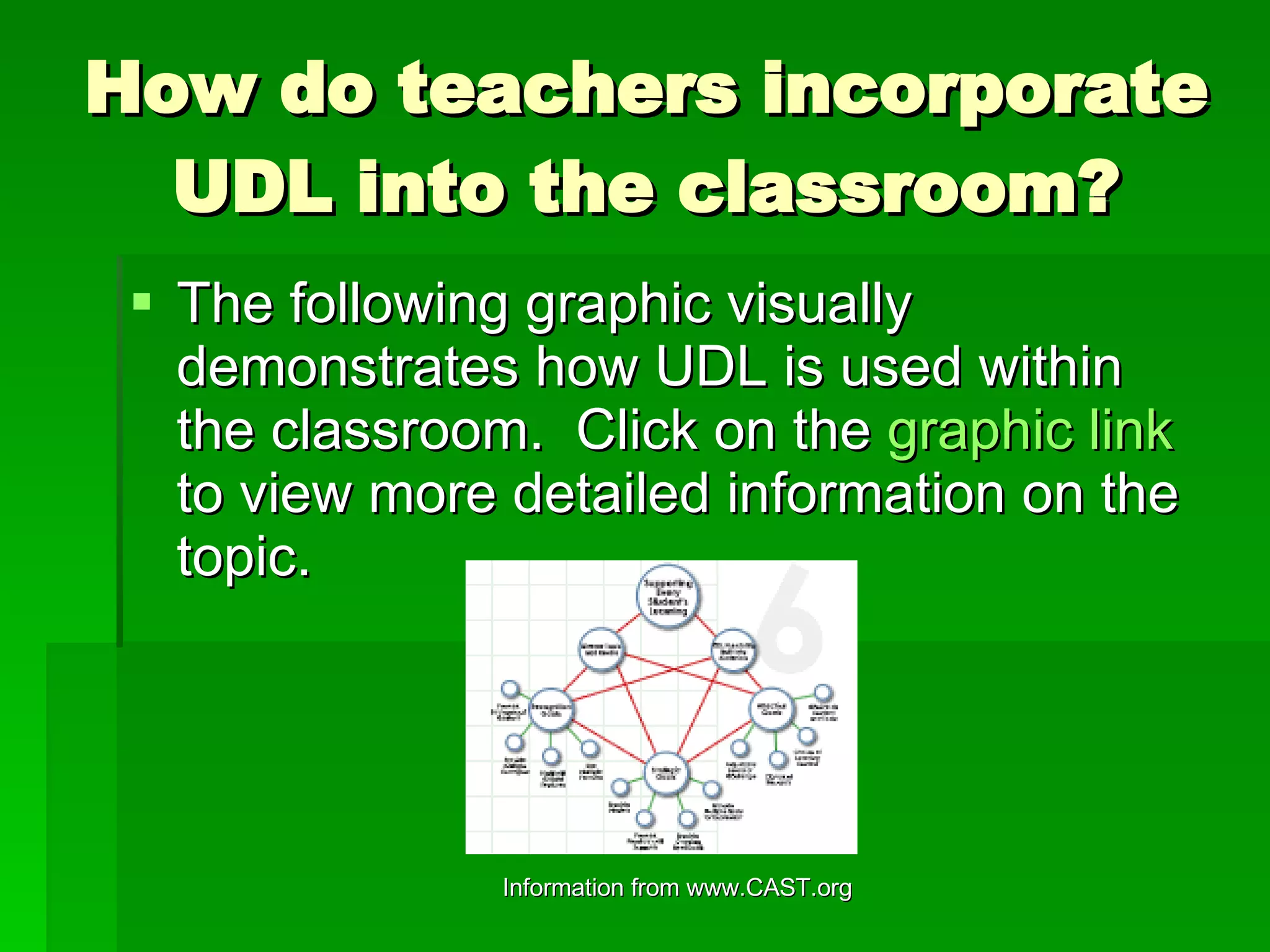
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a framework for designing curricula that provides multiple means of engagement, representation, and action and expression to reduce learning barriers and support all students. UDL originated from Universal Design, which aims to make architecture accessible to all. UDL builds on this by incorporating flexibility into educational methods, materials, and assessments to accommodate learner variability. By understanding brain research on the recognition, strategic, and affective networks, UDL aims to provide diverse pathways that support access and engagement for all students.