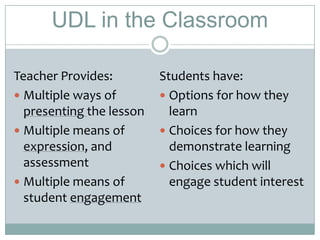
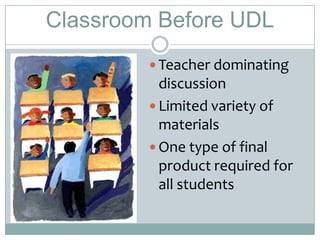
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a framework that provides flexibility in how information is presented, how students demonstrate their knowledge, and how students are engaged. UDL removes barriers to learning by anticipating the needs of all students. It involves presenting lessons in multiple formats, allowing for varied expressions of knowledge, and engaging students through different activities and technologies. UDL benefits all students by accommodating different learning needs and styles.