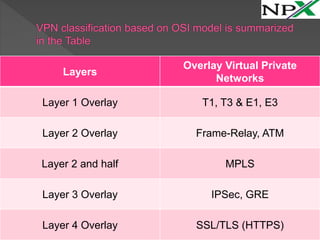
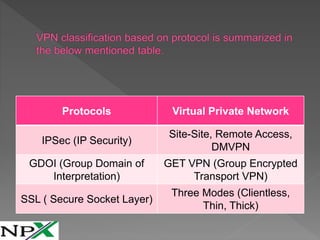
Layer 1 Overlay VPNs use dedicated connections like T1/E1 leased lines to connect branches in a secure manner. Layer 2 Overlay VPNs connect branches over multi-access networks like frame relay. Layer 2.5 Overlay VPNs use MPLS, which inserts an MPLS header between layer 2 and 3 headers. Layer 3 Overlay VPNs use IPSec to encrypt data and GRE for routing/multicast over public networks. Layer 4 Overlay VPNs use SSL/TLS to encrypt data at the transport layer for applications like web browsing.