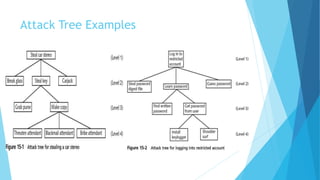
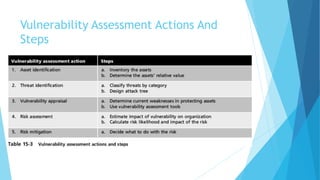
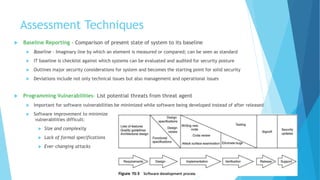
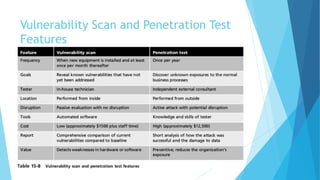
Vulnerability assessment is the systematic evaluation of an organization's exposure to threats. It involves identifying assets, evaluating threats against those assets, determining vulnerabilities, assessing risks, and selecting appropriate controls. Various techniques can be used including asset identification, threat modeling, vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and risk assessment. The goal is to establish a security baseline and mitigate risks through hardening systems and ongoing monitoring.