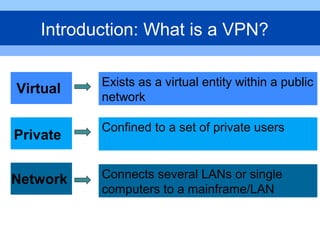
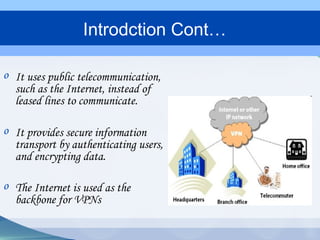
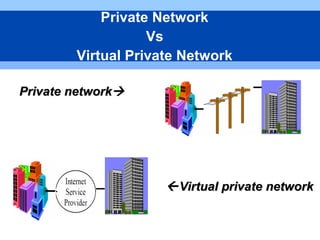
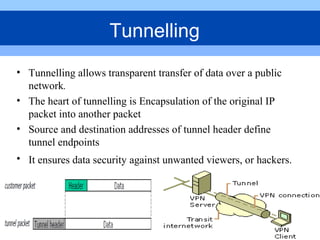
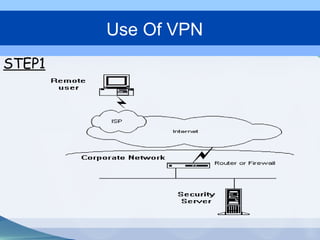
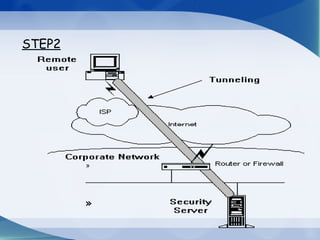
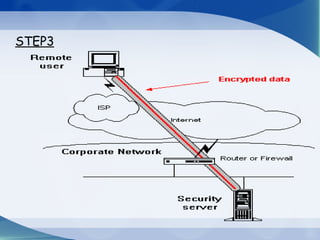
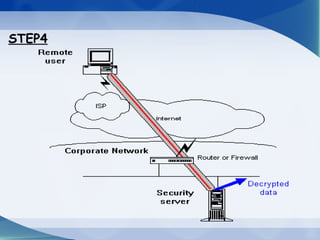
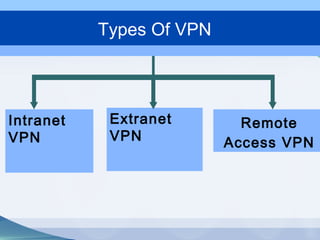
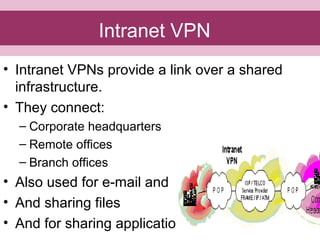
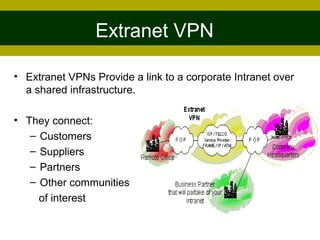
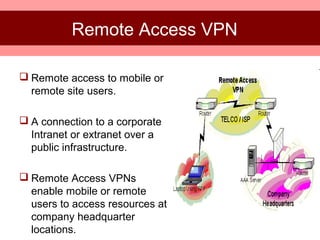
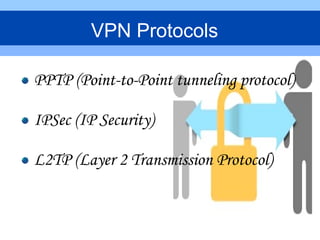
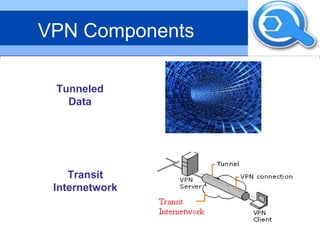
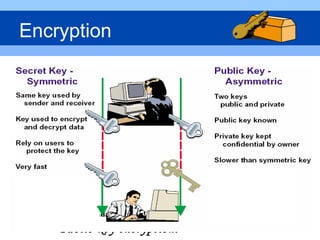
This document provides an overview of virtual private networks (VPNs). It defines a VPN as using public networks like the Internet to connect private networks securely through authentication and encryption. The document discusses the need for VPNs to reduce costs, improve communication, and ensure security. It covers VPN types, components, protocols, and security measures like firewalls and encryption. Advantages include cost savings and mobility, while disadvantages include security understanding and performance issues outside an organization's control. The future of VPNs is described as widespread use through standardization.