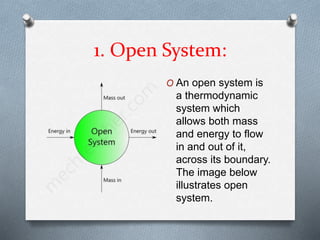
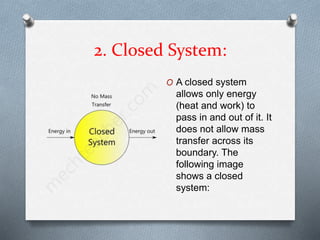
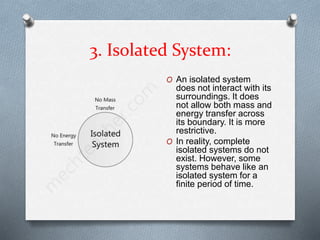
This document defines different types of thermodynamic systems - open, closed, and isolated. An open system allows both mass and energy to flow in and out across its boundary, like a container of heated water. A closed system only allows energy like heat to pass through its boundary, like water heated in a closed vessel. An isolated system does not interact with its surroundings and does not allow mass or energy transfer across its boundary, like a perfectly insulated rigid closed vessel.