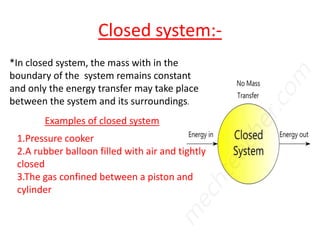
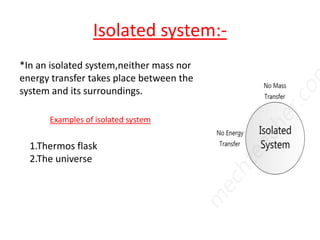
This presentation defines a thermodynamic system as a quantity of matter that is the focus of analysis to study changes in properties from the exchange of heat and work with surroundings. Thermodynamic systems can be open, closed, or isolated. An open system allows for mass and energy transfer with surroundings, like engines. A closed system keeps mass constant while allowing energy transfer, like a pressure cooker. An isolated system exchanges neither mass nor energy, like a thermos flask or the universe.