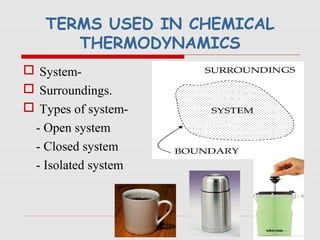
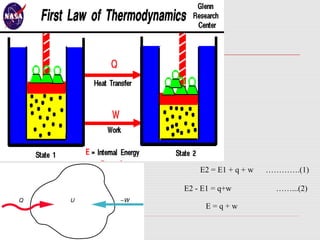
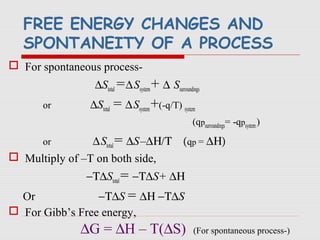
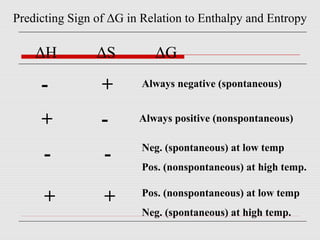
The document is a synopsis on thermodynamics by Dr. Rachana Choudhary covering fundamental concepts such as energy changes in chemical reactions, the laws of thermodynamics, and entropy. It discusses the differences between the first and second laws, as well as Gibbs free energy and its implications on spontaneity in processes. Conclusively, it outlines the significance of thermodynamic principles in understanding energy transformations throughout various processes.