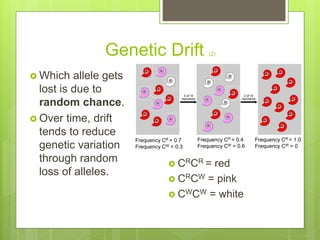
This document provides an overview of evolution and natural selection. It discusses how Darwin proposed natural selection as the mechanism for evolution, with genetic variation within populations and environmental pressures resulting in some individuals being better able to survive and reproduce. Over generations, this leads to adaptation and potentially speciation. The document also notes other factors like genetic drift, mutation, and migration that can influence gene frequencies randomly or non-randomly. It provides examples like genetic bottlenecks and founder effects to illustrate these concepts. An interactive quiz is included to help reinforce the key points.