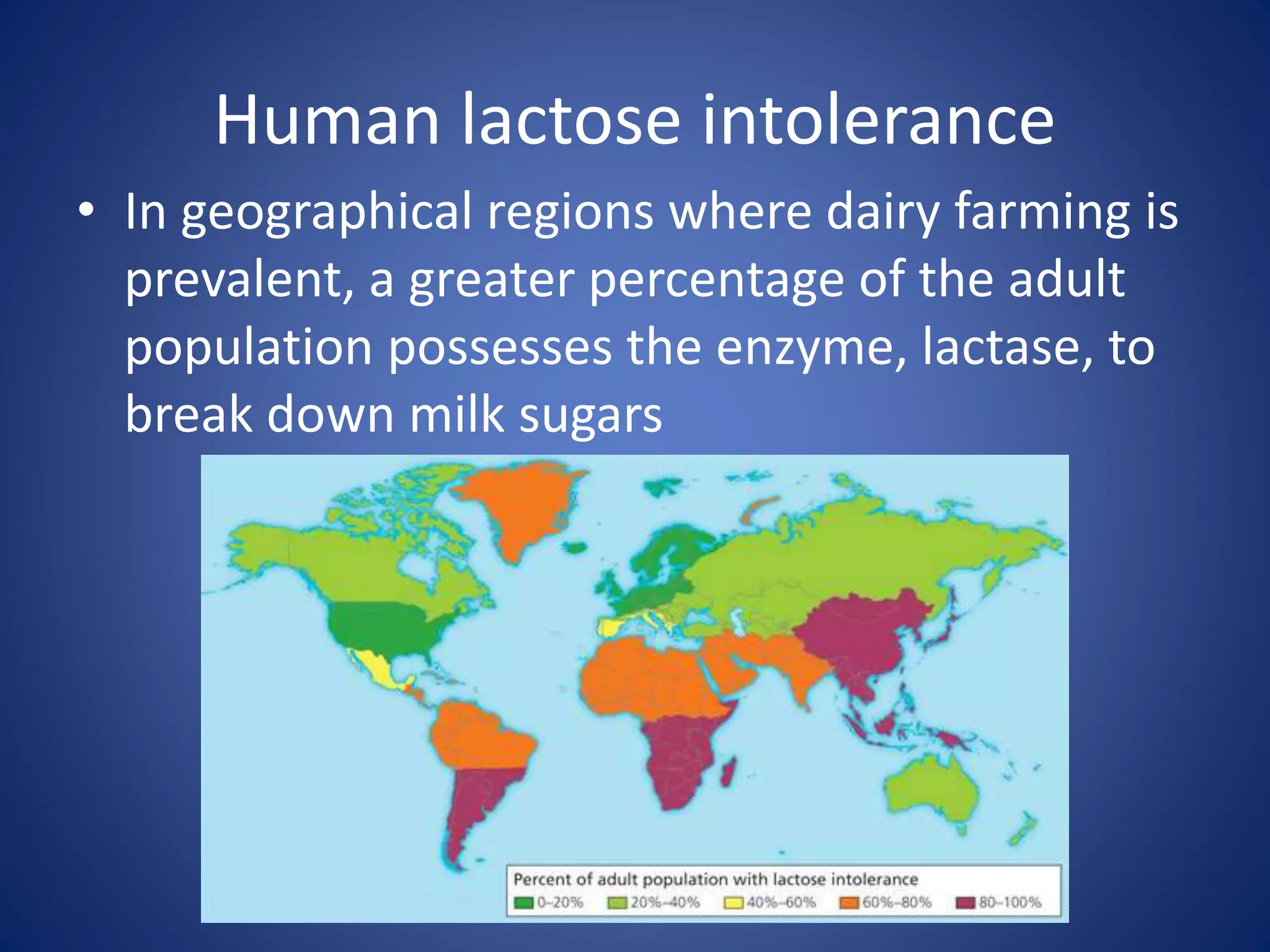
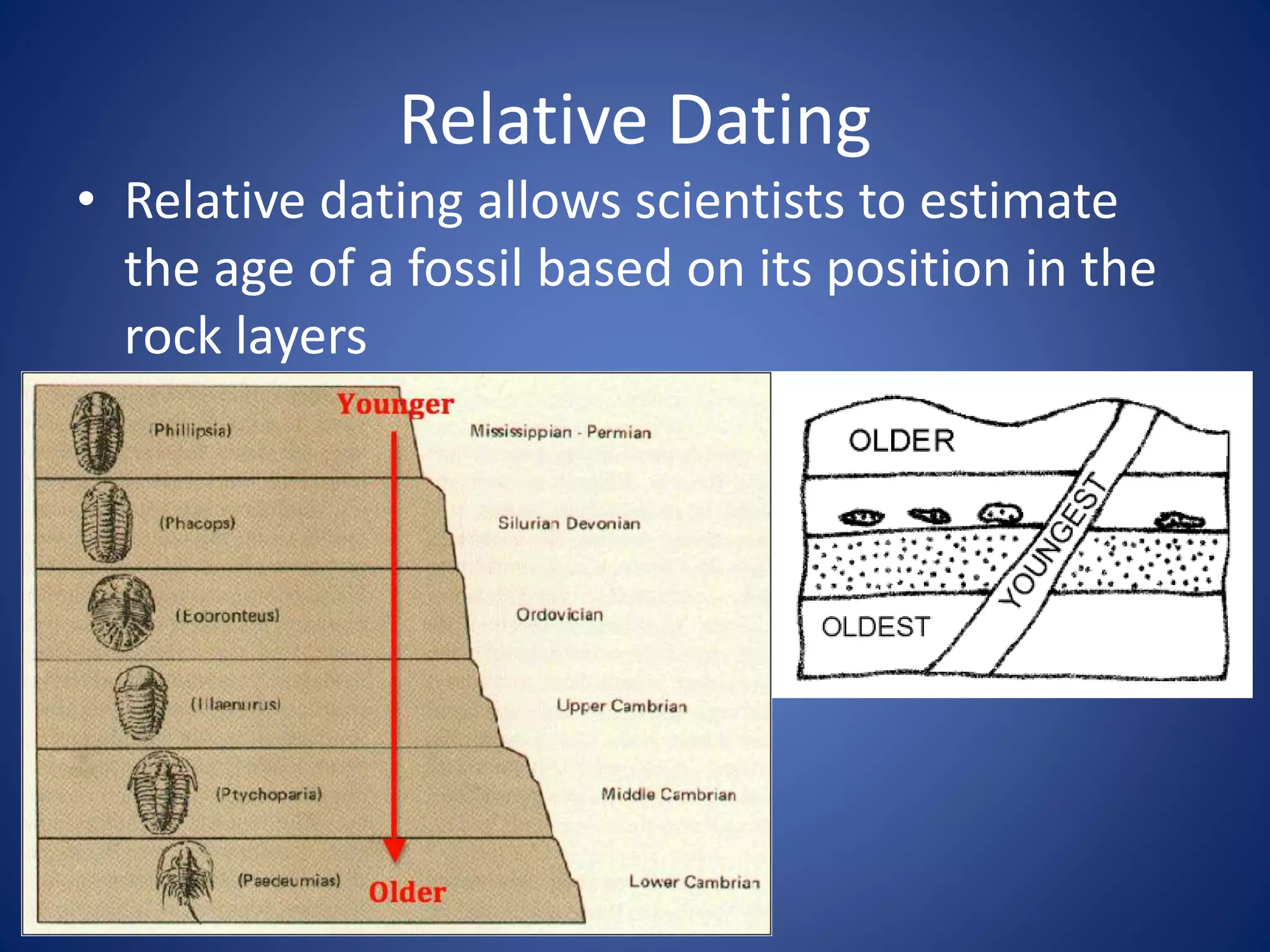
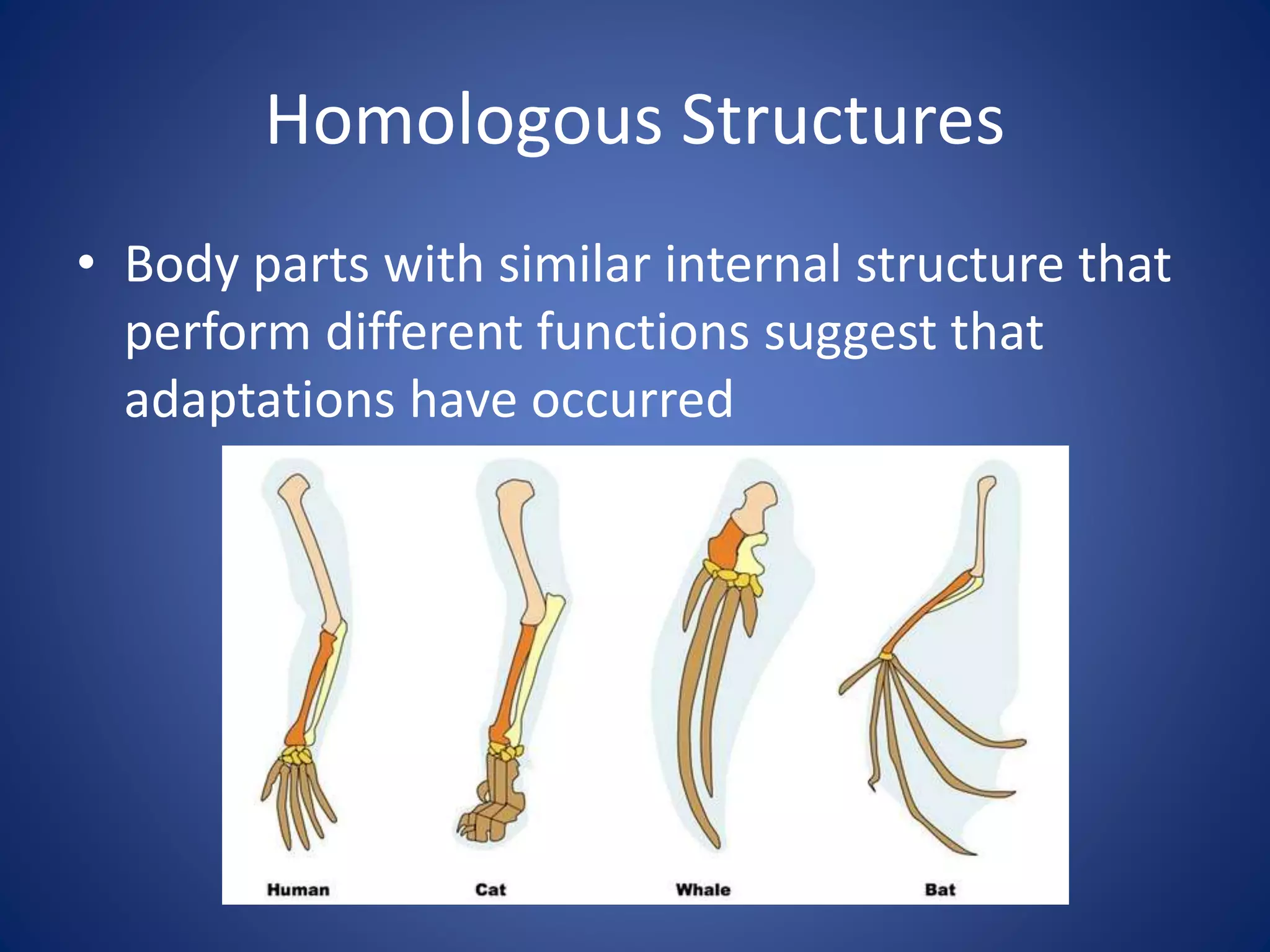
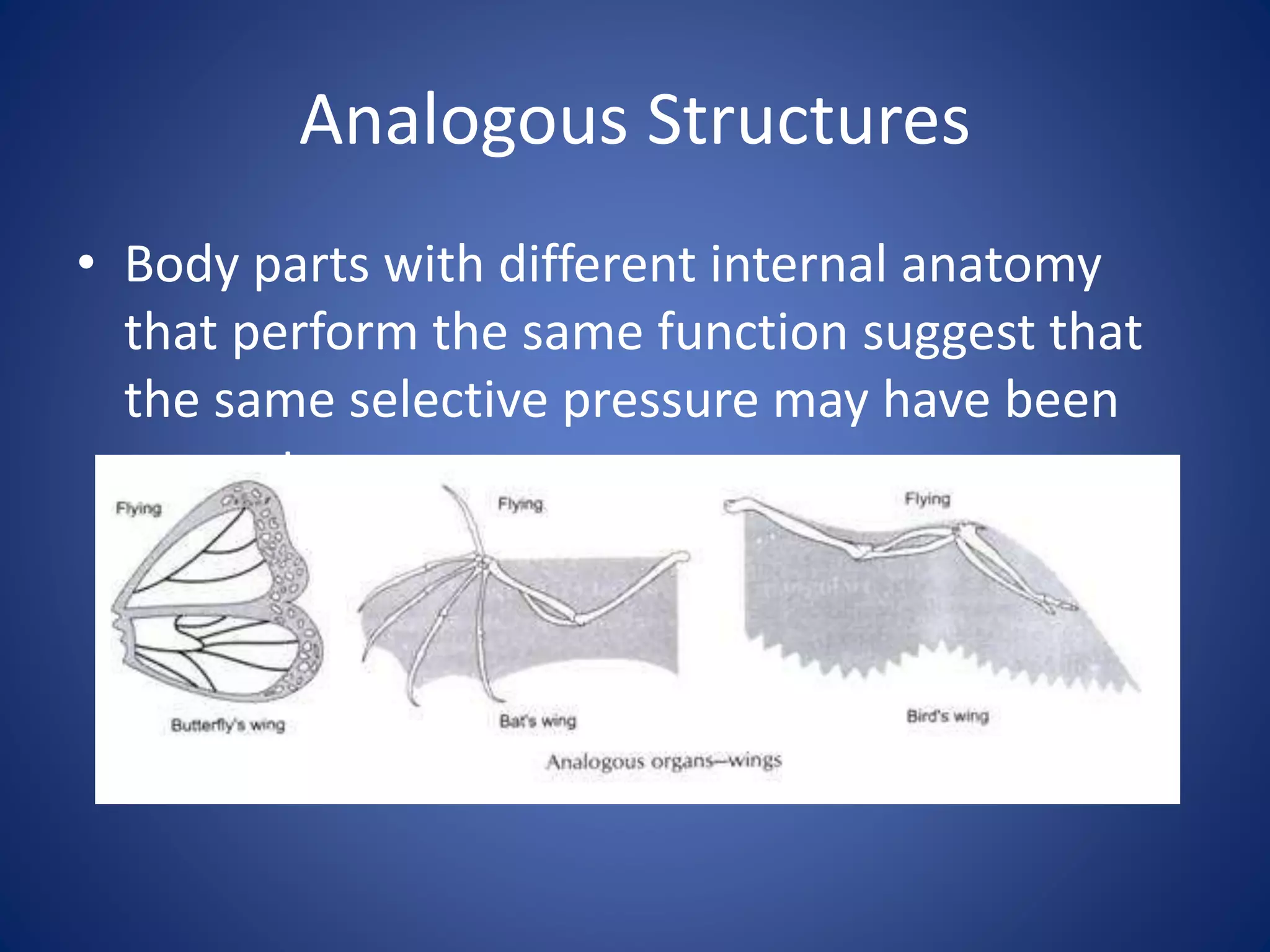
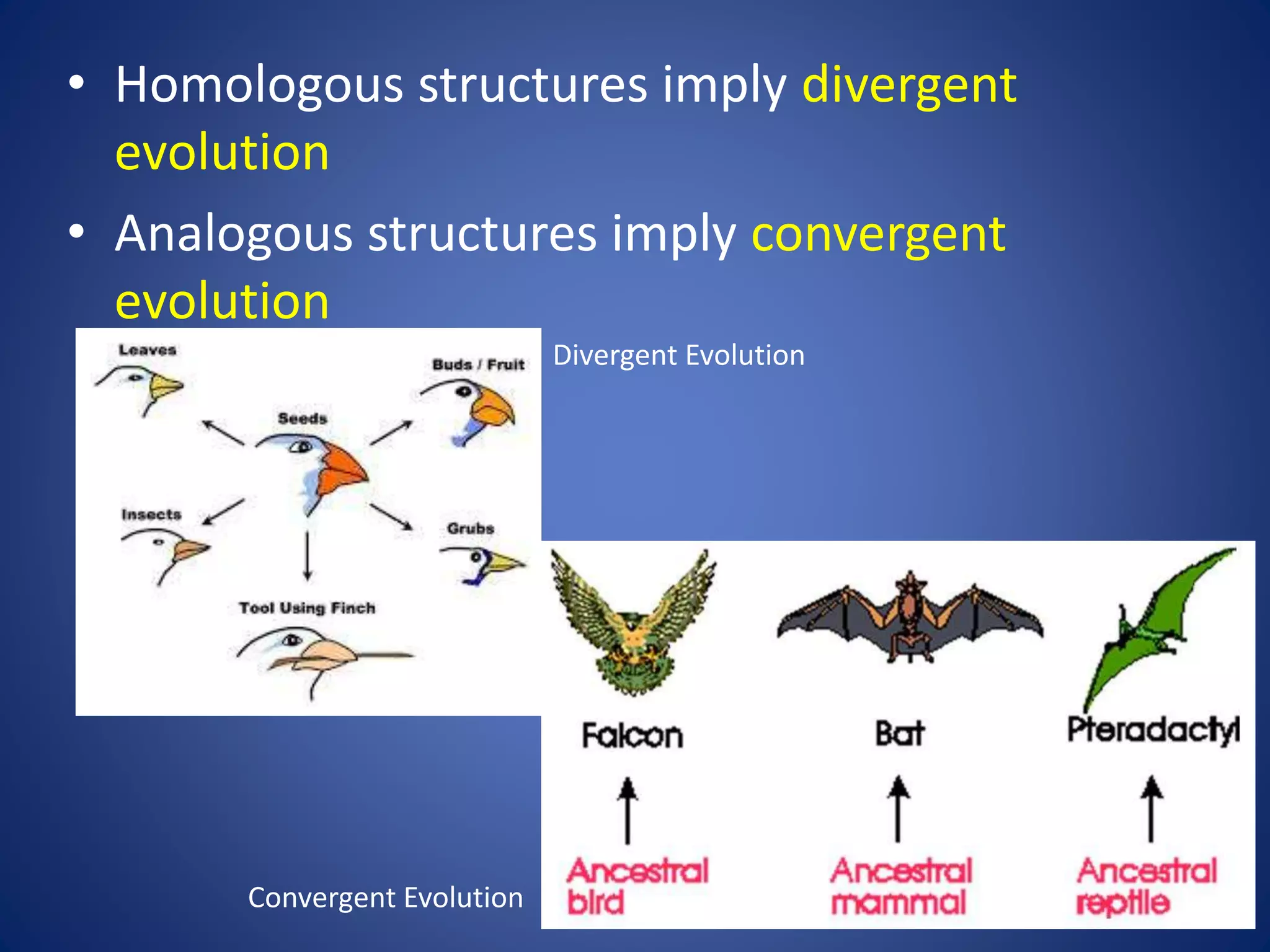
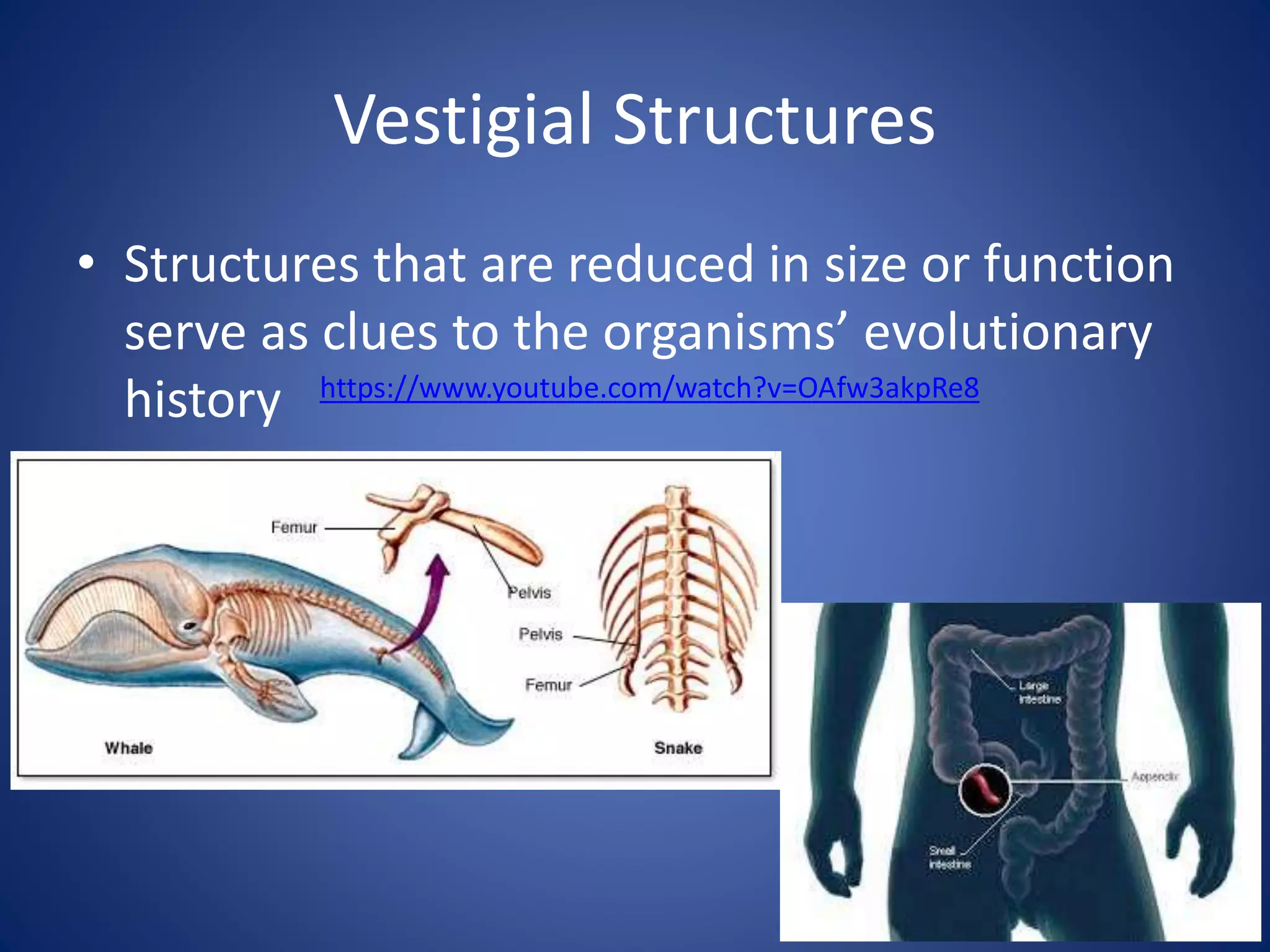
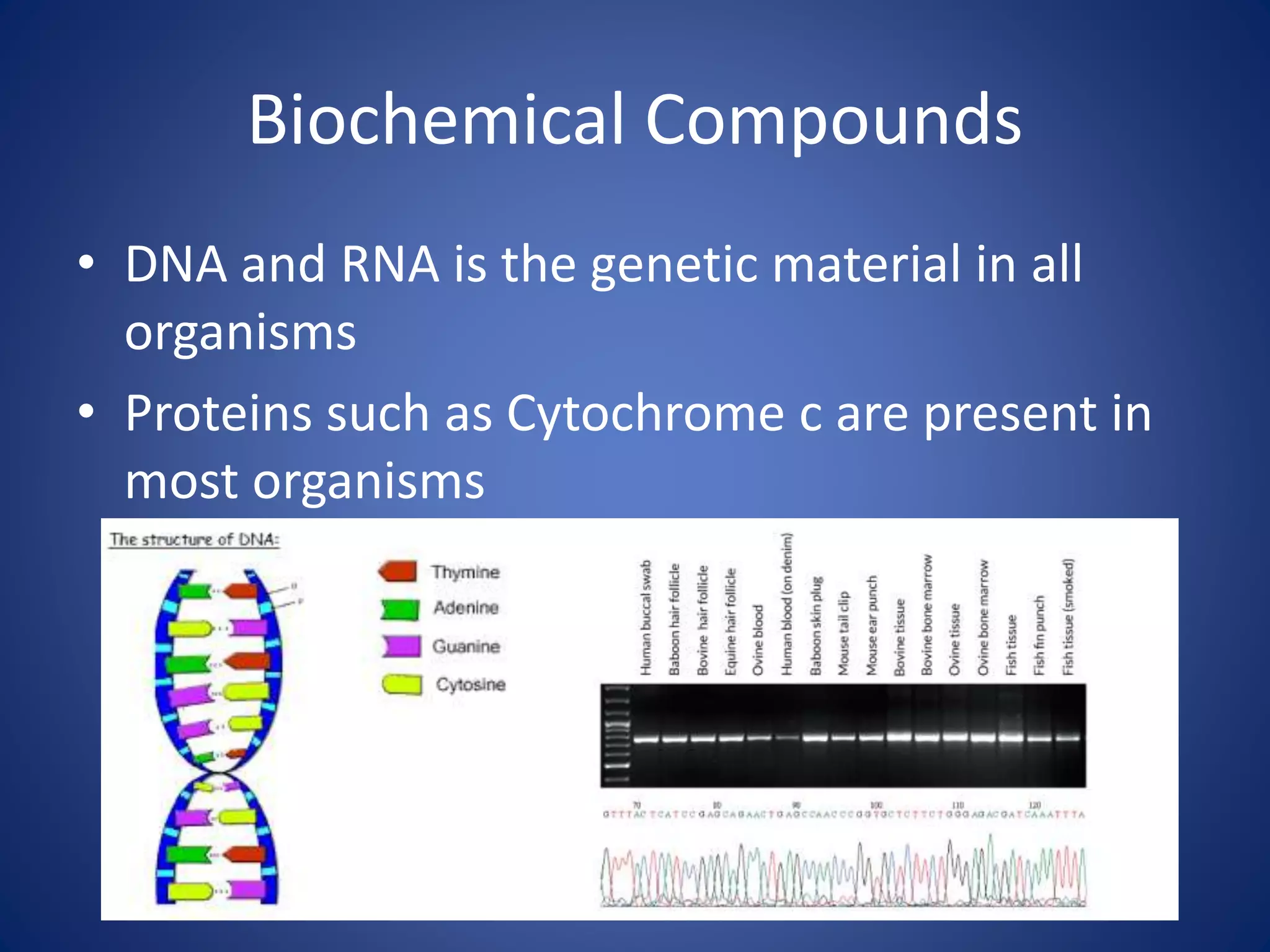
Evolution explains how modern organisms arose from ancient organisms through genetic changes over generations in response to environmental pressures like natural selection. Key ideas include Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection, where traits better suited to the environment increase an organism's chances of survival and reproduction; fossils provide evidence of changes over time; and homologous and vestigial structures provide clues about evolutionary relationships among species.