Embed presentation
Downloaded 401 times








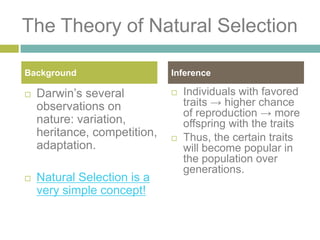

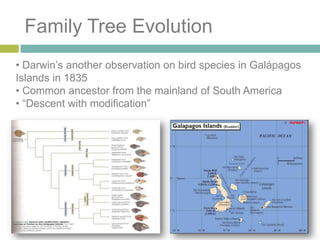


Charles Darwin developed the theory of natural selection after making observations on his voyage on the Beagle and gathering evidence that species adapt to their environments over generations. Through natural selection, individuals with traits better suited to the environment are more likely to survive and pass on those traits, causing populations to evolve over time. Darwin's observations of related but different species on the Galapagos Islands provided evidence that all life shares a common ancestor that diverges through this process of descent with modification.













