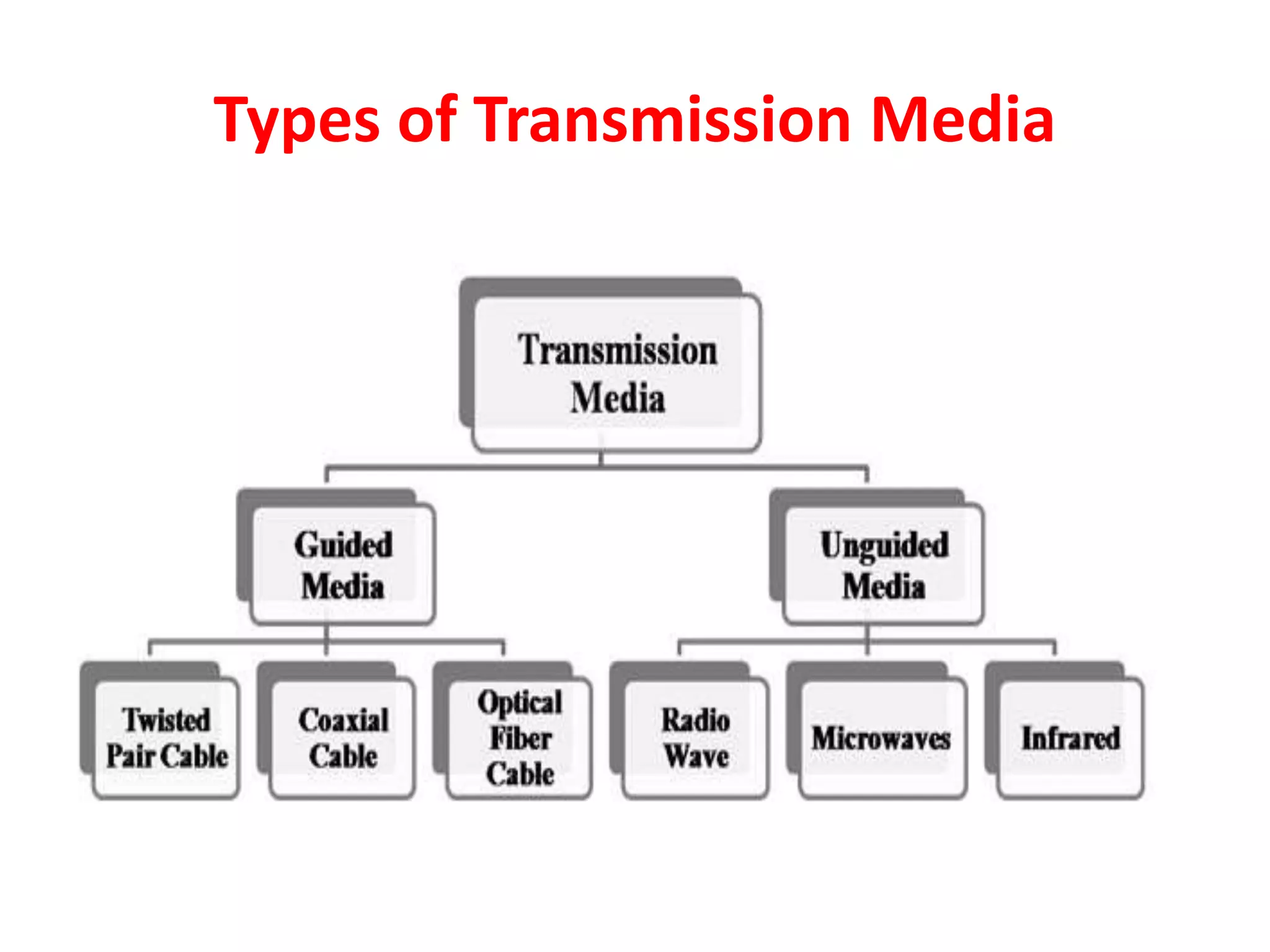
The document outlines various types of networks categorized by area coverage, including LANs (local area networks), MANs (metropolitan area networks), and WANs (wide area networks), describing their geographical scope, setup costs, and data transfer rates. It also details different transmission media such as twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, fiber-optics, microwaves, radio waves, and infrared waves, explaining their characteristics, speed, and common uses. The document highlights the importance of selecting appropriate media for effective data transmission and communication.