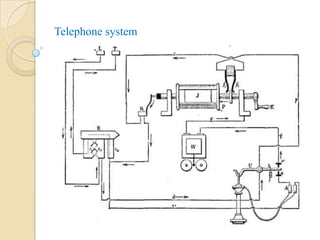
This document provides an overview of basic telecommunication concepts. It defines telecommunication as the transmission of information that allows communication over distance. Examples of telecommunication systems include telephone, satellite, mobile cellular, radar/sonar, and microwave radio. The key components of a telecommunication system are a transmitter that converts a message into a signal, a transmission medium that carries the signal, and a receiver that converts the signal back into usable information.