This presentation summarizes multicarrier modulation techniques OFDM and FBMC.
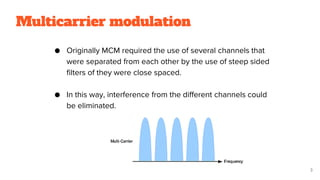
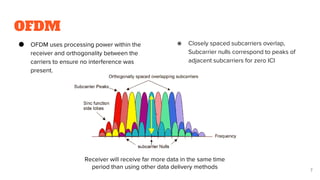
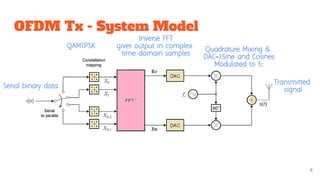
It begins with an overview of multicarrier modulation and its uses of multiple closely or non-orthogonally spaced carriers to avoid interference. It then provides details on OFDM including its system model of serial to parallel conversion, modulation, IDFT/DFT and parallel to serial conversion.
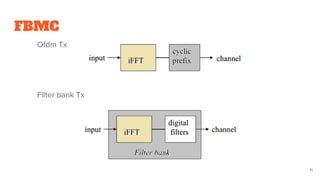
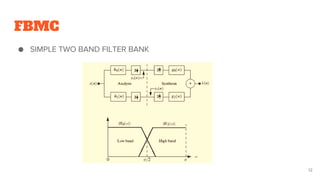
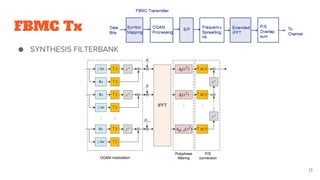
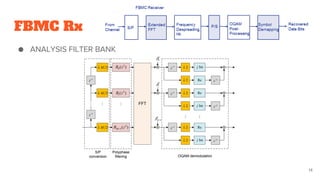
FBMC is then introduced as an evolution of subband processing that addresses some limitations of OFDM like cyclic prefix overhead. It utilizes analysis and synthesis filter banks at the transmitter and receiver.
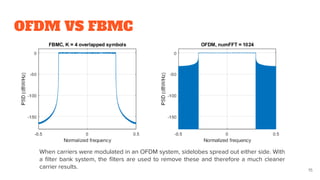
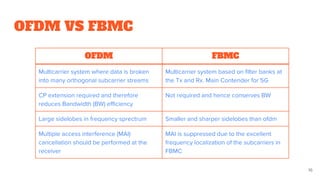
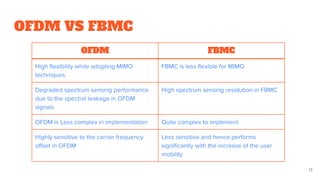
The presentation concludes with a comparison of OFDM and FBMC, noting FBMC's advantages of higher spectral efficiency and better frequency localization but also its increased complexity,