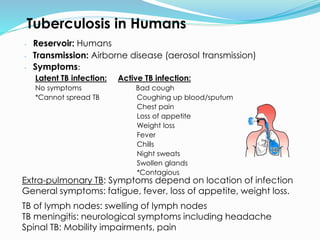
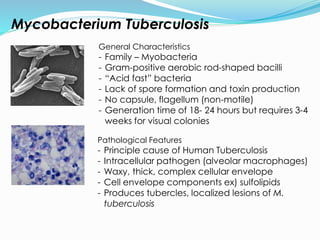
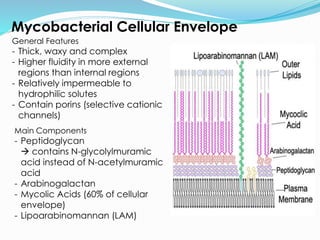
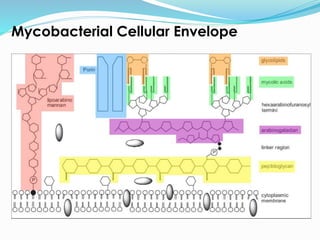
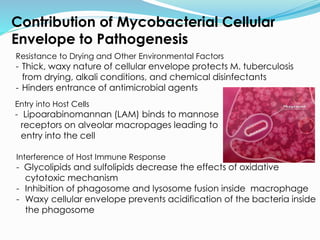
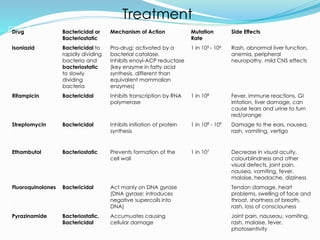
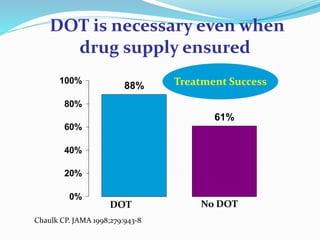
TB, or tuberculosis, is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is spread through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Most people who breathe in the bacteria develop a latent TB infection with no symptoms, but they cannot spread the disease. Active TB disease develops when the bacteria multiply causing symptoms like coughing, chest pain, and weight loss. Diagnosis involves tests like the Mantoux skin test, chest x-ray, and sputum culture. Treatment requires a combination of antibiotics taken for 6-9 months to cure the infection. Drug resistance is a major problem, as some strains are resistant to multiple first-line antibiotics.