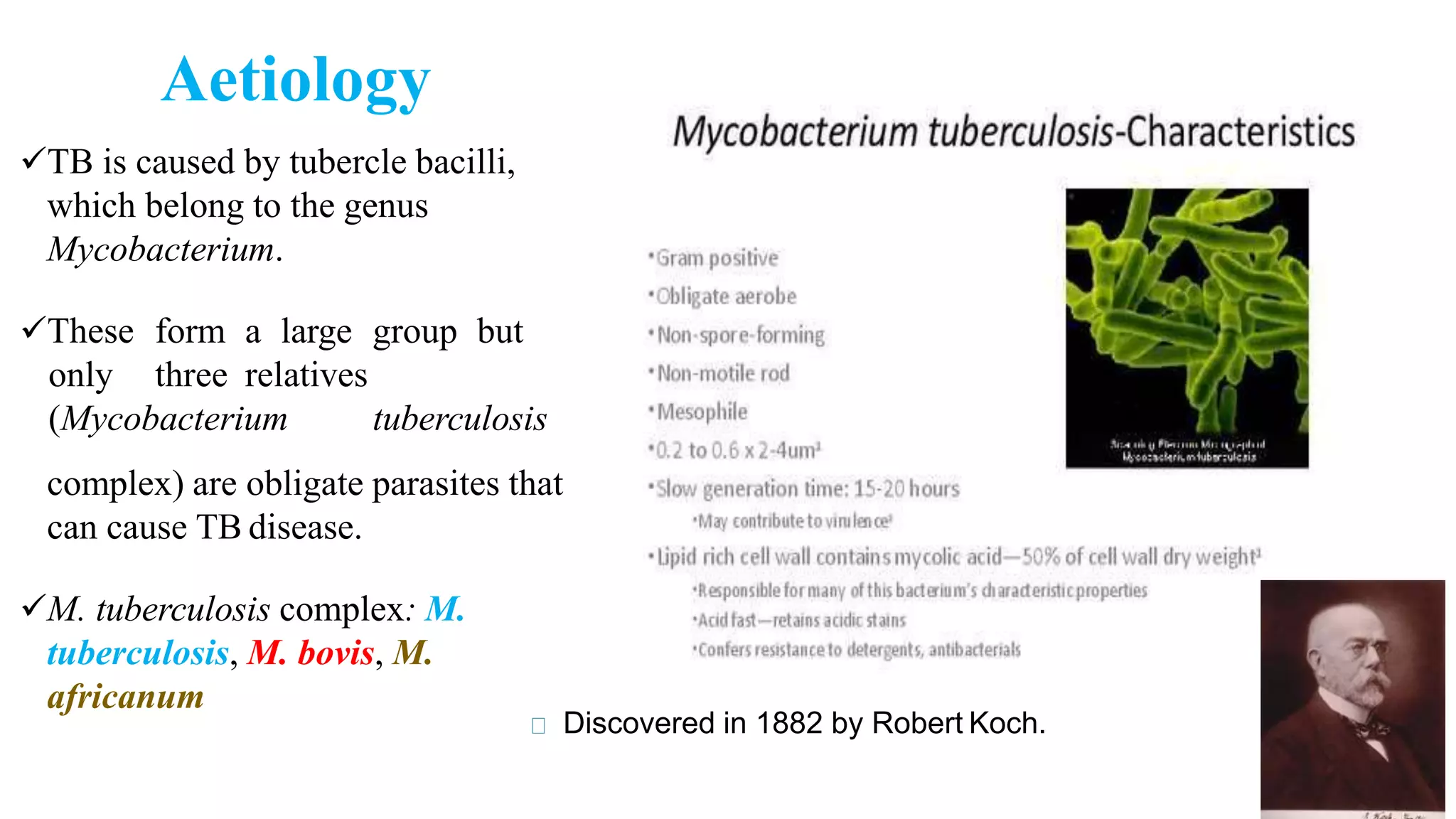
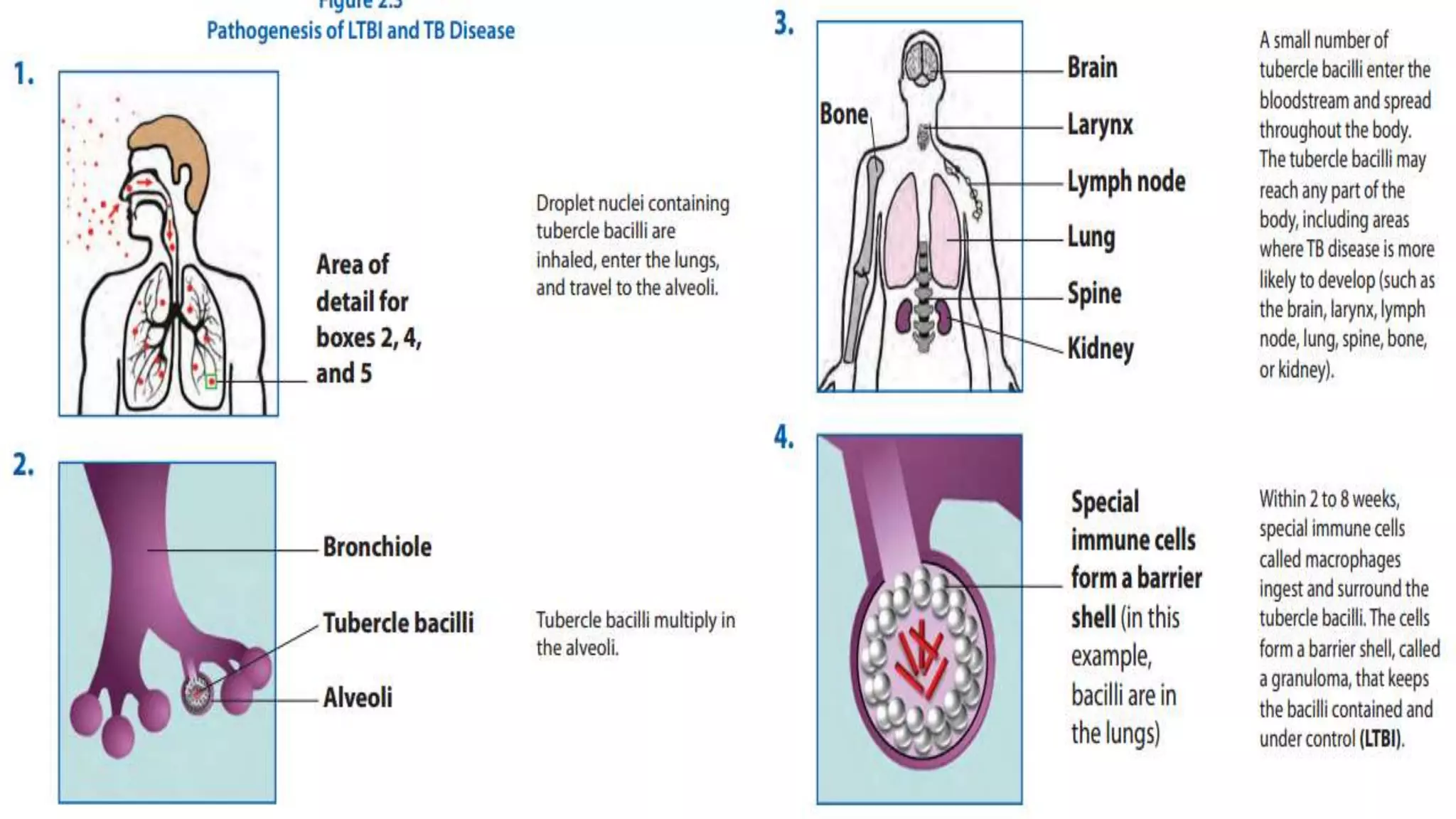
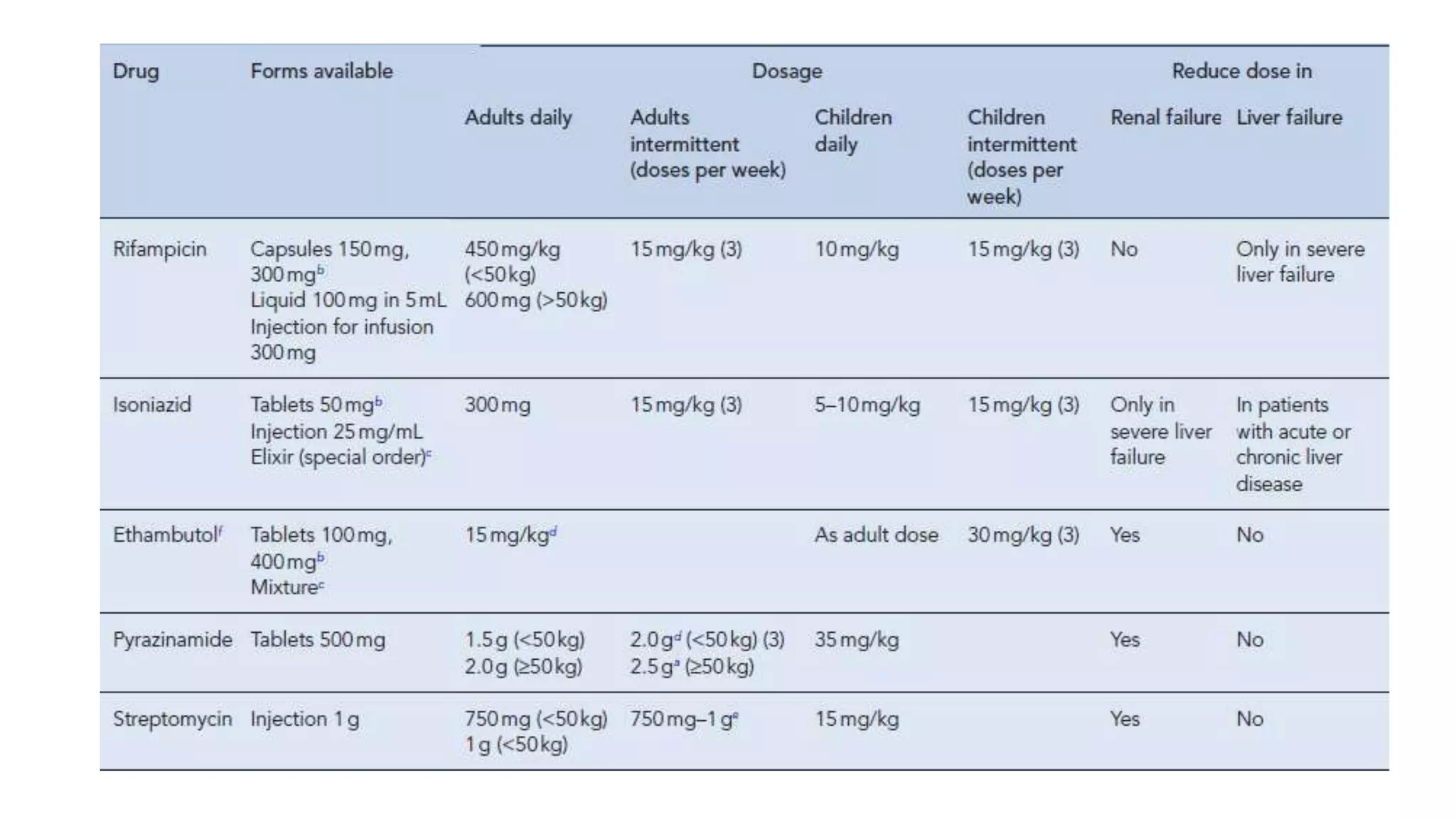
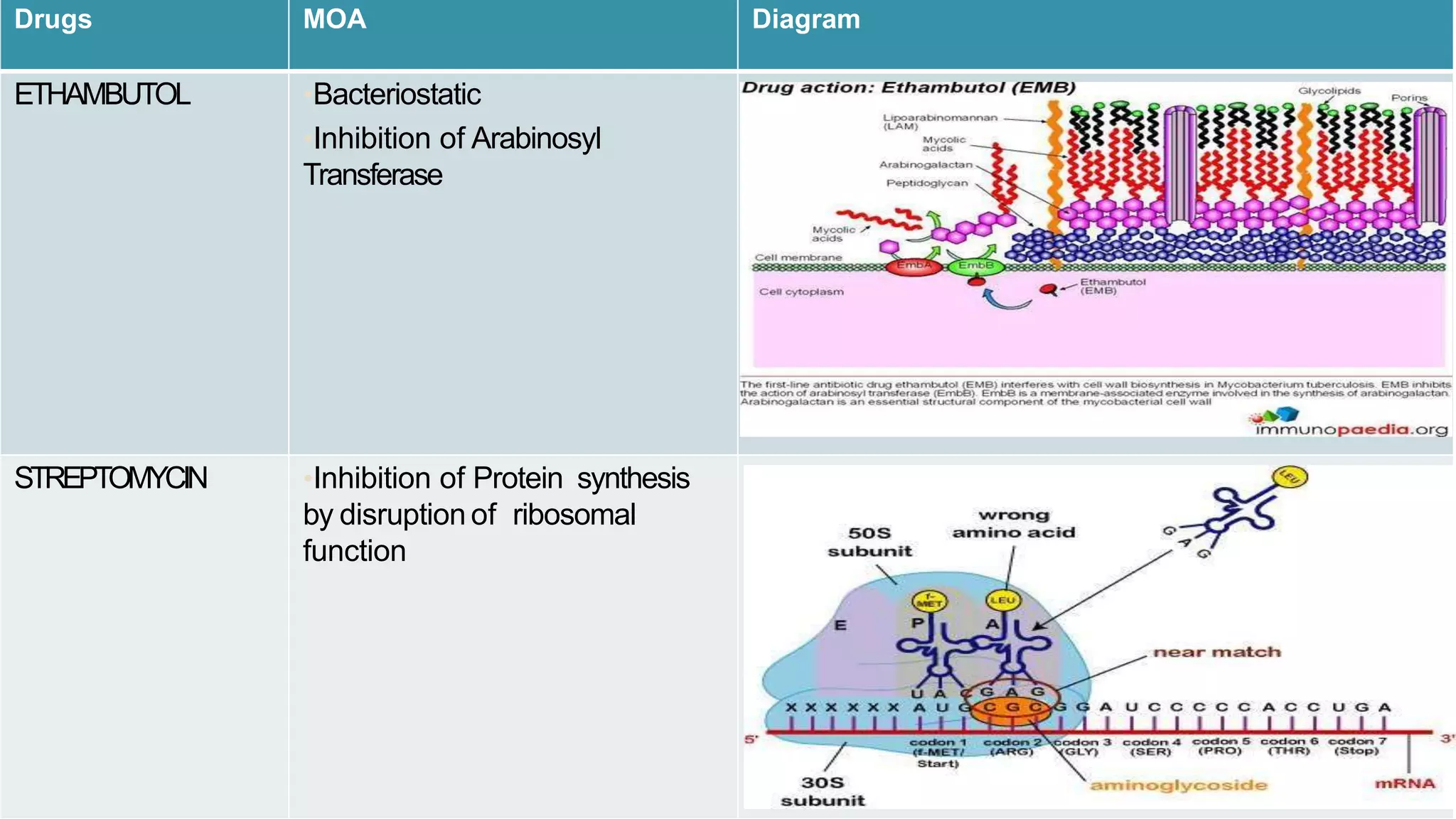
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It typically affects the lungs and can cause symptoms like cough, fever, weight loss, and night sweats. Risk factors include HIV/AIDS, drug use, and other conditions that weaken the immune system. Diagnosis involves tests of sputum, chest x-rays, and tuberculin skin tests. Treatment requires multiple antibiotic drugs taken for 6-9 months. Drug-resistant TB requires specialized treatment with second-line drugs.