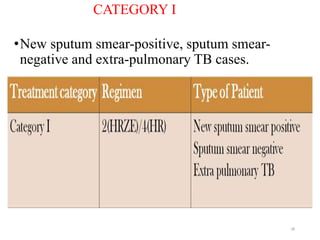
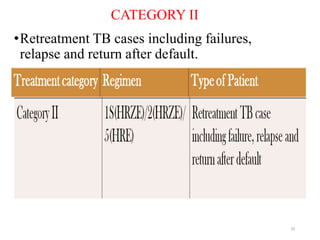
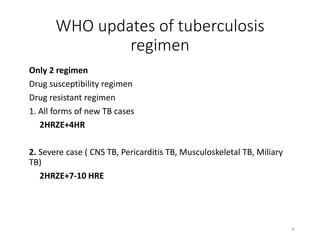
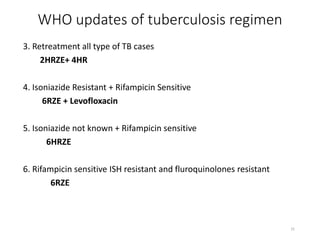
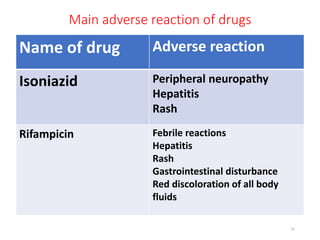
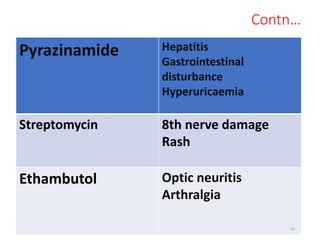
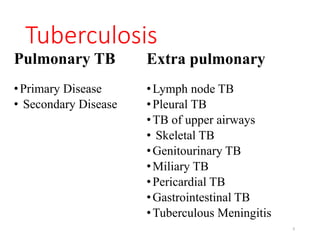
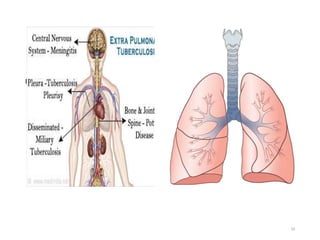
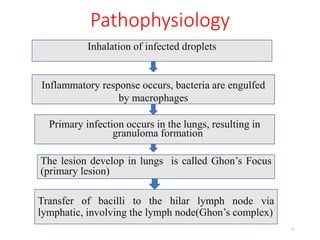
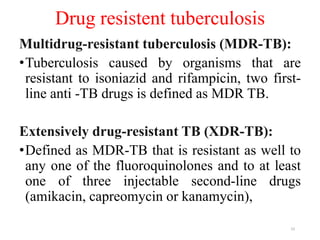
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, primarily affecting the lungs but potentially spreading to other organs. It can be latent, where bacteria are controlled by the immune system without symptoms, or active, where symptoms emerge, leading to contagiousness. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical examination, and various laboratory tests, while treatment includes first-line and second-line antibiotics, often requiring combination therapy.














![Medicines are available in fixed dose
combination (FDC)
HRZE
• Isoniazide [75 mg]
• Rifampicin [150 mg]
• Pyrazinamide [400mg}
• Ethambutol [275mg]
HR
•Isoniazide (150mg)
•Rifampicin (150mg)
HRE
• Isoniazide [75 mg]
• Rifampicin [150 mg]
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tuberculosispresentation-240615090204-6f38ebc2/85/Tuberculosis-presentation-with-introduction-of-its-bacteria-26-320.jpg)